
English Lectures / lipids 1 ENG
.pdf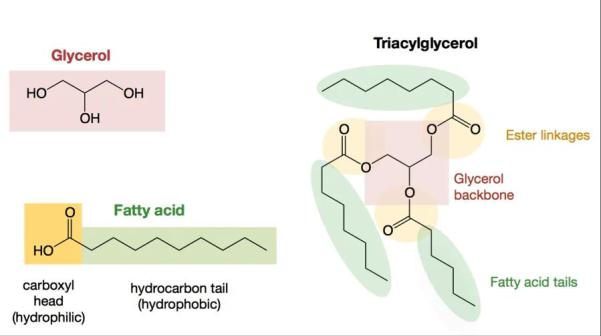
Triacylglycerols
Triacylglycerols are the most common lipids in a human body. On average, their share is 1623% of adult body weight.
The functions of triacylglycerols:
•reserve-energy - in average, any person has enough reserves of subcutaneous fat to maintain vital activity for 40 days of complete starvation,
•as a part of subcutaneous and mesenteric adipose tissue, mechanical protection of a body and internal organs.
•heat-saving – due to the thickness of subcutaneous fat, thermal insulation is achieved
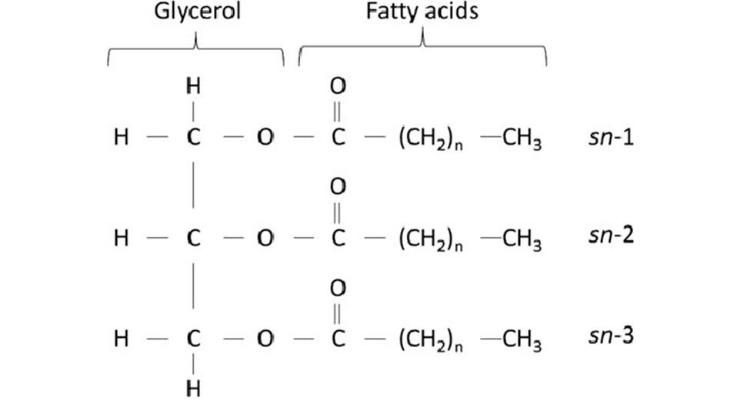
The composition of the TAG includes trihydric alcohol glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids are dominated by saturated (palmitic, stearic) and monounsaturated (palmitoleic, oleic). By structure, simple and mixed TAGs can be distinguished. In simple TAGs, all fatty acids are the same. In mixed TAGs, fatty acids are different.

Triacylglycerols
Fatty acids
These are long chain organic acids containing one polar carboxyl group and a hydrocarbon radical, which may contain from 3 to 24 carbon atoms. Due to the presence of a hydrocarbon radical, most fatty acids are not soluble in water.
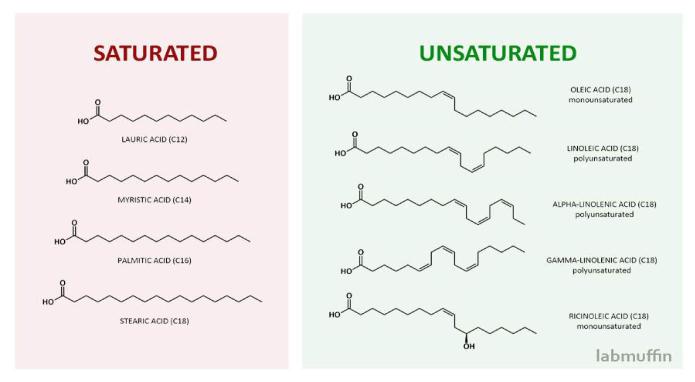
Fatty acids are a structural component of several classes of lipids. Lipids include saturated (do not contain double bonds) and unsaturated (contain double bonds) fatty acids, and they both consist, as a rule, of an even number of carbon atoms.
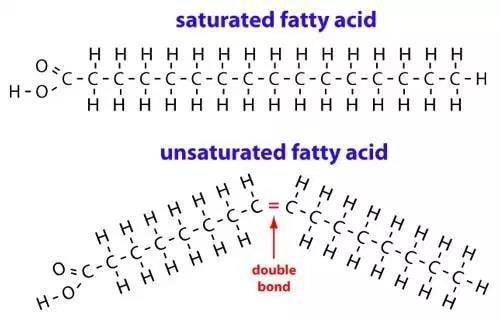
Unsaturated and saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids that do not contain double bonds are called saturated. The main saturated fatty acid in human lipids is palmitic (up to 30-35%). Fatty acids containing double bonds are called unsaturated.

Unsaturated and saturated fatty acids
•Triacylglycerols, which include short chain or high unsaturated fatty acids, typically have lower melting points. Therefore, at room temperature they are in the form of oils. This is characteristic of plantderived triacylglycerols, which contain a large proportion of unsaturated acids.
•In contrast, animal fats are characterized by a high content of saturated fatty acids and are usually solid.
Fatty acids in human triacylglycerols
Saturated Fatty Acids (Solid)
•Oil
•Palmitic
•Stearin
Unsaturated (liquid)
•Oleic
•Linoleic
•Linolenic
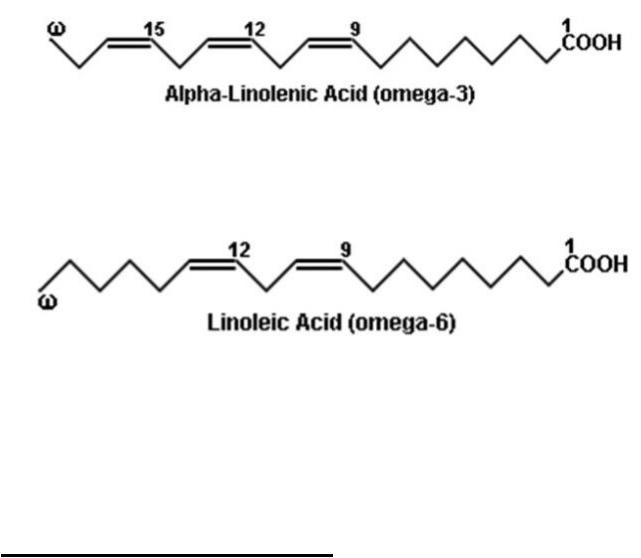
Of particular importance for the body are polyunsaturated fatty acids: linoleic and linolenic. In a body, they are not synthesized and, in their absence, a violation of cholesterol metabolism, dermatitis and other pathologies is noted in food.
Essential fatty acids
•Essential fatty acids include 18-atomic acids of the omega-6 and omega-3 families: linoleic acid with two double bonds and α- linolenic acid with three double bonds.
•The main role of these acids in animals and humans is that they can be biochemical precursors of physiologically significant long chain fatty acids with 20-22 carbon atoms.

Fatty acids
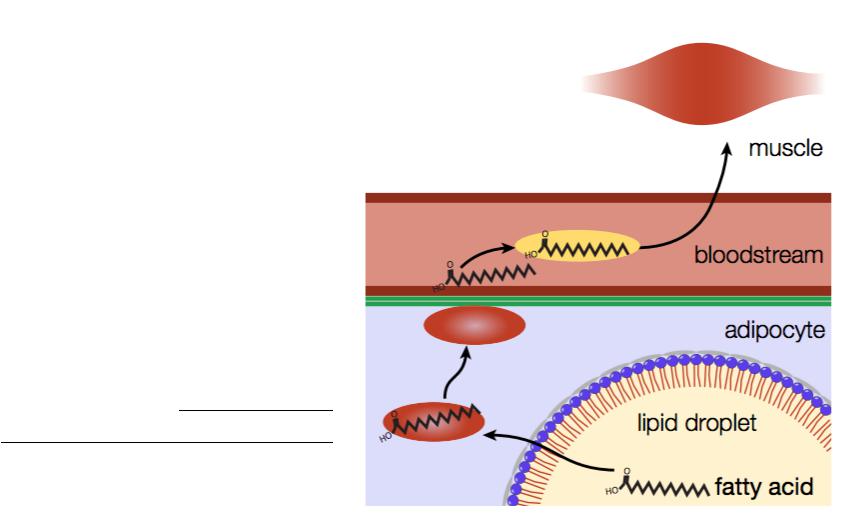
Transport of fatty acids by albumin in the blood
•Albumins, which forms complexes with them, provides this transport.
•Such complexes are formed by the formation of weak types of bonds: hydrophobic interaction of fatty acid radicals and ionic bonds of COOH groups of fatty acids with lysine radicals of the albumin molecule.
•Therefore, the fatty acids in the complex are chemically free.
