
English Lectures / lipids 1 ENG
.pdf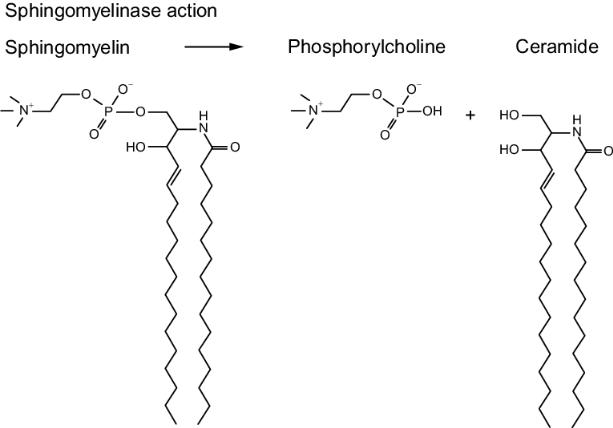
Sphingomyelins
As a result of the addition of phosphoric acid ceramide bound to choline to the OH group, sphingomyelin is formed. Sphingomyelins are the main components of myelin and the membranes of brain cells and nerve tissue.
Glycolipids
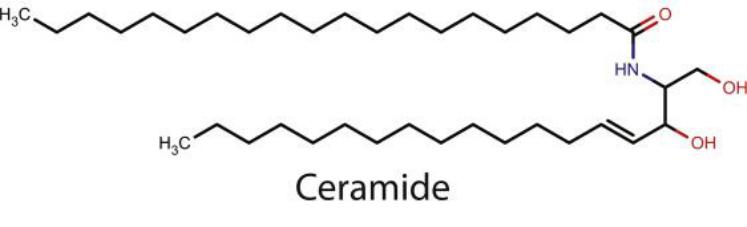
Ceramides are the basis of a large group of lipids – glycolipids. Hydrogen in the hydroxyl group of ceramide can be replaced by different carbohydrate fragments, which determines the belonging of a glycolipid to a certain class. Glycolipids are found mainly in the membranes of cells of the nervous tissue.
Cerebrosides
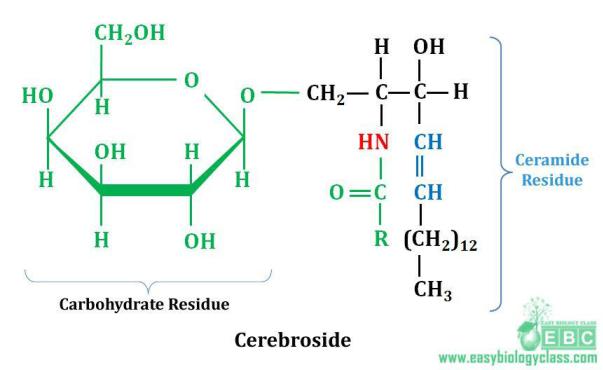
Cerebrosides incorporate monosaccharides. The most common cerebrosides, which include galactose (galactocerebroside), less commonly glucose (glucocerebroside).
Globosides
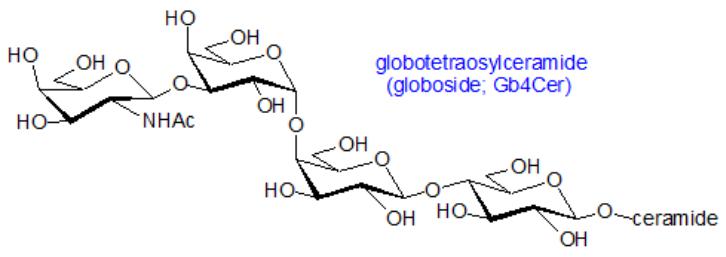
Globosides differ from cerebrosides in that they contain several carbohydrate residues associated with ceramide. Cerebrosides and globosides are classified as neutral sphingolipids, since they do not contain charged groups.
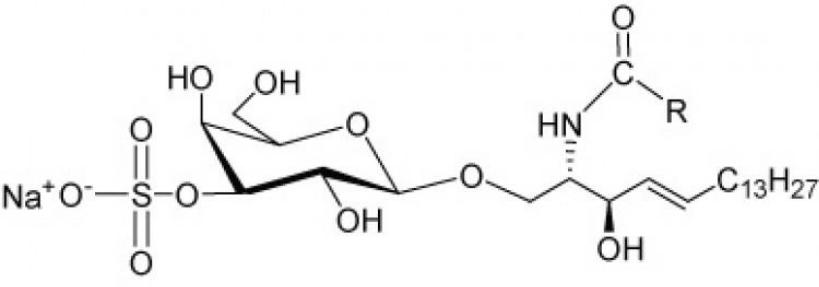
Sulfatides
The hydroxyl at the third carbon atom of the monosaccharide, which is part of cerebroside, can bind the residue of sulfuric acid, i.e. sulfate. In this case, sulfatides are formed that have the properties of acids and are therefore called acid sphingolipids. About 25% of brain cerebrosides are sulfated derivatives. Sulfatides are found in significant quantities in the white matter of the brain.
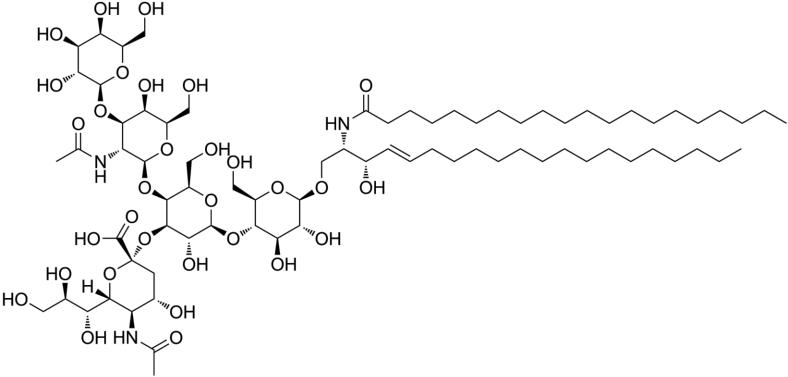
Gangliosides
These are the most complex lipids in composition. They contain several carbohydrate residues, among which N- acetylneuraminic acid is present. Neuraminic acid is a carbohydrate consisting of 9 carbon atoms and is included in the group of sialic acids.
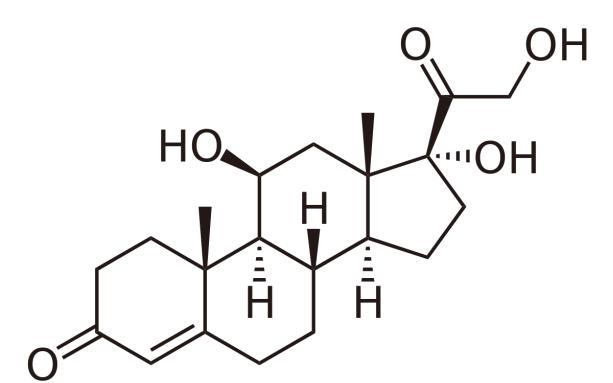
Steroids
These are derivatives of reduced condensed ring systems – cyclopentaneperhydrophenanthrenes. In the human body, the main steroid is cholesterol, the remaining steroids are its derivatives. Cholesterol is part of the membrane and affects the structure of the bilayer, increasing its rigidity. Bile acids, steroid hormones and vitamin D3 are synthesized from cholesterol. Impaired cholesterol metabolism leads to the development of atherosclerosis.
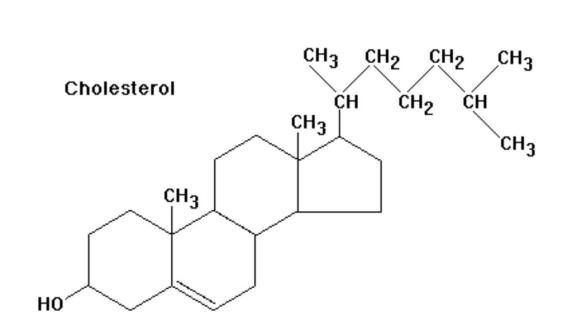
Cholesterol
The presence of a hydroxyl group allows you to assign cholesterol to alcohols, therefore its correct chemical name is "cholesterol", however, the term "cholesterol" is often used in the medical literature. The addition of fatty acids with an ester bond to a hydroxyl group leads to the formation of cholesterol esters. In an unesterified form, cholesterol is part of the membranes of various cells.
Role of lipids
•Energetic – when 1 gram of fat is burned, 39kJ is released
•Thermal insulation
•Protective (depreciation) – fats protect internal organs from mechanical damage and fix them.
•Construction – fats act as a structural component of membranes; especially nervous tissue is rich in them.
•Hormonal – perform a regulatory function, being the basis of steroid hormones. In addition, fats are solvents of many non-polar compounds.
Glycerides
Glycerides (neutral fat) are esters of the trihydric alcohol glycerol and higher fatty acids. Depending on how many higher fatty acid molecules are bound to the glycerol molecule, there are mono-, di-, tri-glycerides.
