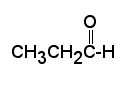- •Topic№10: Aldehydes and ketones. Carboxylic and carboxylic acids.
- •1) The conception of carbonyl compounds. Aldehydes and ketones, their structure.
- •3) The general characteristic to reactionary ability of carbonyl compounds.
- •4) Nucleophilic addition reaction of aldehydes and ketones.
- •5) Oxidation-reduction reaction of aldehydes. Dismutation of aldehydes. Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
- •6) Carboxylic acids. Nomenclature. Physical and chemical properties of carboxylic acids.
- •7) Notion about derivatives of carboxylic acids.
- •9) Nucleophilic substitution reaction of sp2-hybridization carbon atom:
- •Hydrolysis under acidic conditions:
Topic№10: Aldehydes and ketones. Carboxylic and carboxylic acids.
Basic questions:
1. The conception of carbonyl compounds. Aldehydes and ketones. Structure and nomenclature.
2. The general physical properties of aldehydes and ketones.
3. The general characteristic to reactionary ability of carbonyl compounds.
4. Nucleophilic addition reaction of aldehydes and ketones.
a) Formation of a hydrate via a nucleophilic addition(addition of water)
b) Aldol condensation reaction
c) Formation of acetals or hemiacetals via a nucleophilic substitution
5. Oxidation-reduction reaction of aldehydes.
6. Carboxylic acids. Nomenclature. Physical and chemical properties of carboxylic acids.
7. Notion about derivatives of carboxylic acids.
8. Electronic structure of carbonyl groups and carboxylate (acilate) ions. СН-acidity of -carbon atom.
9. Nucleophilic substitution reaction of sp2-hybridization carbon atom:
a) acylation reaction – formation of anhydrates.
b) reaction of complex ester, thioester, amides. Hydrolysis of these compounds.
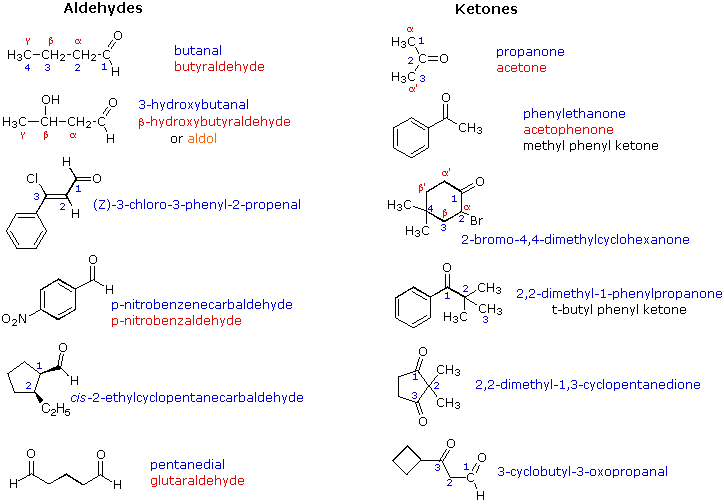
1) The conception of carbonyl compounds. Aldehydes and ketones, their structure.
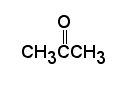
Carbonyl compounds are compounds, which contain a carbonyl group C=O.
Structure:
carbonyl groups consists of a carbon-oxygen double bond
the bond is polar due to the difference in electronegativity
![]()
aldehydes / ketones differ in what is attached to the carbon
In aldehydes - at least one H attached to the carbonyl group, while in ketones - two carbons attached to the carbonyl group. Nomenclature: The names of aldehydes and ketones are simply derived by dropping "-e" from the root and adding "-al" or "-one" respectively. A position number is needed for ketones since the carbonyl group may be on any number of several carbons in the "middle" of a chain. The carbonyl on the aldehyde is always on the number one carbon so no position number is needed.
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
2) The general physical properties of aldehydes and ketones.
|