- •Rig types & components rig processes
- •June, 2002 Contents
- •Drilling programme
- •Casing and cementing programme
- •Bits and Hydraulics programme
- •Mud programme
- •Drilling procedures programme
- •Figure 02
- •Semi-submersibles
- •Figure 03
- •Drill ships
- •D. Platform rigs
- •The drilling types
- •Rotary drilling:
- •Cable tool drilling:
- •Land rig components
- •1. Mast or Derrick
- •Figure 07
- •2. Substructure
- •Figure 08
- •1 0. Tongs
- •11. Prime Movers (Engines )
- •12. Transmission
- •13. Draw Works
- •Figure 12
- •Figure 13
- •14. Drilling Line
- •15. Rotary Table
- •Figure 14
- •19. Top drive
- •20. Heave (Motion) Compensation
- •Drill string Compensator:
- •Riser and Guideline Tensioners
- •Figure 18
- •21. Drill String
- •Figure 19
- •Figure 20
- •Figure 21
- •I) Hole Openers
- •Figure 22
- •22. Casing head
- •23. Mud pumps (Slush Pumps)
- •24. Kelly Line-Rotary Hose (Mud Hose)
- •25. Shale Shaker
- •26. Desanders and Desilters
- •27. Degassers
- •28. Mud Pits
- •29. Bop’s (Blow-Out Preventers)
- •Figure 25
- •Figure 26
- •Rig personnel
- •List of Common Drilling Terms
- •3.The drilling mud
- •Composition and nature of drilling muds
- •Types of mud
- •Mud Properties Termenology
- •De nsity
- •Gel strength:
- •Filtration
- •Alkalinity
- •Chloride Content
- •Installing Christmas Tree
- •Directional Drilling
- •Drilling to total depth (td)
- •Conventional coring:
- •Sidewall coring
- •Tripping
- •Figure 27
- •Stuck pipe
- •1. Differential sticking
- •2. Mechanical sticking
- •Fishing
- •Wireline logging (electric) logging
- •Cement Figure 30
- •(Figure 31)
- •Completing the well & Setting Production Casing
- •Perforating production casing
- •Drill Stem Test (dst)
- •Acidizing
- •Fracturing
- •Installing the Christmas Tree
- •5.Mud Logging Definition
- •Types of mud logging units
- •Duties & responsibilities
- •I) mud logging unit captain
- •6.The mud logging theory & lag
- •Answers
- •Trip-out monitoring procedures
- •7.Sample collection and description
- •Preparation for collection of cutting sample
- •Shaker Samples
- •Sample Descriptions
- •Rock Types
- •Describing and logging oil shows
- •Acetone Test
- •Heat Test
- •Hot Water Test
- •Acid Test
- •Some Criteria & Procedures For Rock & Mineral Identification Testing Methods:
- •General remarks on sample escription
- •Contamination of cuttings
- •8.Gas system
- •Gas Curve
- •Types of recorded gases
- •1) Cuttings gas (formation gas)
- •2) Background gas
- •3) Trip gas
- •4) Connection gas
- •4) Circulation gas
- •Gas detection and analysis monitoring equipment
- •Gas trap assembly
- •Fid gas detector
- •Fid gas chromatograph
- •9.Sensors
- •Sensors specifications
- •1.Hook load sensor
- •2.Torque sensors Electric torque type:
- •Mechanical torque type:
- •3.Standpipe and choke pressure sensors
- •1. Strain gauge type:
- •2. Current loop type:
- •7.Analog rotary speed sensor
- •8.Pit volume sensors
- •9.Flow out sensors
- •10.Mud temperature sensors
- •11 .Mud density sensor
- •12. Mud conductivity sensor
- •13. Depth sensor
- •14. Pump stroke sensor
- •15. Digital rotary speed sensor
- •16.Gas trap assembly
- •17. Hydrogen sulphide gas detector - h2s
- •Basic Mud Logging
Semi-submersibles
A semi-submersible is a floating drilling rig. A typical layout is shown below in figure 03.
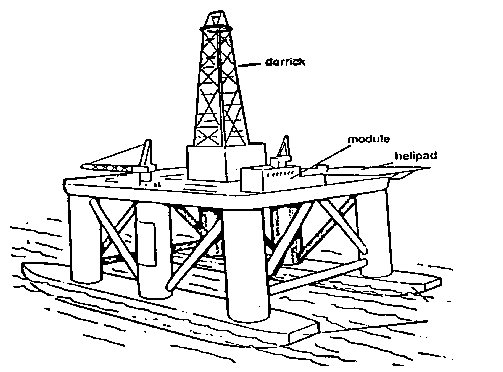
Figure 03
The following are some advantages and disdvantages of Semi-submersibles:
Advantages
Has a good safety record.
Provides a relatively stable platform.
Can function under more severe weather conditions.
Can drill in deep water - up to 2000 ft.
Can be self-propelled.
Disadvantages
Requires marine risers and a sub sea stack.
Has a limited cargo capacity.
Requires support vessels.
Drill ships
These are special types of ships that are built for deep water drilling. They range in length between 200-450 feet. Their cargo carrying capacity and general mobility make them especially useful for drilling in remote areas. An example is shown in( figure 04) below.

Figure 04
Some advantages and disadvantages of drill ships are:
Advantages
High carrying capacity.
Can drill in remote areas.
Can operate in deep water.
Self propelled.
Disadvantages
The lack of suitable risers to support drilling mud circulation between well head and drilling floor.
Not as stable as jackups and semi-submersibles.
requires a subsea stack.
D. Platform rigs
A platform is a fixed installation offshore from which development drilling and petroleum production is carried out. A steel platform design is shown as an example in figure 05 below.
The deck, supported by a steel jacket, carries equipment, accommodation modules and a helicopter pad (helideck). It also supports one or more drilling rigs with associated equipment.
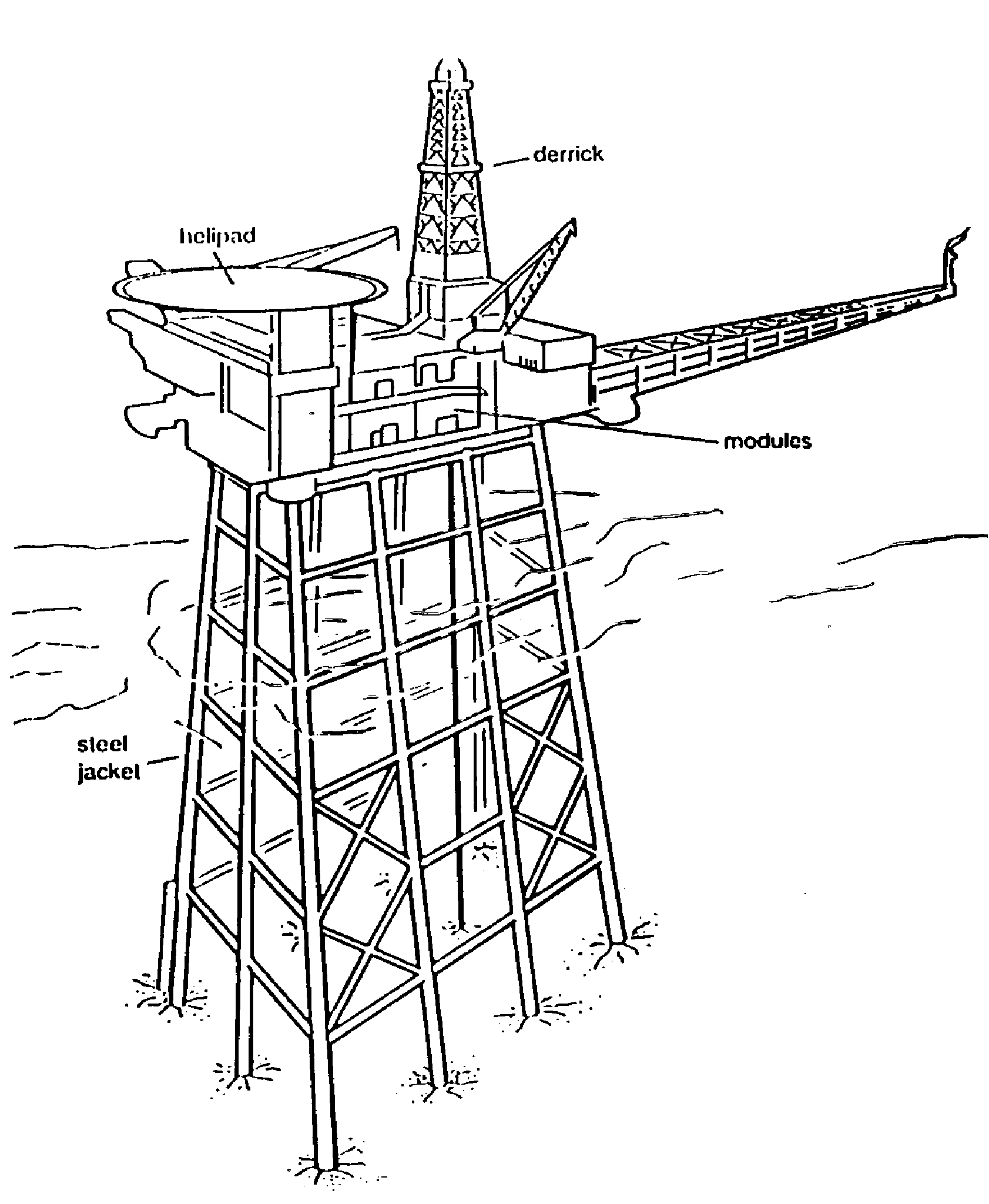
Figure 05
The drilling types
The basic function of a drilling rig is to drill a bore hole. This hole must be drilled in an accurate, economic and safe way. Drilling rigs are of two main types: rotary and cable tool.
Rotary drilling:
The rotation is generated either by a rotary motor to a rotary table or a top drive motor that directly rotates the drill string. The rotary table transfers power to the bit via the rotary and kelly bushings. Weight is supplied by allowing a small amount of the drill string weight to rest on the bit.
Cable tool drilling:
With the wireline method, a cable is used to connect the bit to the surface and a pounding motor is used to effect the weight on the bit.
RIG COMPONENTS
Rigs are made up of various components. However the following discussion is restricted to land rig components, most of these components are also found offshore.
Jack up rigs and fixed platforms are very similar to land rigs. They are not subject to wave and tidal movements as being fixed in relation to the sea bed during drilling operations. Therefore, they have no need for heave components or sub sea stack BOP’s.
In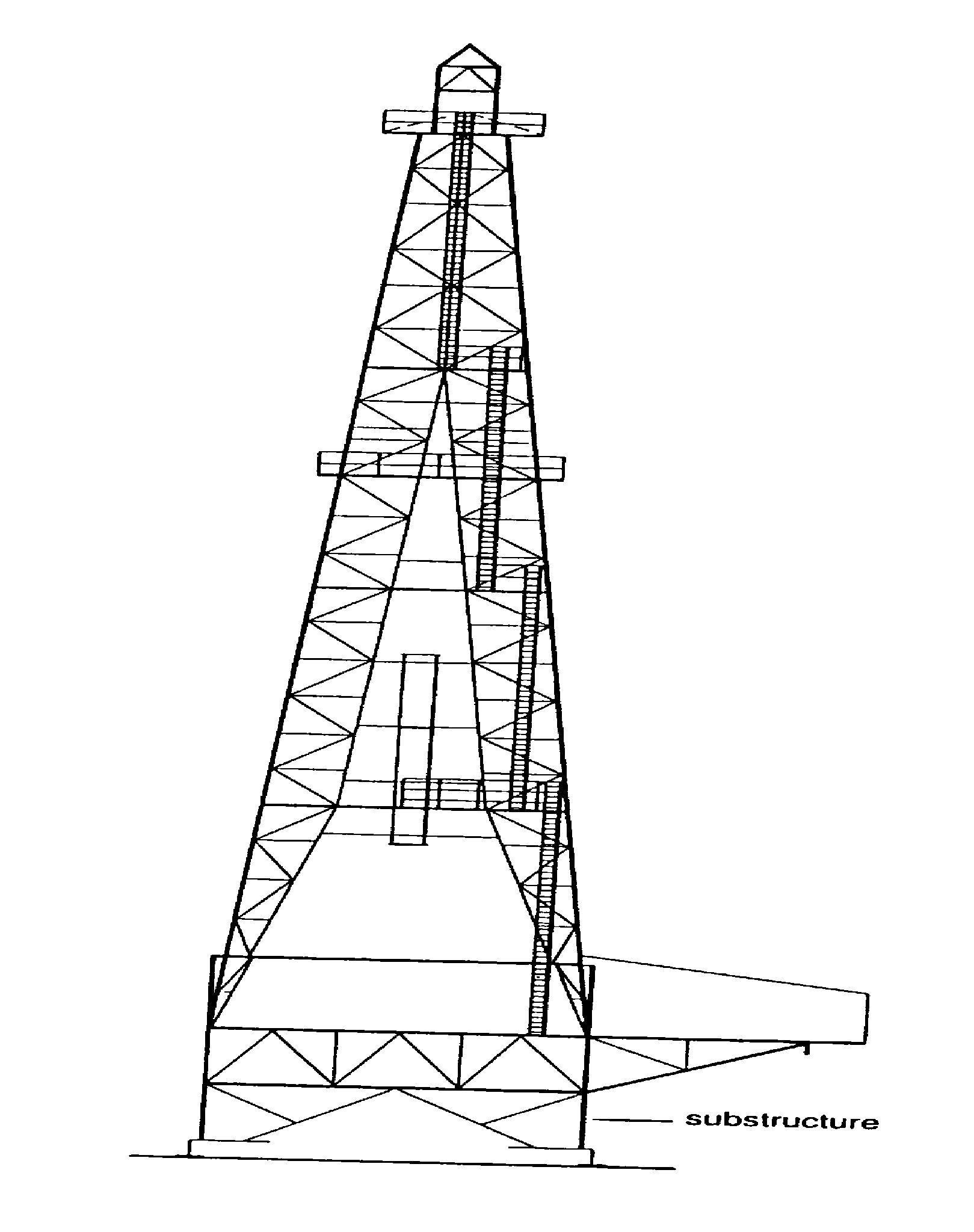 the following few pages we will discuss the main components of
drilling rigs taking land rigs as an example.
the following few pages we will discuss the main components of
drilling rigs taking land rigs as an example.
Land rig components
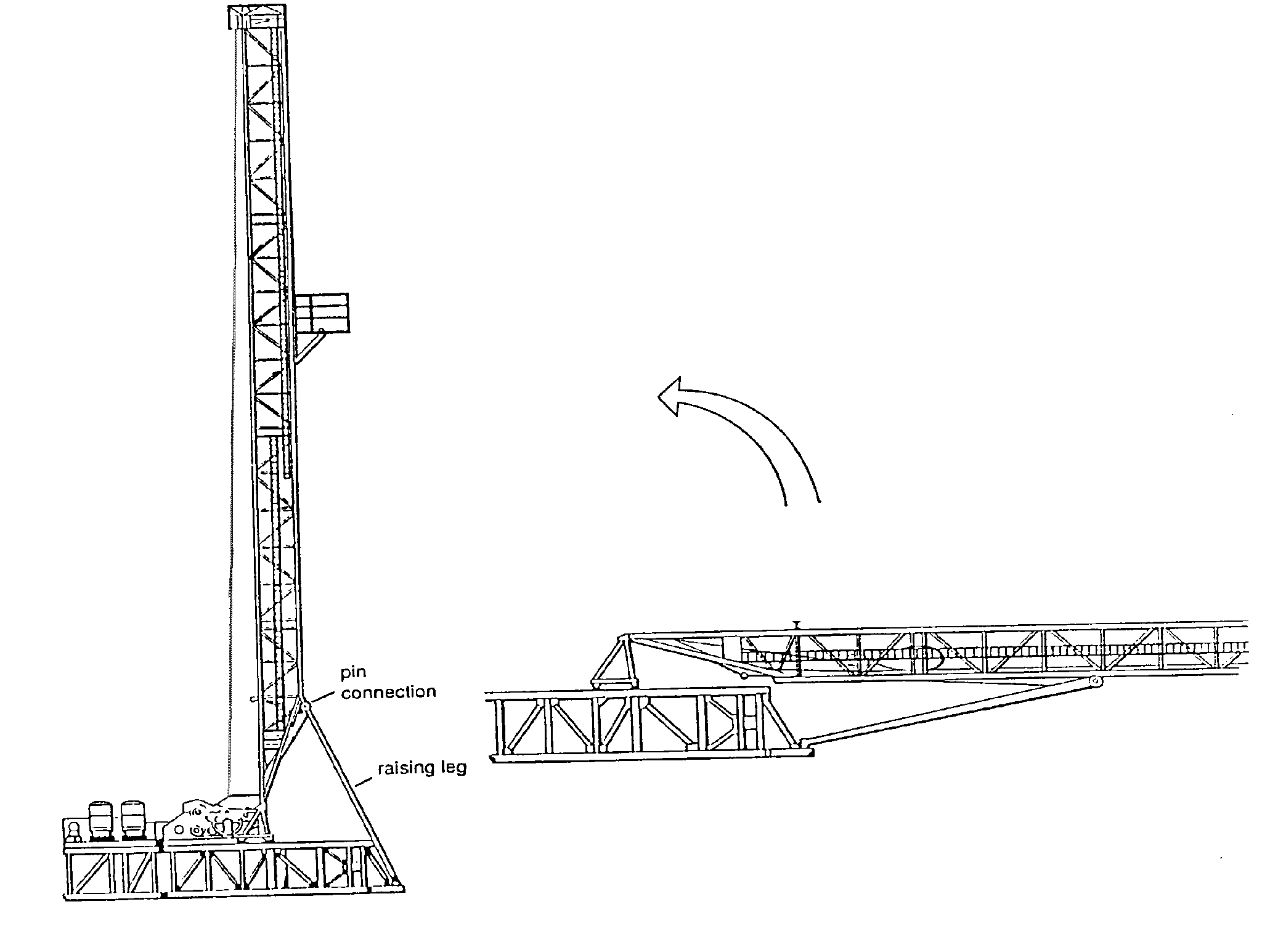
1. Mast or Derrick
a) Masts
Masts are assembled on the ground from large welded sections fastened together with pins. They may then be raised to the vertical position by using the rig’s own power unit and hoisting line. Small masts may be truck mounted while some are telescopic. This rigging-up time for masts tends to be less than that for conventional derricks.
Rigging-up time is the time spent to assemble a mast into the vertical position on-site. It also includes the time to install the power unit, all cables and piping. Masts are used for lighter work. Cantilever masts (also known as jack-knife derricks) are also common. Figure 06 shows a typical mast layout. (Fig. 06)