
- •Contents
- •Lesson 1 the basic components of road transportation
- •The Basic Components of Road Transportation
- •Lesson 2 highways
- •Highways (General notions)
- •German Autobahn
- •Lesson 3 urban streets and rural roads
- •Urban streets and rural roads
- •Lesson 4 roadway engineering road covering
- •Road Covering
- •Flexible and rigid pavements
- •Lesson 5 roadway engineering flexible pavement
- •Flexible Pavement
- •Lesson 6
- •Rigid Pavement
- •Lesson 7 requirements for present-day roads
- •Requirements for Present-day Roads
- •Lesson 8 the geothermal method of pavement heating
- •The Geothermal Method of Pavement Heating
- •Lesson 9 first smart highways in the usa
- •Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian with the help of the vocabulary listed above. First Smart Highways in the usa
- •Lesson 10
- •5 Road planning and administration in the usa
- •Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian (Russian) with the help of the vocabulary listed above. Road Planning and Administration in the usa
- •Lesson 11
- •Cement. Cement grades
- •Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian (Russian) with the help of the vocabulary listed above. Cement. Cement Grades.
- •Lesson 12 road materials portland cement. Basic ingredients
- •Portland Cement. Basic Ingredients
- •Lesson 13 portland cement manufacturing
- •Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian (Russian) with the help of the vocabulary listed above. Portland Cement Manufacturing
- •Lesson 14
- •Road materials
- •Asphalt
- •These words and word-combinations are from the text below. Study and memorize them.
- •Asphalt, air-blown asphalt, straight-run asphalt, poured asphalt;
- •Asphalt Paver
- •Aggregate, fine aggregate, coarse aggregate;
- •Concrete. Properties and Use
- •Concrete Bridge
- •Restore the sentences. Consult the text above.
- •Заповнювач, крупний заповнювач, дрібний заповнювач.
- •Version 2 Task 1
Road Covering
To support heavy vehicles moving at high speeds, a modern road is made up of several layers. Roads that carry more traffic at higher speeds, like highways, are built to stronger standards than roads that carry less traffic, such as rural collector roads. The number of layers in a road often depends on the intended use of the road, but generally roads have three distinct layers. From bottom to top, the layers are the roadbed, the base course, and the wearing course.
The roadbed is the very bottom layer of a road. Natural soil is the most common roadbed material. The roadbed is shaped to make a smooth, level surface that will support the layers built over it. Engineers use bulldozers and other construction equipment to distribute soil evenly along the roadbed.
The base course rests directly on top of the roadbed and is often made up of compacted gravel. Soil can be stabilized by adding materials such as calcium chloride, bituminous material, lime, or portland cement to the soil. Drainpipes are usually installed within the base course to control rain and moisture drainage. Some roads include a second base layer, called the top course, for extra support.
A road’s top layer, which directly supports moving vehicles, is called the wearing course. It is made of a solid layer of pavement and is designed to be smooth and to withstand erosion from traffic and weather.
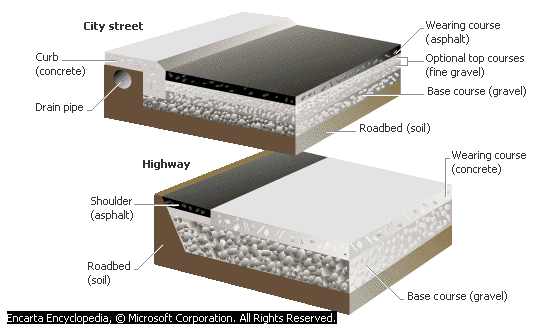
Flexible and rigid pavements
-
Flexible and rigid pavements each contain several different layers of materials. The layers below combine to support the traffic moving along on the surface layer, which is known as the wearing course. Asphalt makes up the wearing course of flexible pavement and is often found on residential streets in cities. Rigid pavement made of concrete is more durable and is a popular choice for highway construction.
Task 6
Answer the following questions using the information from the text above.
Why are modern roads made up of several layers?
How many layers do modern roads generally have? What are they?
Which is more durable, asphalt or concrete?
What is the most common roadbed material?
5. What is used to distribute soil evenly along the roadbed?
6. What materials are used to stabilize soil in the process of road construction?
7. What is installed within the base course to control rain and moisture drainage?
Task 7
Fill in prepositions if necessary. Consult the text above.
1. The number .… layers …. a road often depends .… the intended use …. the road.
2. Roads that are built .... stronger standards carry more traffic .... higher speeds.
3. The base course rests .... top .... the roadbed.
4. Drainpipes are installed .... the base course.
5. A road’s top layer is designed to withstand .... erosion .... traffic and weather.
Task 8
Transform the following sentences according to the model. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian (Russian).
Model
The road is made up of several layers. The road will be made up of several layers.
1. The highways are built to strong standards.
2. The pavement is made up of several layers.
3. The roadbed is shaped to make a smooth, level surface.
4. The soil is stabilized by adding materials.
5. Bulldozers and other construction equipment are used to distribute soil evenly along the roadbed.
6. The wearing course is designed to withstand erosion from traffic and weather.
7. Drainpipes are installed within the base course to control rain and moisture drainage.
Task 9
Translate into English.
1. Земляна полотнина дороги, уздовж земляної полотнини дороги, вирівнювання земляної полотнини.
2. Поверхня, горизонтальна поверхня, створювання горизонтальної поверхні.
3. Дренажна система, розміщення дренажної системи.
4. Дорожнє покриття, зносостійкість дорожнього покриття, формування дорожнього покриття, основа дорожнього покриття.
5. Шар, шар дорожнього покриття, нижній шар дорожнього покриття, верхній шар дорожнього покриття, шар зносу, зношування верхнього шару дорожнього покриття.
6. Грунт, зміцнювання грунту, розподіляти грунт уздовж дорожнього полотна.
7. Сучасні стандарти, відповідно до сучасних стандартів, будування доріг згідно із сучасними стандартами.
8. Бульдозер, використовувати бульдозери, використання бульдозерів.
Task 10
Translate the sentences into English using the active vocabulary and the text above.
1. Відповідно до сучасних стандартів, дорожнє покриття складається із трьох шарів: дорожнього полотна, основи покриття і шару зносу.
2. Природний грунт є звичайним матерілом для формування дорожнього полотна.
3. Стабілізация грунту створюється за допомогою присадочних матеріалів.
4. Дренажна система розміщується біля основи покриття.
Бульдозери використовуються для розподілу грунту уздовж дорожнього полотна.
6. Зношування верхнього шару дорожнього покриття – одна з головних проблем дорожнього будівництва.
Task 11
You are a road designer. Speak on the structure of the road you are going to design. Use the following key expressions.
Make up of several layers.
Build to strong standards.
The number of layers.
The roadbed material.
The base course.
Compacted gravel.
Adding materials.
Drainpipes.
The wearing course.
