
- •Тема 1. Основные задачи Министерства по чрезвычайным ситуациям Республики Казахстан (мчс рк). Центральный аппарат мчс рк.
- •Тема 2. Структура Гражданской обороны Республики Казахстан
- •Тема 3. Закон Республики Казахстан «о гражданской обороне», 7.05.1997 г.
- •Тема 4. Закон Республики Казахстан «о чрезвычайных ситуациях природного и техногенного характера», 5.07.1996 г.
- •Тема 5. Действия по защите населения при радиационном и химическом заражении местности. Осуществление санитарно-гигиенических и профилактических мероприятий.
- •Тема 7. Методика оценки радиационной и химической обстановки объекта хозяйствования. Отравление сдяв.
- •Тема 8. Организация Гражданской обороны высшего учебного заведения. Организационная структура Гражданской обороны объекта хозяйствования. Формирования го, назначение и порядок их создания.
- •Тема 9. Защита растений от оружия массового поражения. Защита животных от рв, ов, бс.
- •Тема 11. Защита продовольствия, кормов, воды и водоисточников от рв, ов, бс. Способы обеззараживания продуктов, кормов и воды в различных условиях. Меры предосторожности.
- •Тема 12. Обучение и морально-психологическая подготовка населения. Основы обучения по го.
- •Тема 13. Подготовка различных категорий населения по го. Тактико-специальные занятия и учения с формированиями го.
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE
OF THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN
JSC “S.SEIFULLIN KAZAKH AGROTECHNICAL UNIVERSITY”
N. Kundyzbayeva
METHODICAL INSTRUCTIONS
FOR IMPLEMENTATION PRACTICAL CLASS
on discipline of «Fundamentals of life safety»
for students of all specialties
Astana 2013
Content
p
Practical work № 1. Primary problems of the ministry of emergency measures of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The central device of ministry of emergency measures Practical work № 2. Structure of the Civil Defence Republic of Kazakhstan Practical work № 3. Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan «About a Civil Defence», 7.05.1997 Practical work № 4. Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan «About emergencies of natural and technogenic character», 5.07.1996 Practical work № 5. Actions on protection of the population at radiating and chemical infection of district. Realization of sanitary-and-hygienic and preventive actions Practical work № 6. The international organizations which problems include various aspects of a security of ability to live of the person. Sources of radiating pollution (infection) of an environment and unit of their measurement Practical work № 7. Procedure of an assessment of radiating and chemical conditions of object of managing. poisoning by strongly operating poisonous substances (SOPS) Practical work № 8. Organization of the Civil Defence of a higher educational institution. Organizational structure of the Civil Defence of object of managing. Formations of the Civil Defence, purpose and the order of their creation Practical work № 9. Protection of plants against the weapon of mass defeat. Protection of animals from radioactive substances (RS), poison gases (PG), bacterial means (BM) Practical work № 10. Recommendations on conducting plant growing in conditions of radioactive, chemical and bacteriological infection of territory. Recommendations on conducting animal industries in conditions of radioactive, chemical and bacteriological infection of territory Practical work № 11. Protection of the foodstuffs, forages, water and water sources from RS, PG, BM. Ways of disinfecting of products, forages and waters in various conditions. safety measures Practical work № 12. Instruction and moral-psychological preparation of the population. Bases of training of the Civil Defence. Practical work № 13. Preparation of various categories of the population of the Civil Defence. Tactic-special employment and doctrines with formations of the Civil Defence |
3
9
13
16
19
22
25
28
31
34
36
40
43 |
PRACTICAL WORK № 1. PRIMARY PROBLEMS OF THE MINISTRY OF EMERGENCY MEASURES OF THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN. THE CENTRAL DEVICE OF MINISTRY OF EMERGENCY MEASURES
The purpose and objective studies: To study the activity of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Contents of exercises:
1 The main tasks of the Ministry
2 Main functions and powers of the Ministry
3 Property of the Ministry
4 Organization of the Ministry
1 The main tasks of the Ministry are the formation of public policy in the field of prevention and liquidation of emergency situations of natural and man-made disasters, the Civil Defense of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the oversight of the implementation of civil defense, inter-sectoral coordination, state control and supervision in the field of fire and industrial safety, occupational health and safety at hazardous production facilities, supervision of Safety in industry, mining supervision, formation and development of state material reserves, maintenance and further development of the state system of prevention and liquidation of emergency situations, organization of prevention and fire fighting.
The Ministry has regional offices in the regions and the cities of Astana and Almaty and agencies: the Committee for State Control and Supervision of emergency and the Committee for State Material Reserves.
The Ministry is a legal person in the legal form of a public institution, has printed stamps with the name in the official language, forms a standard form and in accordance with the laws of the account in the Treasury bodies.
Ministry enters into civil law relations in its own name. The Ministry has the right to be a party of civil relations on behalf of the state, if it is authorized to do so in accordance with the law.
Department for its competence solutions, designed the orders of the Minister, which shall be binding on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Registered office of the Ministry: 473000, Astana city, street, Beybitshilik, 22.
Funding of the Ministry carried out only from the national budget. Ministry is forbidden to enter into a contractual relationship with the subjects of business duties, which are functions of the Ministry.
If the Ministry of legislation entitled to carry out the activities of revenue, income derived from such activities shall be transferred to the republican budget.
2 In accordance with the tasks Ministry performs the following functions: 1) strategic, providing formation of public policy in:
- Prevention and management of natural and man-made disasters, civil defense, cross-sectoral coordination of state control and supervision in the field of fire and industrial safety, occupational health and safety at hazardous production facilities, supervision of Safety in industry, mining supervision and compliance civil defense, as well as in the state material reserve;
- Organization of the development and implementation of programs to address the problems of prevention and liquidation of emergency situations, civil defense, fire and industrial safety;
- The development of proposals for the use of available in the state and mobilization reserves inventory logistics, food, medical and other resources, and the use of funds from the reserve of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan for the prevention and elimination of emergency situations;
- Develop a plan for civil defense peacetime and wartime and present it for approval to the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
2) in the implementation of public policy:
- Coordinate the work of state bodies in the field of natural and man-made disasters, civil defense, fire and industrial safety;
- Cooperates with local authorities in the field of natural and man-made disasters and civil defense;
- Prepare and submit reports on the status of population and facilities management of emergency situations and civil defense;
- Organize research, promote knowledge, education of the public and experts in the field of natural and man-made disasters, civil defense, fire and industrial safety; - By the decision of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan manage directly the elimination of regional and global emergencies;
- Provides the combat and mobilization readiness of the military units of the Civil Defence and Fire Service units;
- Decide on the preparation and conduct of the Civil Defense, mandatory for central and local executive bodies, other organizations and the population of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
- Determines the need for weapons, equipment, security and other logistical facilities for civil defense;
- For emergency response mobilizes material resources, means of communication and transmission of information organizations, in accordance with applicable law;
- Directs the activities at the national level interagency state commission for the prevention and elimination of emergency situations and the National Commission for the oil spill response;
- Conducts the overall management and coordination of departments of the Ministry and territorial bodies that implement functions to prevent emergencies, civil protection, control and supervision in the field of fire and industrial safety, occupational health and safety at hazardous production facilities, ensuring the safe conduct of work in the industry, mining supervision and compliance with civil defense, as well as in the state material reserve;
- Holds direct control of civil defense;
- Organize the management of military units and formations of the Civil Defense during the rescue and other emergency operations;
- Holds direct control of civil defense forces in preventing and dealing with emergencies, it commands monitoring service, monitoring the situation and forecasting and warning system of the Republican and Republican information and control system for emergency situations;
- Organize training within the military units of the Civil Defense, and the heads of the organizations of civil defense, civil defense people, develops for that purpose the training program;
- Performs the creation, registration and registration of the emergency services and civil defense units;
- Coordinates the activities of rescue services and units created by the decision of the central executive bodies;
- Coordinates the activities of subordinate research organizations in the field of fire, safety and civil defense, as well as specialized research and design-engineering organizations on fire, safety and civil defense;
- Performs state administration in the field of security and safety at hazardous production facilities;
- In accordance with the law is concerned to ensure the state secrets of the Civil Defense, State Fire Service and the state material reserve;
- Carry out international cooperation, provides foreign organizations and citizens in the area of prevention and liquidation of emergency situations, civil defense, fire and safety, as well as in the state material reserves in Kazakhstan, organizes humanitarian actions.
The Ministry for the implementation of the main objectives and the performance of its functions has the right to:
1) within the limits of their competence binding regulations;
2) to make proposals to improve legislation on matters within its competence;
3) approve or negotiate the norms, standards and regulations in the field of emergency;
4) to make proposals for the establishment, reorganization and liquidation of the organizations under the Ministry;
5) to request and receive from the central and local executive bodies, other organizations, officials and citizens with information and information on matters within its competence;
6) to make proposals to the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan on attracting capabilities of law enforcement agencies, military units of the Armed Forces, other troops and military formations of the Republic for the elimination of accidents and natural disasters, public order and the protection of areas in emergency situations;
7) have special vehicles equipped with duly approved identification marks, special signals and communications;
8) have uniform throughout the country radio band in the manner prescribed by law;
9) to prepare draft international treaties and agreements on its own jurisdiction, within their powers to make treaties of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the exercise of their inventory;
10) to publish journals, operating manuals, bulletins and other publications on the prevention and elimination of emergency situations of natural and man-made disasters, civil defense, fire and safety, as well as in the state material reserve.
3 Ministry has the right management, separate property, which belongs to the Republican property.
The property is formed by the Ministry of the property transferred to it by the State.
The Ministry has no right to alienate or otherwise dispose of the property assigned to it.
Ministry may be entitled to dispose of the property in the cases and within the limits established by law.
4 Ministry headed by Minister of Emergency Situations (hereinafter - the Minister), who is appointed and dismissed by the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Minister for the post is Deputy Chief of the Civil Defense of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Figure 1.1).
The Minister has deputies (vice-ministers) who are appointed and dismissed by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan on the recommendation of the Minister. Minister organizes and directs the work of the Ministry, is personally responsible for the performance of the tasks assigned to the Ministry and the performance of its functions.
For these purposes, in accordance with law:
1) defines the duties and powers of deputies, heads of departments, divisions, territorial bodies and subordinate organizations of the Ministry;
2) appoint and dismiss employees of the Ministry, Vice-Chairman of the Ministry, heads of territorial bodies of Emergency Situations, the territorial bodies of the Committee for State Control and Supervision of emergency, under the Ministry of organizations, as well as their deputies, except those appointment and dismissal of which is within the jurisdiction of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan; 3) approve the structure of the Ministry;
4) submit proposals on the list of positions of the Ministry, to be replaced by high-ranking officers;
5) approve the list of positions to be filled officers of the troops of the Ministry;
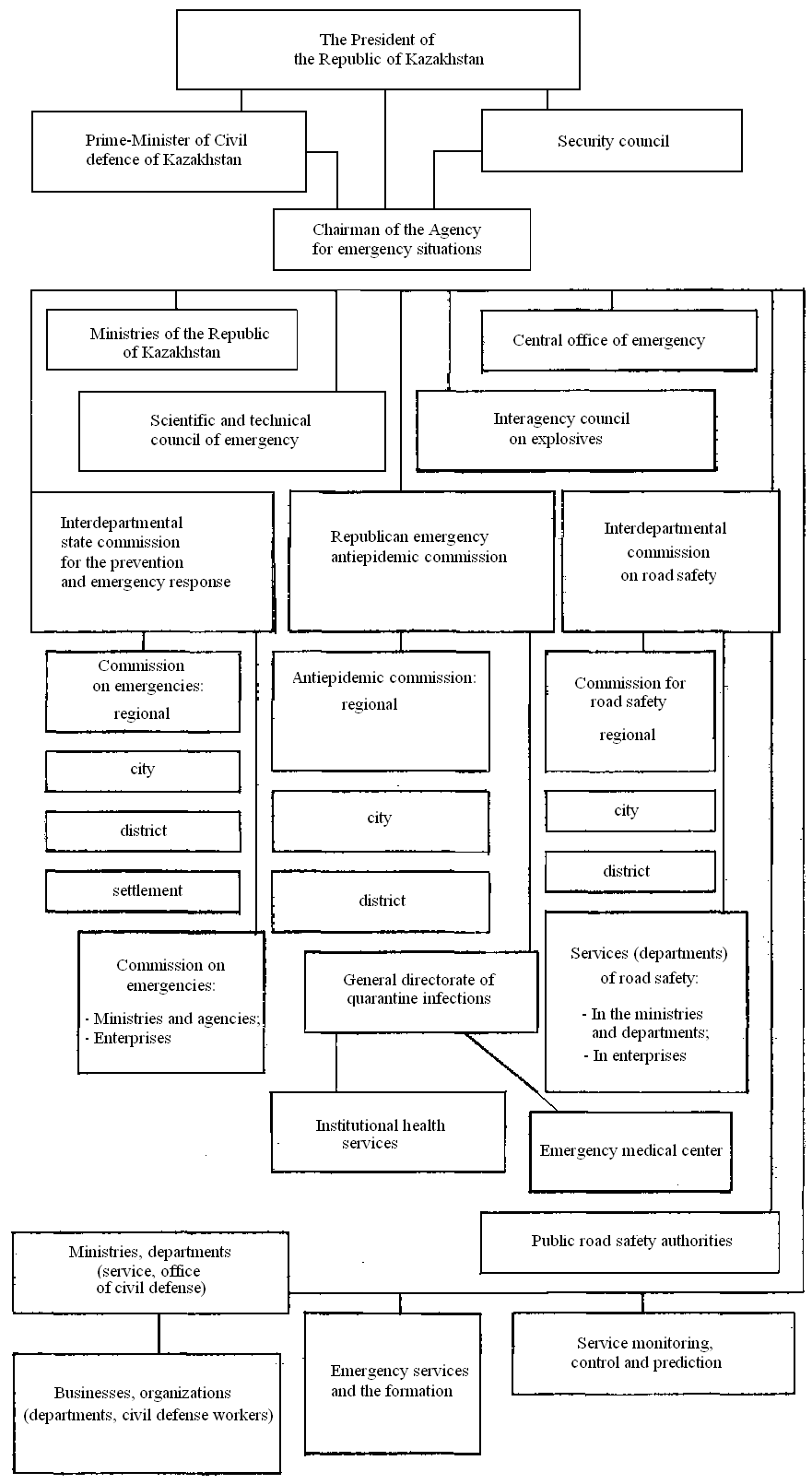
Figure 1.1 - Structure of the state system to prevent and eliminate emergency situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan
6) addresses issues of service and the military have a special rank officers of the State Fire Service in the Ministry, assigning them due process of law degrees, as well as their re-certification;
7) submit proposals to the Ministry of Defence of the Republic of Kazakhstan on the call for military service officers from the reserve;
8) makes a submission to the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan for the award of a particularly distinguished employees of the Ministry of state awards and honorary titles;
9) solves the promotion and impose disciplinary sanctions on the employees of the Ministry;
10) signs the orders of the Ministry, as well as give instructions obligatory for employees of the Ministry;
11) within its jurisdiction approves regulations on structural units and regional offices of the Ministry;
12) within its jurisdiction approve the statutes of subordinate state agencies as well as the structure and number of staff within the limits of the authorized strength, established by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
13) represents the Ministry in all government agencies and other organizations of the Republic of Kazakhstan, as well as in international organizations; 14) claims within the established government of Kazakhstan staff number limit staffing the central apparatus of the Ministry, local government and subordinate state institutions;
15) approve the Statute of Civil Defense and Emergency Situations;
16) forms a commission to investigate accidents, natural disasters and their consequences, as well as accidents at hazardous industrial facilities and loss of explosives;
17) for the implementation of the direct management of emergency management:
18) in coordination with local agencies and modes of behavior of citizens living in the areas of emergency;
19) suspended from duties assigned to direct the work in disaster management officials did not comply with the assigned tasks, and then bring them to justice in due course.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 Examine the main tasks of the Ministry.
2 Observe the main functions of the Ministry.
3 Observe the basic rights of the Ministry.
4 Observe the organization of the activities of the Ministry.
5 Draw the structure of the state system of prevention and liquidation of emergency situations in the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Literature:
1 Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan «About emergencies of natural and technogenic character», 5.07.1996
2 Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan «About salvage and rescue services and the status of rescuers », 27.03.1997
3 Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan «About a civil defence», 7.05.1997
4 S.V. Belov, A.V. Ilnitskaja, A.F. Kozjakov, L.L. Morozova. A safety of vital functions. – М.: Higher school, 1999. – p. 448.
7 Safety of vital functions. Manual. P.1-2. – М.: 1998. – p. 244.
9 Information-methodical collection of materials of emergency and civil defence. Releases 2000-2008, АСD of the RК.
PRACTICAL WORK № 2. STRUCTURE OF THE CIVIL DEFENCE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN
The purpose and objective studies: To study the structure of the Civil defense (CD) of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Contents of exercises:
1 The purpose and composition of the forces CD.
2 The purpose of the military units CD.
3 The purpose of the territorial and object units CD.
4 Purpose formations defense and emergency services
5 The purpose of the operational and rescue squads and fire departments.
1 Forces of CD designed to perform tasks CD to protect the public, organizations and territories, rescue and emergency operations in the lesions, chemical, biological, radiological, bacteriological contamination in peacetime and wartime.
Forces of CD consist of:
- military units;
- territorial and object units;
- formation of Civil Defense and Emergency Services;
- operational and rescue squads and fire departments.
The use of force by the decision CD Chief appropriate level.
According to international standards of alert forces, which include units of defense and operational rescue teams must be prepared to work in standalone mode for 14 days.
This is achieved by education, training, planning and training exercises. Level of readiness is determined during special inspections in accordance with established procedure, the relevant assessment criteria.
Under the authority, each of the components of the forces CD have their specific tasks and conditions of activity, the training and the training and certification of personnel. But at the same uniform for all leading and guiding their work documents for rescue work is the law of CD, operating instructions and instructions on the formation of CD.
2 The special role of the forces assigned to military units CDRK. In Kazakhstan, there are three units of the CD, staffed with specialists and all the necessary rescue equipment, facilities and equipment.
CD troops are designed to protect the population, territory and facilities management under the threat of a disaster, and in times of peace and war.
In peacetime, these troops are engaged in immediate goals for continuous improvement of their training, if necessary, directly involved in the processes of life support in certain regions of the country, in the prevention of disaster protection and the delivery of humanitarian assistance by appointment, in the elimination of emerging large-scale emergencies.
In wartime, they are concerned with the direct destination in the areas of application of modern means of destruction, chemical, biological, bacteriological, and radiological contamination, conducting evacuation operations and restoring vital facilities management and territories.
3 Formation of CD due to its greatest size and proximity to the homes of various immediate incidents and emergencies are the main basis of the forces CDRK.
They are designed for rescue and other emergency operations with the threat of a disaster and the use of modern means of destruction in peacetime and wartime.
Under the law on the formation of CD created by the territorial-production basis and are divided into territorial and object formation.
The base for all units CD are objects.
Territorial formations are designed to solve specific problems in the most important objects, parts of the region on their own or in conjunction with site-groups and in collaboration with the forces were attached.
Territorial formation created by a decision of akim appropriate level.
The composition and size of the units is determined based on sufficient demand, providing protection for people and organizations in the areas of peace and war, on the following principles:
-For the regions that are prone to earthquakes, the formation of CD are preparing a rate of 1 lifeguard for 10 population,
-Industrial regions prone to floods, fires and other potential dangers, forming CD preparing a rate of 1 lifeguard for 15 ... 20 inhabitants.
The object used for formation of the work of on-site, but can also be used for the relief efforts and off-site, to fulfill the tasks of the territories.
The decision on this can take local agencies, as appropriate.
The object created by the formation of enterprises, organizations and citizens in the community order of the Chief CD object.
If necessary, can be created and other abnormal formation of the Civil Defense, not in the set list.
So decided by the heads of the relevant CD.
To perform specific tasks in large enterprises in the central executive bodies may be set up specialized staff formation.
CD to the formation they are not, but may be involved in disaster management in accordance with the approved plans interaction.
If necessary for the liquidation of particularly complex emergencies, based on the circumstances, the decision of the local executive body may be created combined rescue teams from the existing CD regional, facility and specialized units CD, etc. General management by the head of rescue operations.
The dismantling of collective units produced after the rescue, allowing all formations on the Consolidated formation CD, begin the task as intended.
States and the standards developed by CD equipping units of central and local executive bodies, organizations in coordination with the regional offices of ME.
The organizational structure of units CD can be specified and refined as necessary and based on the real situation.
Regional and site-formation to address the relevant CD chiefs may be included in the composition of groups of national, regional, city services, civil defense and emergencies.
4 Defense and emergency services are established to ensure that the defense and special events in preparation for this purpose capabilities. They report directly to the head of CD. They are the basis for the organization, company profiles and corresponding destination. On the basis of established services such as:
- Engineering, medical, fire and public safety,
- Information, warning and communication
- Radiation and chemical protection, energy and transport,
- Provision of fuel and lubricants, the organization of trade and supply,
- Construction, repair and maintenance of roads and bridges,
- The protection of animals and agricultural plants etc.
Defense and emergency services are created by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the decisions of the appropriate level of Mayor, the head of the organization.
The list of national defense and emergency services is determined by the Government. They state the position of the central executive body of the Republic of Emergencies.
Responsible for readiness of command and control, capabilities, civil defense and emergency services rests with the heads of central and local executive bodies and organizations, on the basis of which they were created.
CD formation by purpose are divided into:
- The basic formation: exploration, rescue, medical, engineering, fire, emergency, technical, radiation and chemical protection;
- Providing formation: communications, logistics, transportation, public safety, the protection of animals and plants, and others.
For disaster management in peacetime from the existing groups of CD and staff specialized units established emergency response units of permanent readiness.
Number one unit emergency response:
- Area - no less than 150 people.
- The city - at least 100 people.
- District - at least 50 people.
Maximum time alerting units installed CD:
- No more than 2 hours - for emergency response unit;
- No more than 4 hours - for the main groups;
- No more than 6 hours - for all other groups.
Completed with the formation of CD men and women of working age, with the exception of:
- disabled groups 1,2,3;
- pregnant women;
- women with children under 8 years;
in time of war - military service with the mobilization prescription.
5 Operations and rescue teams, as the forces of high alert, set up in the national, regional and local scales. Their representatives are Republican operative and rescue team, the regional operational airmobile rescue teams - North, South, East, West, Central.
A number of cities and regional centers established local operational and rescue teams, in some sectors - specialized and paramilitary rescue services and units.
A characteristic feature of these units and services is financed from the national budget.
Fire Departments, as Standby Force, set up and operate in the fire service of the Emergencies Ministry.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 The composition of forces CD.
2 Observe the military units CD.
3 Explore the purpose of the territorial and object units of CD.
4 Observe the purpose formations defense and emergency services.
5 Study destination quickly and rescue squads and fire departments.
Test questions:
1 Which of forming part of the forces CD of the Republic of Kazakhstan?
2 As classified by the nature of the forces CD?
3 As, according to the law of the Republic of Kazakhstan are forming CD and how they are divided?
4 What document are defined: a list of regional and site-level units, the order of their establishment and operation, the timing of alerting?
5 What kind of services are based on organizations, businesses and the corresponding profile of destination?
6 What determines the list of national defense and emergency services?
7 How to divide forming CD as intended?
8 To what extent are created, as the forces of increased operational readiness and rescue?
Literature:
1 Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "About a civil defence ", 07/05/1997.
2 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
3 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
PRACTICAL WORK № 3. LAW OF THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN «ABOUT A CIVIL DEFENCE», 7.05.1997
The purpose and objective lessons: Learn Law of Kazakhstan "About a civil defence ", 07.05.1997
Contents of exercises:
1 Relations regulated by law.
2 Organization of work and measures of civil defence (CD).
1 With the ever-increasing requirements to ensure national security, to the stability of the economy, to improve the social welfare of the population, one of the most important functions of the state, part of its defense activities is the organization and conduct of the Civil Defence.
This is clearly reflected in the Law of RK "About a civil defence".
As defined in the law, Civil defense - is a national system of controls and a set of national events in order to protect people, facilities management and the country from the effects of damaging (destroying) factors of modern means of destruction of natural and man-made.
Law reveals the main tasks and the organizational principles of construction and operation of the Civil Defense in the Republic of Kazakhstan, the powers and functions of government agencies, officials and citizens.
Impact of the law on CD apply to all government authorities, organizations and all citizens of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The law defines the main tasks of CD.
Law on CD significantly complements and develops and strengthens the basic provisions and requirements of the legislation of Kazakhstan on emergencies.
Of particular importance in the law given warning and information on actions at threat and occurrence of disasters. Single CD signal is a signal "Attention all!", reports sirens and other signaling means.
The law marked a special significance in activities CD issues a clear statement of work for the management, organization and control performance requirements
2 According to the law of the Republic of Kazakhstan:
- In the Republic of Kazakhstan, the general management of civil defense exercises, Prime Minister;
- Central and local executive bodies, organizations of civil defense guide led the first leaders (ministers, regional governors, cities, districts, the first leaders of organizations), which positions are senior CD.
They are personally responsible for the organization of work, the state and the implementation of measures GO.
Implementation of measures imposed on the appropriate CD executive bodies, which perform the functions of:
across the country - the central office MES RK;
in the province, city,
area of the city - department, division or senior official
of akim;
in the central
executive body - the main office or
specialist defense and emergency;
in the organization - headquarters of CD or excepted
defense and emergency specialists.
If necessary to ensure that the defense and special events in preparation for this purpose capabilities are civil defense and emergency services, and for the evacuation CD - evacuation, evacuation selection commission.
Implementation of the measures requires a clear CD orientation in its main provisions, the training and education of personnel groups CD, system readiness forces to act in various situations.
Therefore, with the personnel groups CD according to the law should be carried out in a timely planning workshops, special tactical exercises as the main most effective form of training to perform the tasks as intended; training on notification and fees.
Important place in the work of civil defense forces assigned to CD, which consist of the units of the Civil Defense, defense and forces formations defense and emergency services, operational and rescue teams, paramilitary and specialized rescue services and fire departments.
They take an active part in the rescue and other emergency operations with the threat of a disaster, and in times of peace and in times of war.
Therefore CD force must be trained, equipped with machinery, equipment and human resources.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study the structure of the Low.
2 Designation of the Civil Defense.
3 Observe the main objectives of the Civil Defence.
4 Observe the organization of work, the state and the implementation of measures of CD.
Test questions:
1 When the Law was passed?
2 What are the requirements?
3 What is regulated in the Law?
4 What is the Civil Defense, as defined in the law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "About a civil defence "?
5 What is a warning signal of CD?
6 Who, according to the Law the general management of the Civil Defense?
7 What are the executive bodies responsible for the fulfillment of measures of CD?
Literature:
1 Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "About a civil defence ", 07.05.1997.
2 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
3 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
PRACTICAL WORK № 4. LAW OF THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN «ABOUT EMERGENCIES OF NATURAL AND TECHNOGENIC CHARACTER», 5.07.1996
The purpose and objective lessons: Learn Law of Kazakhstan «About emergencies of natural and technogenic character», 05.07.1996
Contents of exercises:
1 Relations regulated by the Law.
2 Terms and definitions used in the Law.
3 The rights and obligations of the citizens of the Republic of Kazakhstan, foreign citizens and stateless persons in emergency situations.
4 Measures for the prevention of emergency situations.
1 Protecting the public, the environment and facilities management of emergency situations and the consequences thereof, is one of the priority areas of public policy. The law regulates the social relations in the Republic of Kazakhstan on the prevention and elimination of emergency situations of natural and technogenic character.
2 Law the following basic terms and definitions:
Emergency response - rescue, emergency recovery and other urgent works carried out in an emergency and life-saving and preserving health, reducing the damage and material losses, as well as the location of the zones of emergency situations;
Prevention of emergency situations - a set of activities carried out in advance and aimed at the greatest possible reduction in the risk of emergencies, maintaining the health and life of humans, reducing the damage and material losses.
3 Citizens of the Republic of Kazakhstan shall have the right in the field of natural and technogenic character:
- To be informed of the risks they may be exposed in certain places of stay in the Republic of Kazakhstan, and the measures necessary security;
- Apply in person, sent to state and local government individual and collective appeals for the protection of citizens, environment and facilities management of emergency situations and consequences thereof;
- Participate in activities for the prevention and elimination of emergency situations, use the collective and individual protection, other property intended for the protection of citizens;
- The protection of life, health and personal property in the event of emergencies;
- For insurance, compensation and benefits for the damage caused to their health by engaging them to perform duties in emergency situations;
- Social security in case of disability due to injury or illness, widowhood, killed or died from injury or disease, if they occurred as a result of the duties on disaster management, in accordance with the laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan on the state social benefits;
- For damages caused to their health and property due to emergency situations.
Citizens of the Republic of Kazakhstan must in emergency situations of natural and technogenic character;
- Comply with the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the field of emergency situations and protect against citizens, the environment and facilities management;
- To inform the relevant authorities about the threat of accidents, disasters and catastrophes, which could lead to emergency situations;
- Observe safety measures in the home and the daily work and economic activity, to prevent violations of the industrial and technological discipline, safety, which can lead to emergency situations;
- Know the signals of Civil Defense, the rules of conduct and procedures for the threat of or emergency situations, learn the basic methods of protection techniques in first aid to the victims, rules for the use of collective and individual protection means, constantly improve their knowledge and these skills;
- Takes part in exercises and training on disaster management, care of the means of protection of the population, environment, and facilities management.
Foreign citizens and stateless persons who have rights and responsibilities in the area of natural and man-made disasters, citizens of the Republic of Kazakhstan, unless otherwise provided by the Constitution, laws, international treaties ratified by the Republic of Kazakhstan.
4 To interventions for the prevention of emergency situations of natural and technogenic character include:
- Scientific research, monitoring, control environment, forecasting and warning about the threat of accidents, disasters and catastrophes, which could lead to emergency situations;
- Promoting knowledge, education of the public and professionals, protective measures in emergency situations;
- Analysis of technical regulations in the field of natural and man-made.
The main objectives of research in the field of natural and man-made disasters is to develop methods to monitor and develop a database of emergency situations, methods of forecasting, prevention, control measures and protective equipment, target and scientific - technical programs on forecasting, impact assessment, prevention and response emergencies.
Monitoring service, monitoring the situation and forecasting of natural and man-made (seismological service, mudslide warning system, control of radiation safety) are created by specially authorized state bodies, and are included in the state system of prevention and liquidation of emergency situations.
Information in the field of natural and man-up information on the risks and hazards of the organizations the necessary security, effects, measures for the prevention and elimination of emergency situations. She is open and transparent, to be published in the mass media, communication and warning system.
Not allowed concealment, late submission or presentation by officials of false information in emergency situations of natural and technogenic character.
For information - technical support government established a national automated information - operating system for emergencies.
Promotion of knowledge in the field of natural and man-made by specially authorized state bodies and public organizations. To promote knowledge can use the media.
Education is being implemented in the institutions of pre-school and secondary education, the organizations at the place of work and residence, and professionals - in post-secondary institutions and higher education, training and re-training, training centers to act in emergency situations and civil defense organizations in the workplace.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study the structure of the Law.
2 Define the elimination and prevention of emergency situations.
3 Observe the rights and responsibilities of citizens of the Republic of Kazakhstan, foreign citizens and stateless persons in emergency situations.
4 Observe the activities undertaken to prevent emergencies.
Test questions:
1 When the Law was passed?
2 What are the definitions and terms defined in the law?
3 What are the requirements included in the basic principles of the protection of the population and facilities management for various emergencies?
4 What are the powers of public authorities in emergency situations?
5 What are the steps for emergency situations?
6 What is the control and supervision of emergencies?
7 Has the international cooperation in emergency situations?
Literature:
1 Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan «About emergencies of natural and technogenic character», 5.07.1996
2 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
3 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
PRACTICAL WORK № 5. ACTIONS ON PROTECTION OF THE POPULATION AT RADIATING AND CHEMICAL INFECTION OF DISTRICT. REALIZATION OF SANITARY-AND-HYGIENIC AND PREVENTIVE ACTIONS
The purpose and objective studies: To study the action to protect the population and the implementation of hygiene and preventive measures
Contents of exercises:
1 Organization and implementation of personnel and public protection.
2 Types of work done by the implementation of sanitary and preventive measures.
1 The effectiveness of protective equipment in emergency situations is determined by the constant technical readiness for use, as well as a high degree of training of facility personnel and the public.
The first event in the protection of workers and the public in an emergency situation is considered an emergency chemical environment forecasting and warning people about the dangers of defeat.
The second most important activity is the use of means and methods of individual and collective protection. Protection of a specific role for various types of gas masks and purpose. As the event is providing protection chemical detection and chemical control.
A special place in size and importance in the complex of measures of protection given to eliminate or minimize the effects of chemical contamination.
Basic norms of conduct and actions of the population in case of accidents with the release of SOPS.
Personal protective equipment is divided into:
a) respiratory protection;
b) the protection of the skin.
By way of protection they are divided into filtering and isolating. The choice of protection is determined according to their destination, the protective properties, the specific conditions and the nature of the chemical environment of infection (what and at what concentration).
Respiratory protection filter type (industrial gas masks and respirators) are widely used to protect against SOPS as the most affordable, simple and reliable in operation.
Filter means are divided in purpose: to personnel of military forces (combined arms and special), to form a defense and public (civil), the officials of hazardous industries (industrial).
To civilian assets include gas masks GP-5 and GP-7. Gas masks are designed to protect the respiratory, eye and skin from PG, RS, asthma and other harmful substances (except ammonia, ethylene oxide, nitrogen oxides, mercury, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen fluoride). The set of GP-5 are front part, gas bag, anti-fog film, insulation sleeves. Face mask mask GP-5 has a speakerphone. Mask GP-7 allows reception of water or other liquid in the infected atmosphere.
Respiratory protection masks children used PDF-D (2D), PDF-B (2m). The primary means to protect children up to 1,5 years are children's safety camera KZD-4 and KZD-6.
Self-contained breathing apparatus (masks) IP-4, IP-5 are designed for respiratory protection of skin and eyes from any harmful impurities in the air, regardless of its concentration in the performance of work under the conditions of oxygen deficiency or lack thereof.
Apparatus consists of a front part with a connecting tube, regenerative cartridge, breathing bag, frame bag, a set of anti-fog film, insulating sleeves.
As the personal protection of the skin using insulated coats and suits, made of rubberized material, filter instruments to suit or coveralls of a conventional material, impregnated with special chemical compounds or neutralizing absorbent pairs SOPS.
By isolating type are combined-arms protective kit (OZK) and lightweight protective suit L-1.
2 Decontamination is one of the effective measures of radiation protection, as this technique is used to remove radioactive substances from human activities, and thus reduce the effects of radiation on humans.
The basic methods of decontamination of the individual objects are:
for open areas:
- Removal and subsequent disposal of contaminated top soil layer (mechanical method);
- Decontamination method of screening;
- Purification by vacuum;
- Chemical soil decontamination methods (washing);
- Biological decontamination methods (natural decontamination) for roads and paved areas;
- Flush radioactive contaminants with water or decontamination solutions (liquid method) ablation special tools or abrasive preparations;
- Decontamination method of screening;
- Sweeping brushes watering machine (many times);
for the terrain covered with vegetation:
- Felling and backfilling with clean soil after falling off the crown;
- Cutting crown after blowing it with the collection and disposal of buildings and structures;
- O6rabotka decontamination solution (with and without brushes);
- Processing of high-pressure jets of water;
- Purification by vacuum;
- Replacement of the porous structure elements;
- Demolition.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study the classification of personal protective equipment.
2 Observe respiratory protection.
3 Observe the skin protection.
4 Observe the methods and techniques for decontamination.
Test questions:
1 What types of work performed in the organization of personnel and the public?
2 How is the protection of workers and the public?
3 What used personal respiratory protection?
4 What are used personal protective skin?
5 What methods are used for decontamination?
6 What methods are used in the decontamination?
Literature:
2 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
3 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
3 V.G. Atamanyuk. Civil defense. – M.: 1986.
4 M.H. Gabdullina. A manual for the practical and independent work on discipline life safety. - Astana, 2006.
5 Methodology of radiation and chemical environment. Guidelines, developed by the Department of the MTP KazATU. - Astana, 2004.
PRACTICAL WORK № 6. THE INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATIONS WHICH PROBLEMS INCLUDE VARIOUS ASPECTS OF A SECURITY OF ABILITY TO LIVE OF THE PERSON. SOURCES OF RADIATING POLLUTION (INFECTION) OF AN ENVIRONMENT AND UNIT OF THEIR MEASUREMENT
The purpose and objective studies: To study the activities of international organizations tasked with the various aspects of safety of human life, and the types, sources, and units of radiation contamination
Contents of exercises:
1 The activities of international organizations.
2 Types and sources of radiation.
1 Current international cooperation of Kazakhstan in the field of safety of human life based on three main areas: 1) international organizations, 2) international conventions and agreements; 3) multilateral and bilateral relations.
The World Conservation Union, founded in 1948 (based in Gland, Switzerland), is the oldest and the world's largest independent international non-profit organization. The Union brings together 78 states. It plays a leading role in the global environmental movement in the dissemination of a common approach to preserving the integrity and diversity of nature, the use of natural resources for sustainable development principles. Union activity is known for publications such as the Red Book and the «Lists of animals and plants threatened with extinction», «World Conservation Strategy», «List of national parks and protected areas» and others.
In 1957 the United Nations established a special organization - the International Atomic Energy Agency. It consists of 120 states. It headquarters in Vienna. One of the main activities - the problem of the safety of nuclear power plants. It experts to review and make conclusions about the level of safety of specific plant.
Efforts to improve the health of all countries by specialized agencies - the World Health Organization. It was created in 1948 and brings together 165 countries. By means of direct technical cooperation with member countries and by stimulating such cooperation among them, it promotes the development of health services, prevention and control of diseases, environmental conditions, the development of a healthy population, coordination and research for health and biomedical research, planning and implementation of health programs .
Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons has been banning the development, production, stockpiling and use of chemical weapons and their destruction. Almost all members of the United Nations (168 countries) have signed this agreement.
The International Civil Defence Organization was established in 1931, headquartered in Geneva. In accordance with the charter is the development and improvement of the civil defense, methods and technical means to prevent or reduce the effects of hazards peace and war.
Intergovernmental Oceanic Commission was established in 1960 in order to study the value of the ocean to humanity.
The World Meteorological Organization - international intergovernmental organization. It began operations in 1951, brings together 185 countries. Location - Geneva. It is collaborating on weather observations and research, information sharing, etc. In 1976, It made a first statement about the threat of climate.
The best-known international public organization is the «Greenpeace», founded in 1971. It has 27 offices around the world.
The World Wildlife Fund - the world's largest environmental non-governmental international organization, founded in 1961. The Fund aims to preserve biodiversity, promote sustainable use of natural resources and the prevention of unnecessary domestic pollution.
International Socio-Ecological Union - the only public non-profit organization with the goal of «uniting intellectual capacity, material and financial resources, organizational capabilities of members of the union for the protection of nature and the earth of living creatures that inhabit it, for the preservation and restoration of the natural and cultural heritage, physical and mental health, environmental security and sustainable development».
The Global Environment Facility - a financial mechanism to provide grants and concessional loans to recipient countries for projects and activities designed to address global environmental issues.
2 Radiation - is the radiation coming from an object. There are two types of radiation: natural and man-made radiation.
Natural radiation is divided into the space and natural light. Cosmic radiation is produced in stellar explosions in the galaxy and solar flares. Dose of cosmic radiation effect on people. The higher the altitude, the less there is of protective layers of air, ozone, and the more exposure. At an altitude of 2000 m above sea level, the cosmic ray intensity is three times the rate of sea level. Cosmic rays are responsible for nearly half of the dose received from natural radiation sources.
Natural sources of radiation are radioactive substances in the bowels of the earth, the air, water and plants.
Artificial radiation generated by human activities. Nuclear power plants, nuclear-powered icebreakers, nuclear submarines, radioactive facilities, nuclear test sites and more created by human hands. The sources of contamination (contamination) of the environment include the following:
- Uranium industry;
- Nuclear reactors, various types;
- Radiochemical industry;
- The place of processing and disposal of radioactive waste;
- The use of radionuclides in the economic complex (industry, medicine, agriculture, space).
On the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan has five nuclear reactors and installations:
One is located near the city of Almaty in Alatau, the Institute of Nuclear Physics. Other nuclear fast reactor BN-350 - in Aktau, was used primarily as a water desalination plant, is currently not functioning. Three nuclear installations - at the former Semipalatinsk nuclear test site (one plugged), previously used in military and scientific purposes.
There are 4 types of ionizing radiation: α, β, γ, neutron radiation.
α - radiation is characterized by low penetration, but great ionizing power of the human body comes inhalation. Protection - respirator filter mask;
β - radiation is characterized by a greater penetrating power than the α-radiation, but less ionizing than α-radiation. Protection - respirator, skin care products such as OZK, L-1;
γ - radiation is characterized by enormous penetrating ability to penetrate walls of brick and reinforced concrete buildings, tank armor. Protection - shelter underground. Attenuation coefficient for γ-radiation: Tank - 10 times, brick building - 10 times, the car - 2 times
Neutron radiation is described as enormous penetrating and ionizing. Protection - shelter, underground, hydrogen-containing materials.
The doses of radiation:
- Absorbing dose - characterizes the energy of ionizing radiation absorbed by a unit mass of a substance. The unit of measurement in the SI - gray (Gy), off-system unit RAD;
- Exposure dose - for measuring radiation levels in the area, in the room. The unit of measurement in the SI - pendant/kg (C/kg), off-system unit - Roentgen (R);
- Equivalent dose - characterizes the biological effect of radiation. Unit in the SI - Sievert (Sv), off-system unit RE (roentgen equivalent).
The average radiation dose from all natural sources of radiation in the year 200-300 m/R or 0,2-0,3 RE. Dose level, which is for the people not potentially dangerous – 0,5 RAD. At this dose of radiation can cook in the open. In carrying out emergency works in the radiation danger zone as the cumulative dose should not exceed 25 RAD. Development of radiation sickness were observed when the dose of 100 RAD.
The key to protecting the population from radiation: reducing the time spent in the danger zone, increasing the distance (removal) of the radiation source (the affected area), the application of collective and personal protective equipment.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study the activities of international organizations.
2 Define the radiation.
3 Observe the types of radiation.
4 Observe the units of radiation.
Test questions:
1 What are the international organizations working in the Republic of Kazakhstan of life safety?
2 What are the natural sources of radiation?
3 What are the artificial sources of radiation?
Literature:
1 Life Safety. Textbook for high schools/ S.V. Belov, A. Ilnitskaya, A.F. Koziakov, etc. - M.: High School, 1999. - 448 p.
2 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
3 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
3 V.G. Atamanyuk. Civil defense. – M.: 1986.
4 M.H. Gabdullina. A manual for the practical and independent work on discipline life safety. - Astana, 2006.
5 Methodology of radiation and chemical environment. Guidelines, developed by the Department of the MTP KazATU. - Astana, 2004.
PRACTICAL WORK № 7. PROCEDURE OF AN ASSESSMENT OF RADIATING AND CHEMICAL CONDITIONS OF OBJECT OF MANAGING. POISONING BY STRONGLY OPERATING POISONOUS SUBSTANCES (SOPS)
The purpose and objective studies: Master the evaluation of the radiation and the chemical environment of the object management.
Contents of exercises:
1 Method measuring radiation prediction method
2 Evaluation of radiation according to intelligence
1 Method measuring radiation prediction method includes: determining the size of the sector zones of radioactive contamination and applying them on the map.
In the sector of the zone of possible infection provisionally identified:
A - zone of moderate exposure (blue);
B - highly contaminated zone (green);
C - zone dangerous infection (brown);
D - zone extremely dangerous infection (black).
Length of all the zones in centimeters from the start to lay strike on the center line from the band D.
Width in centimeters lay evenly on the left and right of the center line.
The ends of the zones must be rounded.
To determine the area of infection need to take each area as a rectangle, and the resulting area multiplied by a correction factor of 0,9 (due to rounding areas).
Percentage of space occupied by each zone is determined by the total area of the trace contamination of the radioactive cloud (zone A), which is taken as 100 %.
Power weapon and the average wind speed is listed in Table 1.
Table 1 - Dimensions of zones depending on the power stroke and the average wind speed
Option |
Power, Mt |
Wind speed, km / h |
Zone of radioactive infection km |
|||
A |
B |
C |
D |
|||
1 |
0,1 |
25 |
62-9,2 |
42-6,1 |
31-4,0 |
18-2,2 |
2 |
0,1 |
50 |
102-10,2 |
49-6,4 |
35-3,9 |
19-2,0 |
3 |
0,1 |
75 |
118-10,6 |
52-6,3 |
35-3,8 |
19-2,2 |
4 |
0,2 |
25 |
120-11,8 |
57-7,8 |
43-5,3 |
26-2,8 |
5 |
0,2 |
50 |
140-13,4 |
68-8,4 |
50-5,3 |
28-2,8 |
6 |
0,2 |
75 |
154-14,0 |
72-8,4 |
50-5,0 |
30-3,0 |
7 |
0,3 |
25 |
136-13,8 |
69-8,9 |
52-6,0 |
30-3,0 |
8 |
0,3 |
50 |
170-15,2 |
83-9,6 |
60-6,2 |
32-3,2 |
9 |
0,3 |
75 |
190-16,3 |
89-9,8 |
61-6,5 |
34-3,4 |
10 |
0,5 |
25 |
164-16 |
85-10 |
65-7,4 |
41-4,3 |
11 |
0,5 |
50 |
185-17,4 |
87-11 |
78-7,7 |
42-4,4 |
12 |
0,5 |
75 |
190-19,3 |
90-11,4 |
83-7,8 |
45-4,6 |
13 |
0,1 |
25 |
69-9,0 |
40-6,1 |
31-4,0 |
16-2,2 |
14 |
0,1 |
50 |
100-10,1 |
45-6,4 |
37-3,9 |
17-2,0 |
15 |
0,1 |
75 |
117-10,3 |
51-6,3 |
38-3,8 |
19-2,0 |
16 |
0,2 |
25 |
121-11,6 |
54-7,8 |
43-5,3 |
27-2,8 |
17 |
0,2 |
50 |
145-13,5 |
63-8,4 |
50-5,7 |
29-2,8 |
18 |
0,2 |
75 |
155-14,0 |
72-8,4 |
50-5,9 |
32-3,0 |
19 |
0,3 |
25 |
133-13,5 |
65-8,9 |
52-6,4 |
32-3,4 |
20 |
0,3 |
50 |
174-15,7 |
84-9,6 |
60-6,3 |
34-3,8 |
21 |
0,3 |
75 |
194-16,3 |
85-9,8 |
61-6,4 |
37-4,3 |
22 |
0,5 |
25 |
154-15,4 |
84-10 |
66-7,4 |
30-4,3 |
23 |
0,5 |
50 |
175-16,4 |
86-11,1 |
77-7,7 |
45-4,4 |
24 |
0,5 |
75 |
180-18,3 |
91-11,4 |
81-7,8 |
46-4,9 |
25 |
0,1 |
25 |
72-7,2 |
32-6,1 |
22-4,0 |
15-2,2 |
26 |
0,1 |
50 |
81-8,2 |
39-6,4 |
25-3,9 |
14-2,0 |
27 |
0,1 |
75 |
88-9,6 |
42-6,3 |
25-3,8 |
13-2,2 |
28 |
0,2 |
25 |
100-11,8 |
57-7,8 |
43-5,3 |
26-2,8 |
29 |
0,2 |
50 |
106-13,4 |
68-8,4 |
50-5,3 |
28-2,8 |
30 |
0,2 |
75 |
111-14,0 |
72-8,4 |
50-5,0 |
30-3,0 |
2 Evaluation of radiation according to intelligence is the most accurate.
To determine the boundaries of the zones of radioactive contamination and apply them to the circuit to a certain level of radiation measured at different points in the territory and over time, lead to the same time.
The points in the combined, drawing contours, is border zones of radioactive contamination.
Zone A: 8-80 R/h
Zone B: 80-240 R/h
Zone B: 240-800 R/h
Zone D: 800 R/h
Table 2 - K value indicating how many times the dose rate decreased
Time after the explosion, h |
К |
Time after the explosion, h |
К |
Time after the explosion, h |
К |
1 |
1 |
9 |
14 |
17 |
30 |
2 |
2,3 |
10 |
16 |
18 |
32 |
3 |
3,7 |
11 |
18 |
19 |
34 |
4 |
5,3 |
12 |
20 |
20 |
36 |
5 |
7 |
13 |
22 |
21 |
39 |
6 |
8,6 |
14 |
24 |
22 |
41 |
7 |
10 |
15 |
26 |
23 |
43 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
28 |
24 |
45 |
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 Solve one problem. At 14.00, August 15, 2000 at the center of the N-sk ground caused a nuclear strike. Wind direction 206 °. Map scale: 1 cm in 4 km. Assignment:
1) Sector strike next radioactive cloud.
2) Determine the area of the contaminated area (km2, %).
2 Determine the boundaries of the zones of radioactive contamination according to intelligence and to put them on the map.
Test questions:
1 How to identify the affected area prior to radiation?
2 How to determine the dose of radiation received by people and animals during their stay in the areas of infection and at the intersection of these areas?
3 Name the characteristics of the source of chemical contamination.
Literature:
1 N. Akimov, V.G. Ilyin. Civil defense at sites of agricultural production. Second edition, revised and enlarged. - M.: Kolos, 1978. - 327 p.
2 P.T. Egorov, I.A. Shlyakhov, N.I. Alabin. Civil defense. 3rd edition revised. M.:1977 - 301 p.
3 V.G. Atamanyuk. Civil defense. – M.: 1986.
4 Some recommendations on the management of agriculture and forestry in high pollution RS after the accident at the plant. - Kiev, 1987
5 M.H. Gabdullina. A manual for the practical and independent work on discipline life safety. - Astana, 2006.
6 Methodology of radiation and chemical environment. Guidelines, developed by the Department of the MTP KazATU. - Astana, 2004.
7 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
PRACTICAL WORK № 8. ORGANIZATION OF THE CIVIL DEFENCE OF A HIGHER EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION. ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE OF THE CIVIL DEFENCE OF OBJECT OF MANAGING. FORMATIONS OF THE CIVIL DEFENCE, PURPOSE AND THE ORDER OF THEIR CREATION
The purpose and objective studies: To study the organization of civil defense scheme on the example of «Kazakh Agrotechnical University named after S.Seifullin"
Contents of exercises:
1 United Civil defense educational institution.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 Draw the scheme of organization of Civil defense in the «Kazakh Agrotechnical University named after S. Seifullin»
Test questions:
1 Purpose of the plan of civil defense?
2 What are the main requirements for the civil defense plan?
3 What basic data needed to develop a plan of civil defense?
4 What is the order of development, approval and adjustment of civil defense plan?
5 Civil defence plan documents and their content?
6 Summary of the main application plan CD.
7 What formation CD planned en facility management, their purpose and how to create?
Literature:
1 N. Akimov, V.G. Ilyin. Civil defense at sites of agricultural production. Second edition, revised and enlarged. - M.: Kolos, 1978. - 327 p.
2 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
3 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.

PRACTICAL WORK № 9. PROTECTION OF PLANTS AGAINST THE WEAPON OF MASS DEFEAT. PROTECTION OF ANIMALS FROM RADIOACTIVE SUBSTANCES (RS), POISON GASES (PG), BACTERIAL MEANS (BM)
The purpose and objective studies: study methods and techniques of plant protection in the defeat herbicides, biological and radioactive substances.
Contents of exercises:
1 Activities of Civil Defense in the defeat of plant herbicides.
2 Activities of Civil Defense in the defeat of plant biological means.
3 Activities of Civil Defense in the defeat of plants with radioactive substances.
1 To protect plants from weapons of mass destruction in peacetime, conducting a number of organizational, agrochemical and other events. Particular attention is given to prevent the spread of diseases and pests of agricultural crops. Maintained by breeding work on breeding of plant varieties that are resistant to diseases and ionizing radiation. Carry out activities to improve agricultural background, perform quarantine.
All plant protection against weapons of mass destruction organize chiefs CD objects and relevant professionals Plant Protection Service. After the determination of enemy chemical agronomist economy examined all of the fields and farms, using visuals and rapid method, determine the type of herbicide (defoliant, desiccant), and samples were taken for laboratory analysis and define the boundaries of contamination.
Determine the type and dose of herbicide deposited on plants, agronomist economy predicts a possible infestation of plants with the phases of their development, weather conditions, and the possible loss of crops or plant death, and then outlines an action plan to save the crop. Conduct mineral supplements, inter-row cultivation, additional irrigation, etc. Collected from these fields grain used for food only with the permission of the medical service, and in animal feed - with the permission of veterinary experts after determining there residual herbicide.
With the defeat of crops in moderate (50...70 % reduction in yield) as a function of economic management and its technical capacity plants can be plowed as a field then re-planted crops that are resistant to this herbicide, or affected by the crops for harvest in mandatory measures reducing the harmful effect of the herbicide. Obtained with the use of such sites harvest for human consumption or animal feed after the determination of residual herbicide.
With the defeat of crops to a large extent (the death of 90 ... 100 % of the crop), the plants tend to be destroyed. At low altitude plants plowed field, with a large increase in their mowing, are taken out of the field and burned, and the field plowed. Keep in mind that reducing the application of the herbicide on the crop 50 % of the remaining technical quality cotton fiber and seed are greatly reduced. Fiber will be the fourth grade, and the seeds - the third class.
Regardless of the dose of herbicides on infected pastures are not allowed to graze animals or contaminated with herbicides, mowing grass for animal feed. In such areas, can not be taken for drinking, food needs and watering animals water from open sources without the permission of the medical and veterinary services.
In the year of application of the herbicide plowed fields can be used for sowing of winter or spring ripening food and forage crops resistant to enemy use of the drug. 2 In determining whether the use of those funds to establish the form of the pathogen and to survey all fields.
Finds in the air or on the crops of cereal rust determine the possible development of the parasite in the fields and plan the timing and sequence of processing fields with fungicides.
The most effective use of fungicides is determined as follows. The first treatment is carried out by detecting the air or on the stem rust pathogen crops in quantities that can cause Epidemics if the weather is favorable. Then analyze possible contamination of wheat and determine the duration.
To protection potatoes spend spraying fungicides to foliage in combination with foliar phosphate-potash fertilizers.
The first treatment of potato fungicide made immediately after the determination of plant infection and no later than one day before the primary manifestations of the disease. Dates subsequent treatments determines agronomist based on the duration of activity save fungicide on the plants and synoptic weather forecasts for the area. Take into account the minimum and maximum temperature, the amount of effective temperatures, the incubation period of the fungus, the presence of precipitation.
3 Protection in the plants from the damaging effects of nuclear explosions, including the radioactive substances is almost impossible. You can close the film, only small areas. Therefore, in case of enemy nuclear weapons the main activities in the plant will be used to reduce the damage caused by fallout, and to reduce admission to the plant tissue, especially in the economically useful part, radioactive isotopes.
Radioactive products of nuclear explosions can settle on the fields before planting. In this case, the contaminated soil, deep plowing should be done with a full revolution of the formation. As a result of plowing the upper contaminated layer is placed on the bottom of the furrow. A later spend a smaller plow, not to raise the soil surface from the depths of RS.
With the explosion of nuclear weapons during the growing season contaminated RS not only the soil, but also vegetation. This situation can occur during the formation of a trace of the cloud at ground and underground nuclear explosions, and in a period of intense global fallout of nuclear fallout, which can occur within two to three years. In these cases, a complex of protective measures aimed at saving the crop and reduce contamination of crops.
Finally, for many years the soil will contain long-lived isotopes (strontium-90, cesium-137, etc.), which migrate from the soil into the plant. In such situations, the complex of measures aimed at reducing the transition RS in the aerial parts of plants and roots.
4 Principle of veterinary treatment of animals is to remove from the skin of radioactive substances to acceptable values and giving them first aid. Depending on the situation and weather conditions, treatment of the skin of animals is carried out dry, humid, and combined methods.
Decontamination is the removal of radioactive materials from a variety of contaminated sites. The purpose of deactivation - to reduce radioactive contamination to permissible values.
With the defeat of the animals of nerve agents first aid is the immediate introduction of antidotes in place of affected population group or individual way, in carrying out a partial veterinary treatment of skin infection with a drop-liquid chemical agents, the use of personal protective equipment during the evacuation of animals from the lesions and in carrying out a complete veterinary treatment of the skin, if necessary, is the source of infection, and in neutralizing agents who have got into the body with food or water.
Animals caught in the hearth of biological contamination, is subjected to veterinary treatment, which includes the decontamination and removal from the skin of various bacterial disinfectants and preventive vaccines and the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. During infection of the skin with viruses and asporogenous microflora are a solution of the drug in 1,5 ... 2 times lower concentration.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study the event in the defeat of plant herbicides.
2 Observe the events in the defeat of plant biological means.
3 Observe the events in the defeat of plants with radioactive substances.
4 Observe the events in affected animals.
Test questions:
1 What activities are developed with the defeat of plants with herbicides, biological agents, radioactive substances?
2 What measures are designed to reduce crop losses and surface contamination of crops by radioactive substances?
3 What activities are developed in areas of radioactive contamination?
4 What measures are designed to protect animals?
Literature:
1 N. Akimov, V.G. Ilyin. Civil defense at sites of agricultural production. Second edition, revised and enlarged. - M.: Kolos, 1978. - 327 p.
2 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
3 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
PRACTICAL WORK № 10. RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONDUCTING PLANT GROWING IN CONDITIONS OF RADIOACTIVE, CHEMICAL AND BACTERIOLOGICAL INFECTION OF TERRITORY. RECOMMENDATIONS ON CONDUCTING ANIMAL INDUSTRIES IN CONDITIONS OF RADIOACTIVE, CHEMICAL AND BACTERIOLOGICAL INFECTION OF TERRITORY
The purpose and objective studies: Study recommendations on the management of crop and animal production in the conditions of radioactive, chemical and biological contamination area.
Contents of exercises:
1 Recommendations to improve the sustainability of crop
2 Recommendations to improve the sustainability of livestock
One crop, being a major supplier of food, to continue to develop and sustainably operate in extreme conditions. It is recognized that the main factors of its development and stability - improvements to land, increasing the amount of fertilizers, improvement of tillage and crop, finding effective means of protecting plants from weeds and pests, reducing crop losses during storage.
All of these factors require the performance of such activities as widespread use of intensive technologies, timely and complete the full range of agricultural and agro-chemical activities, the creation and introduction of high-yielding and disease-resistant and pest varieties and hybrids of crops, the creation of high-performance and cost-effective machines, preparation skilled machine operators and professionals; development of energy-saving technologies in crop, improving the phytosanitary conditions to prevent the spread of plant diseases and pests, creating a permanent carryover reserve stocks of seed, feed, fertilizer and pesticides reserve, construction of storage facilities for crop production, fertilizer warehouses, chemicals, development of irrigation and irrigated agriculture, as well as greenhouses for sustainable and high-quality crops.
Simplified cultivation technologies of major food and feed crops in farm contamination fallout should focus on the following objectives: preventing dangerous exposure of workers field team, links, getting enough clean production and economical use of energy resources.
2 Stable operation is achieved livestock reliable protection of animals from destruction weapons and the creation of the conditions necessary for its operation. Organization and management of the work to improve the sustainability of livestock entrusted to serve the protection of animals and plants, the heads of collective farms and state farms, and the practical implementation of them – on non-military formations of civil defense.
Animal welfare is a set of activities undertaken to prevent or minimize exposure to weapons of mass destruction, and thus minimize losses and maintain productivity:
a) the establishment and training of groups of institutions and power service, maintenance personnel and workers of livestock means of collective, individual and health protection;
b) implementation of standards for the design and construction of livestock buildings, storage of feed on the farm and facilities, electricity and water supply;
с) compliance with fire safety in livestock farms. Additionally breeders must master techniques withdrawal of animals from burning buildings;
d) creating a feed, antibiotics, vaccines, radiation protectors, antidotes. For sustainable livestock production in the livestock farm and courts should create a permanent stock of feed on 30...45 days for the planned number of livestock, and the object - a reserve feed 6...12 months.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study recommendations on the management of crop production in the conditions of radioactive, chemical and biological contamination area
2 Observe the recommendations on the management of livestock in conditions of radioactive, chemical and biological contamination area.
Test questions:
1 What are the key measures to reduce the entry of strontium-90 from soil to plants?
2 How to feed livestock in areas of high radioactivity?
3 How is the veterinary treatment of animals?
4 How is curative and preventive care to animals?
Literature:
1 N. Akimov, V.G. Ilyin. Civil defense at sites of agricultural production. Second edition, revised and enlarged. - M.: Kolos, 1978. - 327 p.
2 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
3 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
PRACTICAL WORK № 11. PROTECTION OF THE FOODSTUFFS, FORAGES, WATER AND WATER SOURCES FROM RS, PG, BM. WAYS OF DISINFECTING OF PRODUCTS, FORAGES AND WATERS IN VARIOUS CONDITIONS. SAFETY MEASURES
The purpose and objective studies: Learn how to protect and disinfection of food, feed, and water.
Contents of exercises:
1 Protection of feed and products in the field.
2 Protection of food and water in the home.
3 Protect water sources from toxic and radioactive substances and bacterial agents.
4 Disinfection of food, feed and water in the agricultural enterprise.
1 To avoid contamination of grain and other products need to be isolated from the infected air. To do this, turn to seal the storage space and the use of an insulating container and packaging material. When sealing warehouses, grain and vegetable stores carefully sealed all the cracks in the doors, the windows, walling (especially in the ceiling and roof junctions with walls), some of the windows tightly lay brick, glass repair and obscure in the windows of all the cracks with putty, clay, made shutters to close left window openings, repair the door and knocked them impermeable material, is inserted into the vestibule of rubber or felt pads, close up the gap in the roof (ceiling) and walls (sewn planks, roofing, etc.). All pipes and ducts equipped with valves or valves.
Meat, fats, dairy products are protected in refrigerators.
Protection of food and products in the field organized by simple methods, using materials available in the economy. Keep in mind that linen, cotton bags do not protect them are in grain, flour and other products from contamination.
Grain in bundles harbor synthetic film tarp layer of straw, hay or turf. With tarpaulin shelter under it put a layer of straw.
Can reliably protect potatoes and root crops in the pits.
Stacks of hay, straw, harbor canvas, film or straw (Figure 1).
2 For the protection of food and water in the home harbor them improvised materials or are packaged in a protective container. Basements and cellars are sealed in the usual way, they are stored in potatoes, carrots, beets, etc. cover with foil or shift in paper bags and tie. You can put a product in drums, heavy boxes, close and tie them on top of a film or oil cloth, thick paper.
All bulk products (sugar, cereals, flour, etc.), as well as bread, crackers can be reliably protected in packages of construction paper, foil pouches. Their tightly knotted, put in a pot, bucket, cardboard box, plywood box, close the lid, and then wrap or cloth and tie (Figure 2). Butter, margarine, solid fats is best to shift into jars and close the top with plastic wrap, foil, parchment or regular paper and tie. Wrapped and packaged foods should be stored in cabinets, refrigerators, storerooms, cellars, basements.

Figure 1 - Protection of roughage
Supplies of water and liquid fats are best kept in closed bottles, decanters, thermoses, food cans, milk jugs. Large reserves of water stored in drums and other containers.
Figure 2 - Protective packaging and containers to protect
food and water from contamination
Barrels of pickles on top of the film cover, tablecloth and tightly knotted. All the products are in sealed glass jars and cans made of tin (canned fruit, condensed milk, etc.) are protected.
Every family should keep 2 ... 3-day supply of food (in terms of all members of the family) - meat and canned fish, condensed milk, sugar, biscuits and crackers - as well as water (fruit juices, drinks).
3 Open the big sources of water (lakes, ponds, rivers) can not protect against infection, and such work is not planned. Water from artesian wells fed always clean. Suffice it to seal the water tower. We dug wells protect headroom. Around the wooden frame at a distance of up to 1 m thick layer of clay is placed up to 30 cm and compacted (clay prevents runoff and infiltration of rain water into the well through the cracks wooden frame). The clay is poured 15 cm layer of sand, which replace when dirty clean. Top headroom tight lid shut and hang total bucket. Over the well built hut of planks or fence, covered with clay. On the periphery of tear ditches to drain rainwater. Around open wells, constructed of concrete rings, clay layer do not.
4 Methods of disinfection:
Removal of radioactive substances (decontamination). All types of feed contaminated with radioactive dust above the allowable values, it is advisable to keep until the radioactivity has been reduced to an acceptable level. Decontaminate them in the absence of clean feed. To do this, the top 20-cm layer in the stacks of hay is removed, and a layer with the thickness of the sides are cut and fold it for storage, during which the activity will be reduced by the decay of radioactive substances. The same goes for the grain. The rest of hay or grain is subjected to radiometry and their activity within the allowable values are fed to livestock. With grain forage radioactive substances can be washed off with water. Root crops washed repeatedly with water or they are removed by cleaning the upper layer. Inactivate water filtration, distillation, settling. The passage of water through a layer of sawdust, peat, coal delayed radioactive dust and partially dissolved radioisotopes, sand retains only radioactive dust. The most effective decontamination using ion exchange resins. Decontaminate water by settling effectively adding it coagulants (clay, etc.). Food in bags treated with a vacuum cleaner or shift into another container. With solid fat cut surface contaminated layer. Carcass meat is washed with water. Contamination of the meat during the structural lay stored or processed for sausage and canned goods that store, when storing radioactive materials will decay.
If contaminated milk above the permissible values of its processed into butter, condensed milk, powdered milk, cottage cheese, which can be stored for longer.
Degassing. In the farm food and fodder degassed ventilation, heat treatment and chemical method. Hay, straw can be degassed by soaking for two days at 10 ... 12 % solution of ammonia or a solution of lime (pH=9). Root crops degassed chlorinated compounds, followed by washing with water. When infecting feed and food on the premises, transient agent open doors, windows, ventilation devices or render fodder and food outside and ventilated to the disappearance of their agents. Carcass meat disinfecting ventilation, and heat treatment (heat treatment, steaming). Food heat treatment disinfected. Degassed water (in the absence of an uncontaminated, clean water), boiling and chlorination.
Disinfection. Food, feed and water disinfected with chemical and physical methods. Grain forage (oats, barley, corn), infected spores of anthrax, destroy. And it can be decontaminated by soaking for 24 h in 4 % formaldehyde solution, or 2 hours in a 2 % solution of chlorine bleach activated (in tight barrels with lids). After that, the grain is removed from the drum and dried to complete disappearance of the smell. Meat contaminated with spore forms of microorganisms that can be disinfected by steam in a closed boiler pressure or processed for canning, sterilizing at 120 °C.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study ways to protect and feed products.
2 Observe the protection of food and water in the home.
3 Explore ways of disinfecting food, feed and water.
Test questions:
1 What is the main way to protect food, fodder and water from contamination?
2 How to store bread, biscuits and confectionery products by radioactive substances?
3 How to store bulk products (flour, sugar, cereals, pasta) by radioactive substances?
4 How to store meat, butter, sausage, fish by radioactive substances?
5 How to store butter, margarine, and various fats by radioactive substances?
6 How to store vegetables by radioactive substances?
7 How to store vegetables in the field by radioactive substances?
8 How are stored forages (hay, straw) by radioactive substances?
9 How to store drinking water supplies from contamination?
Literature:
1 N. Akimov, V.G. Ilyin. Civil defense at sites of agricultural production. Second edition, revised and enlarged. - M.: Kolos, 1978. - 327 p.
2 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
3 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
PRACTICAL WORK № 12. INSTRUCTION AND MORAL-PSYCHOLOGICAL PREPARATION OF THE POPULATION. BASES OF TRAINING OF THE CIVIL DEFENCE.
The purpose and objective studies: Learn the basics of teaching moral and psychological training of the population.
Contents of exercises:
1 The effect of emergencies on the human psyche.
2 Psychological barriers adaptation.
3 Training mental preparation.
1 One man caught in a disaster, rarely comes out of it unharmed. Some people lose their health has been seriously injured and maimed, others lose their lives in general. The rest live in this world and kept intact their flesh, still get these wounds, which are usually on the face is not visible, but it is extremely painful and difficult to heal. This - the wounds of the soul, the human mind and consciousness. And they are the more, the worse and more vivid picture of the experience.
But, of course, not all people caught in emergencies, receive a strong blow to the psyche, different people react to it differently. In some there is a mobilization of internal resources of life, while others - the reduction or even the failure of performance, poor health, physiological and psychological stress phenomena. It depends on many factors: the individual characteristics of the body, heredity, education, and living conditions, temperament, emotional state.
The human body is suddenly caught in a disaster response stress response. Some (10...15 %) of people in emergencies is the development of severe psychological reactions. Not prepared to act in emergency situations, people often fall into a state of shock.
Some people often find themselves in a variety of extreme situations, others lead a quiet life, without having to overcome any difficulties and hardships. In the first unconditioned reflexes (instincts) awakened act; at second they are in the drowsy state, with no reason to show up.
2 Psychological barrier of adaptation - the ability of the person to resist life-threatening and distressing factors.
Here, in particular, how to behave in an emergency people of different temperaments:
Sanguine - in hazardous conditions immediately mobilized to act decisively, but due to the excess energy may choose the wrong course of action. Phlegmatic - also mobilized, but over deliberate and to decide it needs some time. Choleric - totally unpredictable. He can become a leader, organizing the masses, and a source of panic, depending on the situation. Melancholic in these situations - the most dangerous person because it usually is often a source of panic.
Different reactions to the danger depends on the emotional tendencies of each individual.
Extreme emotional state are affect - overexcitation out of control consciousness, stupor - uncontrollable consciousness numbness inaction.
Both are very dangerous, because leads to either crude, inappropriate actions or to complete inaction.
Affective state or stupor most often by surprise, surprise what happened, as well as the lack of preparation for a meeting with them.
A good place to address these causes requires strong knowledge and skills.
Life creates basically the recurring situations that may analyze in detail, to analyze and find the most correct decision. And having studied well-established rules, a person can get out of disaster with minimal losses. The study of the rules and deal with disaster prevention, many organizations and services.
It should be noted that in all conditions 12...25 % of people do not leave the self-control, they are able to correctly assess the situation clearly and decisively act in accordance with the situation. People of this type of thinking is not primarily about themselves and about how to help others to fix what happened.
Unfortunately, the more common examples of the opposite plan. Fear of the unknown takes courage and intelligence, and with them the ability to resist.
Fear responses can be divided into controlled and uncontrolled.
If you control your own, then you realize the dangers that can occur, and try to avoid them. In this case, you will always find a way out.
Uncontrolled fear, experts say - it's just panic.
Common manifestations of panic helps lack of timely and reliable information.
When the panic runs multiple victims, their influence on each other causing massive emotional (and sometimes mental) disorders.
If the flapper is the leader of the crowd, it could provoke a common disorder that paralyzes the team, would deprive him of the possibility to provide self-help and mutual aid. Almost all victims regardless of the severity of the clinical picture in need of first aid. The first medical aid is necessary 6 % affected the lungs and up to 100 % with severe psychogenic. From experience we know that the greatest difficulties arise precisely when the first medical and first aid to the victim, that is, the identification of patients with acute mental stimulation, to ensure their safety and the safety of others, the exclusion of the possibility of mass panic reactions. In extreme cases, entire communities are often activities that are assigned certain duties to prevent or eliminate, depends on the actions of the individual. The slightest manifestation of confusion and fear at the time of the disaster may lead to severe and sometimes prove fatal.
3 The danger and risk to health, the importance of work - all of this raises a person in his own eyes and in the view of society as a whole. To do this, first of all, you need psychic hardening rights, which prevents the development of panic and allows you to instantly gather and concentrate your will and find the only correct way out of a difficult situation.
All these qualities are usually formed in the mental preparation, which involves constant readiness to work in extreme conditions and includes the following:
1) The ability to resist the action of powerful psychological stressors.
2) The ability to carry out familiar purposeful activity in these conditions.
3) The ability to select the optimal strategy of behavior, capacity for initiative and creativity.
4) The ability to provide a calming or mobilizing effect on others, have the skills regulate their own behavior and mental state.
5) The presence of a balanced set of the fact that the advent of emergency is possible, but not fatal.
These principles are implemented through practical working trainees various content of learning tasks that simulate certain aspects of life in difficult situations.
Most effective methods of training is the training in real situations (people do that kind of activity to which they are prepared, and the conditions are perceived as real). It can be really real situations of disaster management and industrial accidents, and especially the simulated situation, perceived as real learners.
Based on the statistics of accidents and natural disasters, it can be concluded that some of the people that have died, could live, they act more calmly and prudently. This requires advance psychological preparation of the population.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study the effects of emergencies on the human psyche.
2 To study the reaction of people of different temperaments.
3 Observe the reactions of fear.
4 Basics of training preparing the population.
Test questions:
1 What is the purpose of the population and are trained professionals?
2 How many times a year to train formations of CD notification and collection personnel?
3 What is the psychological barrier of adaptation?
4 What are controllable and uncontrollable fear?
Literature:
1 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
2 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
PRACTICAL WORK № 13. PREPARATION OF VARIOUS CATEGORIES OF THE POPULATION OF THE CIVIL DEFENCE. TACTIC-SPECIAL EMPLOYMENT AND DOCTRINES WITH FORMATIONS OF THE CIVIL DEFENCE
The purpose and objective lessons: Learn the rules of information, promotion of knowledge, training, public and professionals in the field of emergency, 17.01.2003.
Contents of exercises:
1 Informing the public in emergency situations.
2 Promotion of knowledge in emergency situations.
3 Teaching the public and professionals in the field of emergency.
1 Local governments quarterly to inform the public about the facts and the organization of risk and the measures necessary to prevent emergencies and protection from them, according to the nature of possible emergencies in the area. Not allowed concealment, late submission or presentation by officials of false information in emergency situations of natural and man-made.
Information alert is transmitted by radio and wire communication channels, on radio and television networks and other means, regardless of the type of organization.
2 Problem promoting knowledge in the field of emergency are:
1) An explanation of how the public and protection from emergency situations of natural and man-made disasters;
2) An explanation of the measures on education for managers, employees, personnel of civil defense, the entire population of responsible attitude to participate in the events of emergencies;
3) Promotion of self-sacrificing actions of personnel administration, forces emergency services and civil defense, the public in the aftermath of natural and man-made disasters;
4) Compilation and dissemination of positive experience in the implementation of measures for the prevention and elimination of emergency situations;
5) Use of mass media opportunities;
6) Development and implementation of projects for the visual aids (posters and billboards), the use of image videos and audio clips, slogans.
3 Teaching the public and professionals are held for the purpose of training, skills for emergency situations of natural and man-made disasters, conducting search and rescue and other emergency operations, knowledge of the basic techniques, and how to self-help, minimize potential losses in the population, reduction of material damage.
Education of the population is in preschool and secondary education, the organizations at the place of work, study and live in the classroom, training and during special exercises with the extensive use of the media, as well as their own.
With staff that are not in the formation of civil defense, the organization is planning classes in the approved program with the delivery of set-off in the amount of the studied subjects. When training people need to pay special attention to the correct action to signal «Attention all!» Learning ways of assisting self-help and mutual aid. The working population should be involved in complex exercises, facility training and all kinds of workouts.
Education is carried out by the non-working population of self-study booklets, brochures, materials periodicals, viewing (listening) and radio programs, as well as bringing him to the exercises and drills.
In higher education training should be conducted in accordance with the program «Health and Safety».
With the personnel of civil defense should be done at least twice a year training under the notification and collection.
Assignments for practical exercises:
1 To study ways to inform the public in emergency situations.
2 Promotion of knowledge in emergency situations.
3 Implementation of the education and training of the public and professionals in the field of emergency.
Test questions:
1 How is the preparation of the population not engaged in the production and maintenance?
2 Which course studying high school students?
3 What is the main signal of civil defense?
4 What types of exercises and training are provided by civil defense and emergencies?
Literature:
1 Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Republican courses Emergency CD. Benefit to help students republican training courses leading staff in Emergency Situations. - Almaty, 2008. - 135 p.
2 G.A. Zaichko, A.E. Prikhodko. Principles of Life Safety (practice). - Astana, 2009. - 163 p.
3 Rules of information, promotion of knowledge, training, public and professionals in the field of emergency, 17.01.2003.
Методические указания по выполнению практических занятий
Тема 1. Основные задачи Министерства по чрезвычайным ситуациям Республики Казахстан (мчс рк). Центральный аппарат мчс рк.
Цель и задача занятия: Изучить деятельность Министерства по чрезвычайным ситуациям Республики Казахстан.
Содержание занятия:
1 Основные задачи Министерства
2 Основные функции и права Министерства
3 Имущество Министерства
4 Организация деятельности Министерства
1 Основными задачами Министерства являются формирование государственной политики в области предупреждения и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций природного и техногенного характера, Гражданской обороны Республики Казахстан, надзора за выполнением мероприятий Гражданской обороны, межотраслевой координации, государственного контроля и надзора в области пожарной и промышленной безопасности, безопасности и охраны труда на опасных производственных объектах, надзора за безопасным ведением работ в промышленности, горного надзора, формирования и развития государственного материального резерва, обеспечения функционирования и дальнейшего развития государственной системы предупреждения и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций, организации предупреждения и тушения пожаров.
Министерство имеет территориальные органы в областях, городах Астаны и Алматы и ведомства: Комитет по государственному контролю и надзору в области чрезвычайных ситуаций и Комитет по государственным материальным резервам.
Министерство является юридическим лицом в организационно-правовой форме государственного учреждения, имеет печати и штампы со своим наименованием на государственном языке, бланки установленного образца, а также в соответствии с законодательством счета в органах казначейства.
Министерство вступает в гражданско-правовые отношения от собственного имени. Министерство имеет право выступать стороной гражданско-правовых отношений от имени государства, если оно уполномочено на это в соответствии с законодательством.
Министерство по вопросам своей компетенции принимает решения, оформляемые приказами Министра, которые имеют обязательную силу на территории Республики Казахстан.
Юридический адрес Министерства: 473000, город Астана, улица Бейбитшилик, 22.
Финансирование деятельности Министерства осуществляется только из республиканского бюджета.
Министерству запрещается вступать в договорные отношения с субъектами предпринимательства на предмет выполнения обязанностей, являющихся функциями Министерства.
Если Министерству законодательными актами предоставлено право осуществлять приносящую доходы деятельность, то доходы, полученные от такой деятельности, направляются в доход республиканского бюджета.
2 В соответствии с возложенными задачами Министерство осуществляет следующие функции:
1) стратегические, обеспечивающие формирование государственной политики в сфере:
- предупреждения и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций природного и техногенного характера, Гражданской обороны, межотраслевой координации, государственного контроля и надзора в области пожарной и промышленной безопасности, безопасности и охраны труда на опасных производственных объектах, надзора за безопасным ведением работ в промышленности, горного надзора и за выполнением мероприятий Гражданской обороны, а также в сфере государственного материального резерва;
- организации разработки и выполнения программ, направленных на решение задач по предупреждению и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций, Гражданской обороны, пожарной и промышленной безопасности;
- разработки предложений об использовании имеющихся в составе государственных и мобилизационных резервов запасов материально-технических, продовольственных, медицинских и других ресурсов, а также об использовании средств из резерва Правительства Республики Казахстан для предупреждения и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций;
- разработки плана Гражданской обороны на мирное и военное время и представления его на утверждение в Правительство Республики Казахстан;
2) в области реализации государственной политики:
- координирует работу государственных органов в области чрезвычайных ситуаций природного и техногенного характера, Гражданской обороны, пожарной и промышленной безопасности;
- взаимодействует с местными исполнительными органами в области чрезвычайных ситуаций природного и техногенного характера и Гражданской обороны;
- готовит и представляет отчеты о состоянии защиты населения и объектов хозяйствования от чрезвычайных ситуаций и Гражданской обороны;
- организует научные исследования, пропаганду знаний, обучение населения и специалистов в области чрезвычайных ситуаций природного и техногенного характера, Гражданской обороны, пожарной и промышленной безопасности;
- по решениям Правительства Республики Казахстан осуществляет непосредственное руководство ликвидацией региональных и глобальных чрезвычайных ситуаций;
- обеспечивает боевую и мобилизационную готовность воинских частей Гражданской обороны и подразделений противопожарной службы;
- принимает решения по вопросам подготовки и ведения Гражданской обороны, обязательные для исполнения центральными и местными исполнительными органами, иными организациями, а также населением Республики Казахстан;
- определяет потребность в вооружении, технике, средствах защиты и других материально-технических средствах в интересах Гражданской обороны;
- при ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций мобилизует материально-технические ресурсы, средства связи и передачи информации организаций в соответствии с действующим законодательством;
- руководит на республиканском уровне деятельностью межведомственной государственной комиссии по предупреждению и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций и Национальной комиссии по реагированию на нефтяные разливы;
- проводит общее руководство и координацию деятельности ведомств Министерства и территориальных органов, реализующих функции по предупреждению чрезвычайных ситуаций, Гражданской обороне, государственному контролю и надзору в области пожарной и промышленной безопасности, безопасности и охраны труда на опасных производственных объектах, надзору за безопасным ведением работ в промышленности, горному надзору и за выполнением мероприятий Гражданской обороны, а также в сфере государственного материального резерва;
- проводит непосредственное руководство Гражданской обороной;
- организует управление воинскими частями и формированиями Гражданской обороны при проведении аварийно-спасательных и других неотложных работ;
- проводит непосредственное руководство силами Гражданской обороны в мероприятиях по предупреждению и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций, находящимися в его ведении службами наблюдения, контроля обстановки и прогнозирования, а также республиканской системой оповещения и республиканской автоматизированной информационно-управляющей системой по чрезвычайным ситуациям;
- организует подготовку личного состава воинских частей Гражданской обороны, руководителей организаций и формирований Гражданской обороны, населения по Гражданской обороне, разрабатывает в этих целях соответствующие программы подготовки;
- осуществляет создание, учет и регистрацию аварийно-спасательных служб и формирований Гражданской обороны;
- координирует деятельность аварийно-спасательных служб и формирований, созданных по решению центральных исполнительных органов;
- координирует деятельность подведомственных научно-исследовательских организаций в области пожарной, промышленной безопасности и Гражданской обороны, а также специализированных научно-исследовательских и проектно-конструкторских организаций по вопросам пожарной, промышленной безопасности и Гражданской обороны;
- осуществляет государственное управление в области безопасности и охраны труда на опасных производственных объектах;
- в соответствии с действующим законодательством принимает меры по обеспечению государственных секретов в области Гражданской обороны, государственной противопожарной службы и государственного материального резерва;
- осуществляет международное сотрудничество, обеспечивает деятельность иностранных организаций и граждан в области предупреждения и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций, Гражданской обороны, пожарной и промышленной безопасности, а также в сфере государственного материального резерва на территории Республики Казахстан, организует проведение гуманитарных акций.
Министерство в целях реализации основных задач и осуществления своих функций имеет право:
1) принимать в пределах своей компетенции обязательные для исполнения нормативные правовые акты;
2) вносить предложения по совершенствованию законодательства по вопросам своей компетенции;
3) утверждать или согласовывать нормативы, стандарты и правила в области чрезвычайных ситуаций;
4) вносить предложения по вопросам создания, реорганизации и ликвидации подведомственных Министерству организаций;
5) запрашивать и получать от центральных и местных исполнительных органов, иных организаций, должностных лиц и граждан информацию и сведения по вопросам, относящимся к его компетенции;
6) вносить предложения в Правительство Республики Казахстан о привлечении сил и средств правоохранительных органов, воинских частей и подразделений Вооруженных Сил, других войск и воинских формирований республики для ликвидации аварий, катастроф и стихийных бедствий, обеспечения общественного порядка и охраны объектов в зонах чрезвычайных ситуаций;
7) иметь специальные транспортные средства, оборудованные утвержденными в установленном порядке опознавательными знаками, специальными сигналами и средствами связи;
8) иметь единые по всей территории республики радиочастотные полосы в порядке, определенном законодательством;
9) готовить проекты международных договоров и соглашений по вопросам своей компетенции, в пределах предоставленных полномочий заключать международные договоры Республики Казахстан и осуществлять их инвентаризацию;
10) издавать журналы, режимные справочники, бюллетени и другие издания по проблемам предупреждения и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций природного и техногенного характера, Гражданской обороны, пожарной и промышленной безопасности, а также в области государственного материального резерва.
3 Министерство имеет на праве оперативного управления обособленное имущество, которое относится к республиканской собственности.
Имущество Министерства формируется за счет имущества, переданного ему государством.
Министерство не вправе самостоятельно отчуждать или иным способом распоряжаться закрепленным за ним имуществом.
Министерству может быть предоставлено право распоряжения имуществом в случаях и пределах, установленных законодательством.
4 Министерство возглавляет Министр по чрезвычайным ситуациям (далее – Министр), назначаемый на должность и освобождаемый от должности Президентом Республики Казахстан.
Министр по должности является заместителем начальника Гражданской обороны Республики Казахстан (рисунок 1.1).
Министр имеет заместителей (вице-министров), назначаемых на должность и освобождаемых от должности Правительством Республики Казахстан по представлению Министра.
Министр организует и руководит работой Министерства, несет персональную ответственность за выполнение возложенных на Министерство задач и осуществление им своих функций.
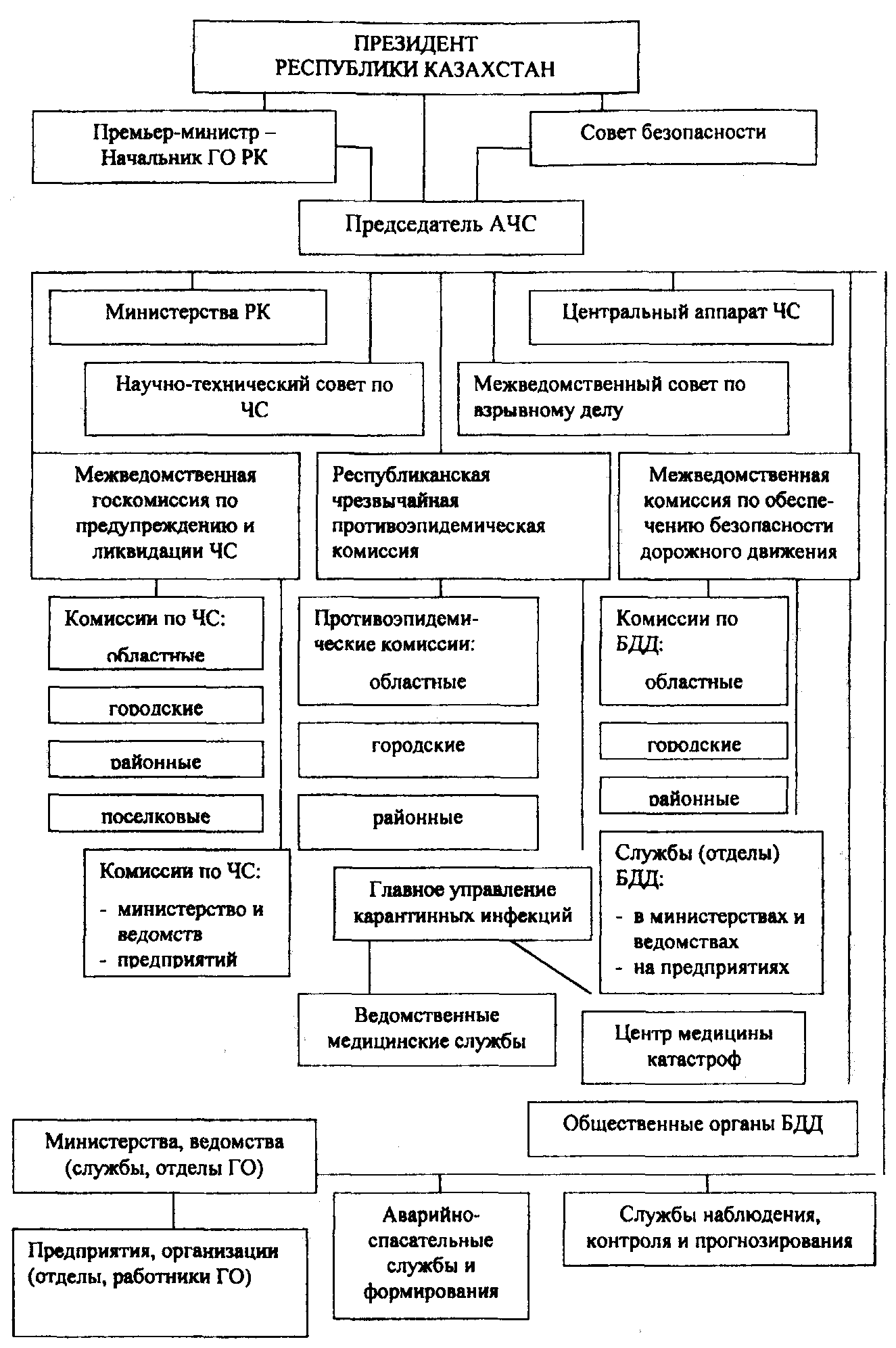
Рисунок 1.1 – Структура государственной системы
по предупреждению и ликвидации
чрезвычайных ситуаций в Республике Казахстан.
В этих целях Министр в соответствии с законодательством:
1) определяет обязанности и полномочия своих заместителей, руководителей ведомств, структурных подразделений, территориальных органов и подведомственных организаций Министерства;
2) назначает на должности и освобождает от должностей работников Министерства, заместителей председателей комитетов Министерства, руководителей территориальных органов по чрезвычайным ситуациям, территориальных органов Комитета по государственному контролю и надзору в области чрезвычайных ситуаций, подведомственных Министерству организаций, а также их заместителей, за исключением лиц, назначение и освобождение от должностей которых отнесено к компетенции Правительства Республики Казахстан;
3) утверждает структуру Министерства;
4) вносит предложения о перечне должностей Министерства, подлежащих замещению высшим офицерским составом;
5) утверждает перечень должностей, подлежащих замещению офицерским составом военнослужащих Министерства;
6) решает вопросы прохождения службы военнослужащими и имеющими специальные звания сотрудниками органов государственной противопожарной службы в Министерстве, присвоения им в установленном законодательством порядке званий, а также их переаттестации;
7) вносит предложения в Министерство обороны Республики Казахстан по призыву офицеров на военную службу из запаса;
8) вносит представления Президенту Республики Казахстан к награждению особо отличившихся работников Министерства государственными наградами и присвоению почетных званий;
9) решает вопросы поощрения и налагает дисциплинарные взыскания на работников Министерства;
10) подписывает приказы Министерства, а также дает указания, обязательные для исполнения работниками Министерства;
11) в пределах своей компетенции утверждает положения о структурных подразделениях и территориальных органах Министерства;
12) в пределах своей компетенции утверждает уставы подведомственных государственных учреждений, а также их структуру и штатную численность в пределах лимитов штатной численности, установленных Правительством Республики Казахстан;
13) представляет Министерство во всех государственных органах, иных организациях Республики Казахстан, а также в международных организациях;
14) утверждает в пределах установленного Правительством Республики Казахстан лимита штатной численности штатные расписания центрального аппарата Министерства, территориальных органов и подведомственных государственных учреждений;
15) утверждает Положение о службах Гражданской обороны и чрезвычайных ситуаций;
16) образует комиссии по расследованию аварий, катастроф, стихийных бедствий и их последствий, а также несчастных случаев на опасных производственных объектах и утрат взрывчатых веществ;
17) при осуществлении непосредственного руководства действиями в чрезвычайных ситуациях:
18) устанавливает по согласованию с местными исполнительными органами режимы проживания и поведения граждан в районах чрезвычайных ситуаций;
19) отстраняет от возложенных обязанностей по руководству работами при ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций должностных лиц, не обеспечивших выполнение порученных задач, с последующим привлечением их к ответственности в установленном порядке.
Министерство имеет коллегию, являющуюся консультативно-совещательным органом при Министре. Численный и персональный состав коллегии и положение о ней утверждаются Министром.
Задания к практическим занятиям:
1 Изучить основные задачи Министерства.
2 Изучить основные функции Министерства.
3 Изучить основные права Министерства.
4 Изучить организацию деятельности Министерства.
5 Зарисовать структуру государственной системы по предупреждению и ликвидации чрезвычайных ситуаций в Республике Казахстан.
Контрольные вопросы:
1 В каком году, и каким Постановлением Правительства РК создана Государственная система предупреждения и ликвидации ЧС (ГСЧС)?
2 Основные задачи ГСЧС?
3 Кто в РК осуществляет руководство ГСЧС?
4 Из каких формирований состоят силы и средства ликвидации ЧС?
Список необходимой литературы:
1 Закон Республики Казахстан «О гражданской обороне», 7.05.1997 г.
2 Закон Республики Казахстан «О чрезвычайных ситуациях природного и техногенного характера», 5.07.1996 г.
3 Министерство по чрезвычайным ситуациям Республики Казахстан. Республиканские курсы ЧС ГО. Пособие в помощь слушателям республиканских курсов повышения квалификации руководящего состава в области ЧС и ГО. – Алматы, 2008. – 135 с.
4 Г.А. Заичко, А.Е. Приходько. Основы безопасности жизнедеятельности (практикум). – Астана: АО КАТУ им. С. Сейфуллина, 2009. – 163 с.
