
- •Other titles in the series include:
- •Overcoming chronic pain a self-help manual using Cognitive Behavioral Techniques frances cole, helen macdonald, catherine carus and hazel howden-leach
- •Isbn: 978-1-84119-970-2 eIsbn: 978-1-47210-573-8
- •Table of contents
- •Acknowledgements
- •Foreword
- •Introduction by Peter Cooper Why cognitive behavioral?
- •Introduction
- •Who might benefit from using this book?
- •What does chronic pain mean?
- •What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
- •How can a book help?
- •How can I get the most out of using this book?
- •What do the chapters cover?
- •How do I start using this book?
- •Four case histories
- •Using the person-centred model
- •Maria and the person-centred model
- •How did the model help Maria make changes for the better?
- •How can the person-centred model help you get ready tomake some changes?
- •Getting started
- •Reducing the impact of pain on your daily life
- •How do you or others see these changes occurring?
- •Understanding chronic pain and pain systems
- •Understanding pain
- •Acute and chronic pain
- •What is acute pain?
- •What is chronic pain?
- •Acute and chronic pain systems
- •The acute pain system
- •The chronic pain system
- •Theories of pain The Gate Control Theory of Pain
- •Other theories of pain
- •Frequently asked questions
- •Understanding investigations for pain
- •Blood tests
- •Waiting for tests and results
- •Understanding the roles of healthcare professionals
- •Healthcare professionals
- •What is the role of a physiotherapist?
- •How do physiotherapists work?
- •What is the role of a specialist pain nurse?
- •What is the role of a pain specialist?
- •What is the role of a psychologist?
- •What is the role of a psychiatrist?
- •Talking therapies
- •Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- •Pain management programmes
- •Understanding medicines and using them better
- •What types of medicines are used to manage chronic pain?
- •How are medicines used? Analgesics
- •Problems with medicines
- •Making better use of medicines
- •Four suggestions for using medications more helpfully
- •Stopping or reducing your medicines
- •Part two Overcoming Chronic Pain
- •Introduction
- •Setting goals
- •What are goals?
- •Informal and formal goals
- •What are smart goals?
- •Setting goals
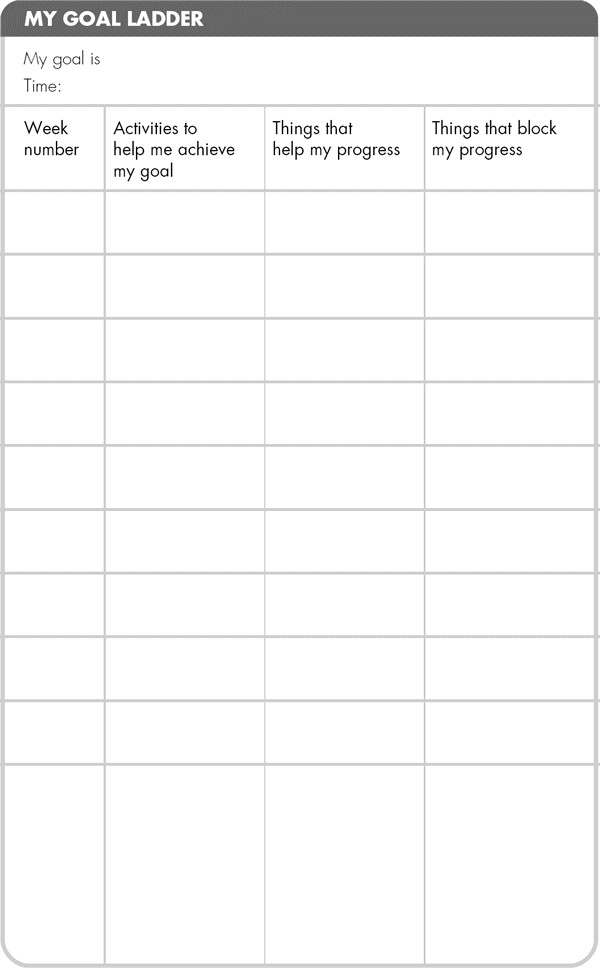
- •Using a goal ladder
- •Achieving your goals
- •Giving yourself rewards
- •What are rewards?
- •Creating a ‘fun presciption’
- •50 Mg of fun three times a day (at least) For maximum benefit, use imagination!
- •Understanding pacing skills
- •What is pacing?
- •What are the different styles of pacing?
- •What type of pacing style do you use at present?
- •If pain levels are low, do you:
- •If pain levels are high, do you:
- •How to change your pacing style
- •Experimenting
- •Planning
- •Priorities
- •How to deal with barriers to realistic pacing
- •Getting fitter and being more active
- •How being more active can help you manage your pain
- •Trying to get fitter: What does having more pain mean?
- •Why do these types of activity cause aches and pains?
- •Assessing your present activity level
- •Frequently asked questions about increasing physical activity
- •How to get started on a basic exercise programme
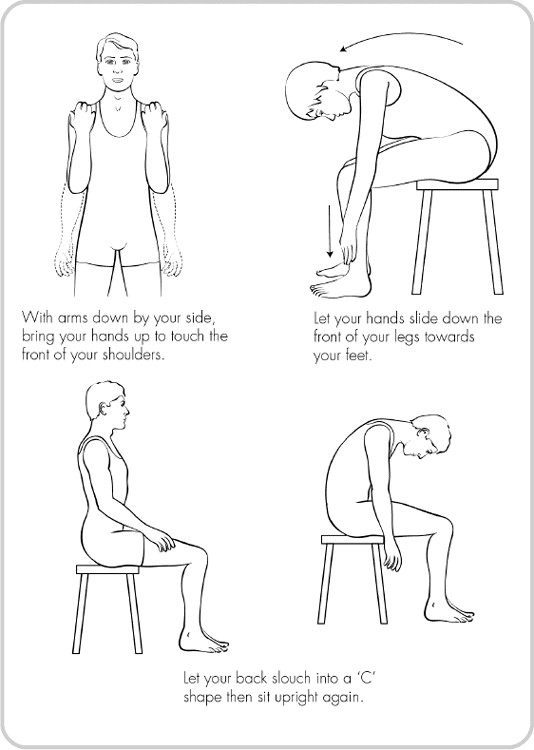
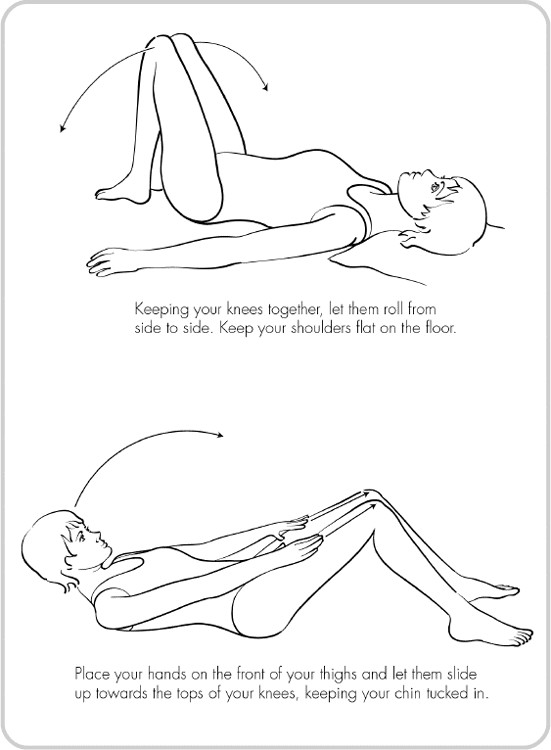
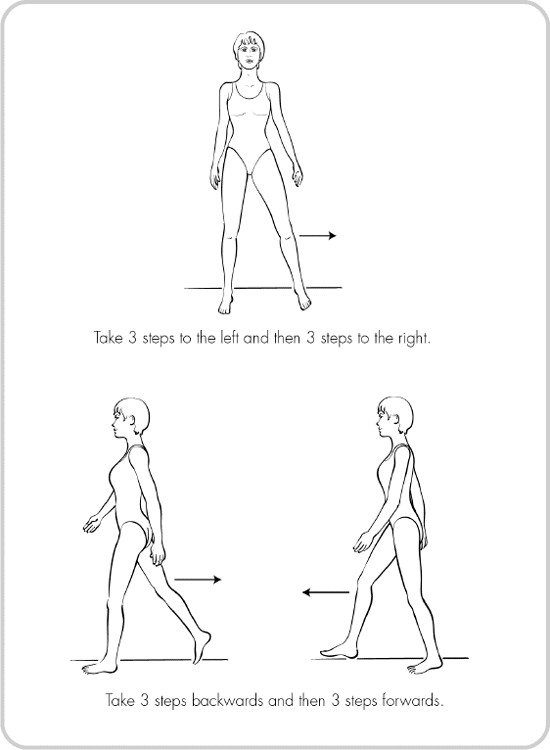
- •Strength exercises – do slowly
- •Stretches for flexibility
- •Understanding problem-solving
- •What is problem-solving?
- •The main steps in problem-solving
- •Putting the problem-solving process into practise
- •Problem-solving guide
- •Understanding sleep and sleep problems
- •What sort of sleeping problems can be caused by chronic pain?
- •What kind of sleep pattern do you have at present?
- •How much sleep do you need?
- •How to use a sleep diary
- •How can you change unhelpful sleep habits?
- •Relaxation
- •What is relaxation?
- •How can relaxation help with chronic pain?
- •What can help you relax?
- •How to practise relaxing
- •Time out relaxation
- •What can make it difficult to practise relaxation?
- •Pain, communication and relationships
- •Part 1: communication and sharing concerns How close relationships can be affected by pain
- •How to manage difficulties in relationships
- •How to change behavior
- •How to communicate and share your concerns
- •Part 2: chronic pain and sexual relationships
- •How to deal with sexual problems
- •How to make sexual relationships easier
- •Managing depression, anxiety and anger
- •What moods can occur because of pain?
- •Part 1: managing depression
- •Why do people become depressed with chronic pain?
- •How depression affects people’s thinking
- •What factors can contribute to depression?
- •Unhelpful thinking in depression
- •Using anti-depressants
- •Part 2: managing anxiety
- •What is anxiety?
- •What are the effects of anxiety?
- •How does anxiety affect the body?
- •Anxiety and chronic pain
- •Managing anxiety by dealing with unhelpful thinking
- •Overcoming avoidance
- •Changing unhelpful behaviors
- •Part 3: managing anger
- •How anger affects you and your pain
- •How chronic pain and anger are linked
- •How being angry can affect other people
- •How to manage anger better
- •A coping plan
- •Acceptance
- •What is acceptance?
- •How can acceptance help you manage chronic pain?
- •What is attentional control or mindfulness?
- •1. Reasonable (thinking reasonably)
- •2. Emotional (thinking emotionally)
- •3. Wise (being mindful)
- •Mindfulness skills
- •1. Observing
- •2. Being ‘non-judgemental’
- •3. Focusing on one thing now and being in the present
- •4. Doing what works
- •Mindfulness exercises
- •Maintaining progress and managing setbacks
- •How can you maintain progress?
- •Obstacles to progress
- •What is a setback?
- •How can you manage a setback?
- •Looking to the future and managing work
- •How are new ways of life and new roles possible?
- •How can you use a positive data log?
- •Thinking through work, training and other options
- •How can you stay at work or return to work successfully?
- •Useful information
- •Professional organizations
- •Self-help groups and organizations
- •Books and publications
- •Self-help books
- •Tapes and cDs
- •Useful videos
- •Wordlist
Books and publications
Coping Successfully with Pain, Neville Shone (Sheldon Press, London, 1992)
Coping Successfully with RSI, Maggie Black and Penny Gray (Sheldon Press, London)
Explain Pain, Lorimer Moseley and David Butler (NOI Press, 2003, www.noigroup.com)
Living With Back Pain, Helen Parker and Chris Main (Manchester University Press, Manchester, 1993)
Managing Pain Before It Manages You (2nd ed.), Margaret Caudill (Guilford Press, New York, 2002)
Manage Your Pain, Dr Michael Nicholas (Souvenir Press, London, 2003) Mastering Pain, R. A. Sternbach (Ballantine Books, 1987)
Pain: The Science of Suffering, P. D. Wall (Weidenfield & Nicholson, London, 1999)
The Pain Relief Handbook, Chris Wells and Graham Nown (1993) (Optima, London, 1993)
Self-help books
Feeling Good – the New Mood Therapy, Dr David Burns (Avon Books, 1980)
Love is Never Enough: How Couples Can Overcome Misunderstandings, Resolve Conflicts, and Solve Relationship Problems through Cognitive Therapy, Aaron T. Beck (Harper Collins, New York, 1989)
Manage Your Mind, Gillian Butler and Tony Hope (Oxford Paperbacks, 1995)
Mind Over Mood, D. Greenberger and C. Padesky (Guilford Press, New York, 1995)
Overcoming Anxiety, Helen Kennerly (Constable & Robinson Ltd, London, 2007)
Overcoming Depression, Chris Williams (Arnold Publishers, London, 2001)
Overcoming Depression, Paul Gilbert (Constable & Robinson Ltd, London, 2007)
Overcoming Traumatic Stress, Claudia Herbert (Constable & Robinson Ltd, London, 1999)
The Illustrated Guide to Better Sex for People with Chronic Pain, R. Rothrock and Gabriella D’Amore
Contact Pain Concern (see p. 285) for booklet.
Tapes and cDs
Coping with Pain
Coping with Headaches and Migraine
Coping with Back Pain
Feeling Good (assertiveness and self-esteem)
Available as Pain Management Packs (3 different pack options) or individually
Produced by Talking Life, in conjunction with the Pain Relief Foundation, Walton Hospital, Liverpool.
Details from:
Talking Life
PO Box 1
Wirral CH47 7DD
Tel: 0151 632 0662
Website: www.talkinglife.co.uk
Single Cassette/CD: Living with Chronic Pain
Produced by Consultant Clinical Psychologist, Neil Berry.
Please send a postal order or cheque for £5.00, made payable to ‘Pain CD’, to:
PO Box 84
Blackburn BB2 7GH
Please indicate whether you require CD or cassette.
Useful videos
The Pain Management Programme video produced by Gloucester Pain Management Programme, Royal Gloucester Infirmary, Gloucester GL1 3NN.
Wordlist
Acute pain
A predictable, time-limited response to injury, following chemical, thermal (heat) or mechanical tissue damage.
Anaemia
Reduced number of red blood cells in the blood, which may lead to tiredness.
Ankylosing spondylitis
A chronic inflammatory disease mainly affecting the spine, resulting in stiffness and loss of movement.
Barriers/blocks
Factors that may get in the way and stop to progressyou achieving what you set out to do, e.g. a heavy cold, a row with the boss, a windy day.
Bone scan
Investigation to test abnormal activity inside bones, which may come from tumours or infection.
Chronic pain
Pain that has been present for three months orlonger. Chronic pain is long-term pain that seems to continue after the normal accepted time of healing for most tissues.
Congenital
Disorder that has existed in the body since birth.
CT scan
This type of scan assesses health and disease in body organs like the kidney and structures like the spinal cord and discs, as well as bones and muscles. The radiation from a CT scan is equivalent to 500 chest x-rays.
De-conditioned
Poor level of fitness in muscles and joints due to reduced level of physical activity.
Fibromyalgia
A widespread chronic pain condition of unknown cause, characterized by tender areas in muscles and poor sleep.
Flexibility
Ability to feel more mobile and less stiff, e.g. so you can put your socks on in the morning.
Goal setting
A skill that helps focus your efforts on achieving milestones.
Goal ladder
The gradual stages that you may achieve, over a time period, in order to reach your ultimate goal, e.g. to walk the dog or return to work.
MRI scan
This type of scan assesses healthy and diseased tissues in the body. It is used to assess all parts of the body, including muscles, joints and spinal discs.
Neuropathic
Name given to disorders of nerves caused by nerve injury, inflammation or degeneration.
Osteomyelitis
Infection usually caused by bacteria in the bone tissue.
Osteoporosis
Loss of structure and density of bones, especially in the spine, wrist and hip.
Pacing
A skill to help you monitor and plan your activity to make sure that you are not doing too much or too little.
PALS
Patient Advocacy Liaison Service, a service provided in NHS hospitals to help patients find out about and use the services available for their care.
Peripheral neuropathy
Disorder affecting the nerves, causing distorted sensations like burning as well as pain. It happens mainly in arms and legs.
Physical activity
Doing things that help you to become fitter, stronger and more mobile.
Radiographers
Staff who carry out x–rays, CT and MRI scan tests.
Radiologists
Specialist doctors who assess, interpret and make reports on x–rays and scans.
Rheumatoid arthritis
A disease affecting joints, causing pain and swollen, sometimes hot, joints. Rarely causes bone changes and deformity of the joints.
Sensory
A term used by doctors to describe a range of body feelings that nerves detect, such as cold, heat, pain, touch, vibration, position of joints.
Setback
An event, illness or increase in pain that disrupts your daily routine for a short time.
Spondylosis
A normal ageing process in the small joints of the spine that sometimes causes pain and stiffness.
Stamina
Ability to keep going for longer, e.g. vacuuming, walking.
Strength
Ability to work hard and do activities that require extra effort, e.g. climbing a flight of stairs.
Appendix
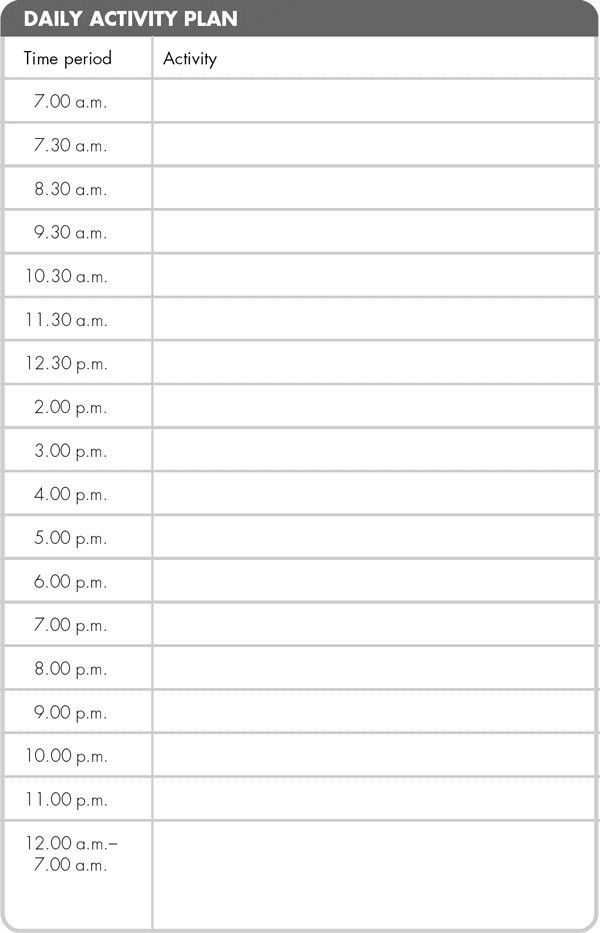
Here is a spare Daily Activity Plan for your own use.

Suggested sexual positions for chronic pain sufferers

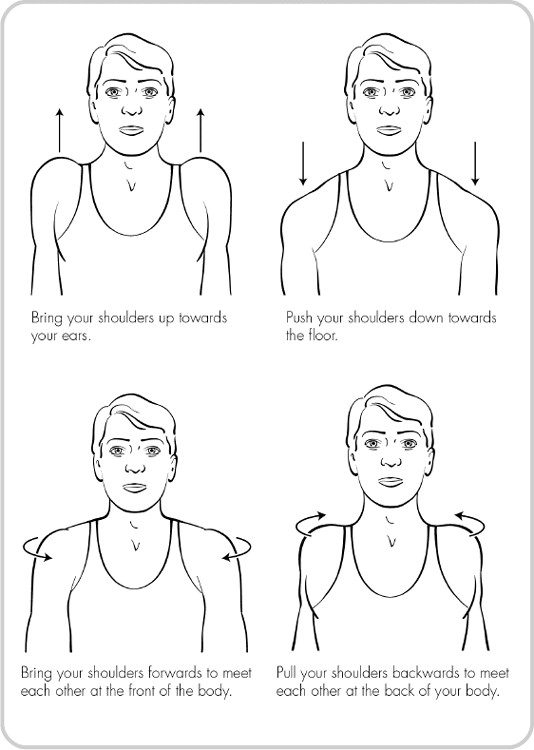
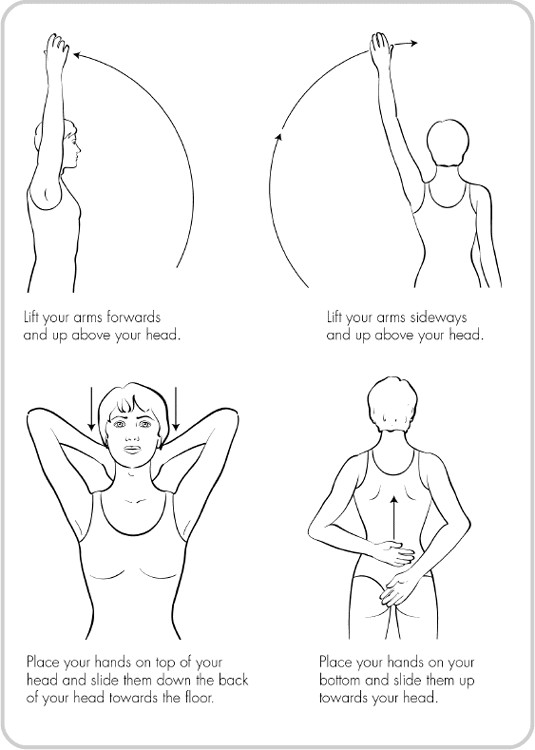
Suggested stretches


Index
NB: page numbers in italics indicate diagrams
acceptance 99, 246–58
see also case histories
and chronic pain 249–52
definition 247–8
emotional thinking 253
making sense of life 248
mindfulness skills 254–8 see also main entry
mindfulness/attention control 252–8
real and ideal exercise 246–7
reasonable thinking 253
summary 258
wise thinking 253–4
active, keeping 58–9, 60
activities/activity programmes 44–5, 58–9, 129–31, 133, 259
see also fitness and activity
alcohol 166
allergic reactions 82
analgesics 75–6, 78–9, 82–3
pain levels and usage 78–9
anger 98, 231–45
see also case histories
coping plans 238–45
dealing with 236, 245
effects of 231–6, 245
effect on other people 237–8
effect on your thoughts/beliefs 233, 234, 235
factors involved 232
and link with chronic pain 233–6, 245
summary 245
unhelpful thinking 236, 245
ankylosing spondylytis 53
anti-convulsants 77–8
anti-depressants 77, 211
anti-inflammatories 76
anxiety 98, 212–30
avoidance 227–8 see also main entry
behaviors, changing 229–30
caffeine intake 230
challenging thoughts: questions and worksheets 221–6, 222–4
challenging unhelpful thoughts 220–1
and chronic pain 215–16
coping self-talk 226
definition 212
effect on body 215, 216
effects of 212–13, 214
fight or flight response 215
summary 230
unhelpful thinking 217–26, 217 see also unhelpful thinking/thoughts
avoidance 227–8
graded exposure 227–9
regular practice 228
task 228–9
blood tests and results 53–5
bone densitometry (DEXA) scan 58
bones 47
C fibres 43–4, 79–80
caffeine 166, 168, 230
cartilage 49
case histories 11–19, 25–9, 103–7
Jim 14–16, 113–14, 115, 119, 121, 126, 191–2, 213–14, 214, 222–3, 222–3
Maria 11–12, 25–9, 26, 112–13, 198–200, 201, 203–5, 207, 228–9, 243–4, 262, 268, 278
Razia 13–14, 103–4, 106–7, 122–3, 127–30, 267
Steve 16–19, 88, 89, 104–5, 151–5, 181, 189–90, 232–3, 235, 237, 238–9, 248–9, 250–2, 264, 268, 275–6
changes 31–5
maintaining 70
reasons for 33–5
targets 31–2, 35, 35
chronic pain and pain systems 37–52, 50–6, 50
see also impact of pain
activities 44–5, 45
acute pain/pain system 39, 42–3, 44–5
C fibres 43–4, 79–80
chronic pain/pain system 39–42, 43–5
definition of pain 38–9
describing pain 37–8, 40
FAQs 49–51
muscles and injury 49
neuromatrix 46
pain messages 47–9
pain puzzles 42
summary 51–2
theories of pain 45–9 see also Gate Control Theory
Citizens Advice Bureau 277
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) 3–4, 61, 69–70, 98
communications and relationships 178–93
see also sexual relationships
behavior, changing your 184–6
goals 184
help from others 183–4
irritability and moods 180–1
negative/unhelpful thinking 186–7
pain behaviors 183
pain management 187
questions and answers 186
relationship difficulties 182–4
sharing concerns 179–82
summary 193
support, ideas for 187
definitions
acceptance 247–8
anxiety 212
fitness 140
goals 100–2
pacing 117–18
pain 2–3, 38–9
problem-solving 150–1
relaxation 171
rewards 110–11
setbacks 261
depression 98, 195–211
anti-depressants 211
contributing factors 197–8, 199 see also depression, factors in
effect of chronic pain 196
negative thoughts chain reaction 196–7
summary 211
techniques 198, 210, 211
unhelpful thinking/thoughts 196–7, 200–10 see also main entry
depression, factors in 197–200
behaviors, unhelpful 197
losses 197–8
other problems 198
person-centred model 198, 199
disability employment adviser(s) 276, 279
drug interactions 81–2
drugs 70
see also medicines
Employee Assistance schemes 274
endorphins 45–6
exercise programme 144–9, 259, 260
constructing your own 148–9
flexibility exercises 148
strength exercises 145–7
warming up/cooling down 145
families and partners see communication and relationships
FAQs 49–51, 139–44
fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) 53
fitness and activity 134–49
activities causing pain 136–7
advantages in reducing activity 137–8
assessing current activity level 137–9
basic exercise programme 144–9 see also exercise programme
benefits for managing pain 134–5
change resulting from increased activity 140
disadvantages in reducing activity 138–9
FAQs on increasing physical activity 139–44
fitness programmes 142–3
goals 143
increasing activity levels 141–2
managing pain 140–1
myths 139
new aches and pains 135–6, 140, 149
setbacks 144
stamina, flexibility and strength 139–40
summary 149
tips 134, 137, 138
tiredness 140
frequently asked questions see FAQs
future roles/ways of life 266–79
see also positive data log; work
coping skills 270–1
options 270–1
summary 279
Gate Control Theory 45–7, 47, 48, 51–2, 86
closing the gate 45–6, 48
opening the gate 45–6, 47
goals 70, 100–9, 143, 184, 263
see also case histories
achieving 108–9
definition 100–1
goal ladders 104–8, 109
informal and formal 101
setting 102–4
SMART – specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, timed 101–2, 259, 263
summary 109
guide to overcoming chronic pain 10, 98
healthcare practitioner/doctor 87–8, 92, 93, 147, 160, 211
healthcare professionals, roles of 61–73
pain management programmes 70–3 see also main entry
pain specialists 64–5, 92, 93, 211
physiotherapists 62–4
psychiatrists 68
psychologists 65–8
specialist pain nurses 64, 87–8
summary 73
talking therapies 68–70 see also cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
hospital specialists 67–8
ibuprofen 76, 83
impact of pain 23–36, 23, 41
see also case histories
making changes 31–5 see also changes
person-centred model 24–30, 25 see also main entry
problem list 31
reducing 31–6
summary 35–6
International Association for Study of Pain (IASP) 38–9
investigations for pain 53–60
blood tests 53–5, 60
scans 57–8
summary 60
waiting for tests and results 58–60
X-rays 55–7, 60
isotope bone scan 58
job support services 273
JobCentrePlus 276, 279
Shaw Trust 273, 276, 279
joints 47, 49
levels of pain see pain levels
maintaining changes 70
see also changes
maintaining depression, anxiety and anger see anger; anxiety; depression
maintaining progress see progress, maintaining
medicines 74–93, 211, 264
analgesics 75–6, 78–9 see also main entry
anti-convulsants 77–8, 83
anti-depressants 77, 83
anti-inflammatories 76, 83
checklist of medicine types 82–3
problems with see medicines, problems with
stopping/reducing see medicines, stopping or reducing
suggestions for using see medicines, suggestions for using
summary 93
medicines, problems with 79–82
allergic reactions 82
dependence 80–1
drug interactions 81–2
faulty C fibres/pain nerves 79–80
side-effects 81
tolerance 80
medicines, stopping or reducing 88–93
advantages and disadvantages 90–1
options 91–3
medicines, suggestions for using 82–9
case history 88, 89
Gate Control System 86
medicine and pain level diary 88, 89
medicine use diary 84–6, 85, 88, 93
predicting rises in pain level 86, 93
mindfulness skills 254–8
being non-judgemental 255
doing what works 255–6
exercises 256–8
focusing 255
observing 254
mood changes 211
moods, managing 70, 194–5, 194–245, 194
see also anger; anxiety; depression
morphine 75, 79, 82
muscles and injury 49
neuromatrix 46, 52
pacing 70, 93, 117–33, 173, 260
advantages/disadvantages 122–3
barriers to 132
case histories 119, 121–3, 126, 127–30
changing your style 124–32
daily activity plan 129–31
experimenting 125
helpful style 121
identifying your own style 119–21, 133
overactive 119, 122, 133
pacing plan 128–9
planning 125–6
priorities 126–7
skills 173, 263
summary 133
underactive 119, 123, 133
pain cycle 97
pain levels 78–9, 86–8, 120–1
pain management 32–3, 61, 70–3, 187
expectations 71
questions 72
self-help groups 72
and strategies 67
pain specialists 64–5
pain systems 70
painkillers see analgesics
paracetamol 75, 78, 82
patient liaison and advice service (PALS) 60
person-centred model 25, 26, 30, 198, 199, 201, 214, 234, 235
physiotherapists 62–4
positive data log 263, 266–70
steps in using 267–70
problem-solving 4, 70, 150–7, 175
advantages/disadvantages of solutions 153–5
choosing best solutions 153–5
definition 150–1
list possible solutions 152–3
problem-solving guide 155–6
recognizing and defining problem 151–2
reviewing progress 155
skills 98, 109
summary 157
progress, maintaining 259–61, 265
see also goals; pacing; rewards
methods of 259–60
obstacles to 260–1
psychiatrists 68
psychologists 65–8
relationship difficulties 98
see also communication and relationships
relaxation 171–7
see also relaxation skills
and chronic pain 172–3
contra-indications/medical problems 176–7
definition 171
overcoming difficulties 175–6 see also problem-solving
pacing skills 173
quick 174–5
scanning 174
summary 177
tapes, listening to 174, 176
techniques 173
time-out sessions 174–5
relaxation skills 67, 70, 93, 98–9, 263
rewards 70, 98, 108, 109, 110–16, 149, 183, 184, 188, 211, 259
case histories 112–14, 115
definition of 110–11
fun and laughter prescriptions 114–15
how rewards help change things 111
listing rewards and achievements 112–13
summary 115–16
scans 57–8
bone densitometry (DEXA) 58
CT 57
isotope bone 58
MRI 57
setbacks 144, 261–5
definition 261
issues, high and low risk 262
management of 263–5
sexual relationships 188–93
see also case histories
comfortable positions for intercourse 192–3, 297
dealing with sexual problems 188–90
pacing, tips for 190–1
thoughts and feelings 191–2
side-effects of medicines 75–6, 77, 79, 81
skills
learning new 260
to reduce impact of pain 5
sleep habits, changing 162–70
bedroom, preparation of 165
bedtime routine 165–6
behavior: stopping or changing 169–70
caffeine and alcohol 166, 168
improving sleep 166–7
improving sleep patterns 168–70
relaxation 168
summary 170
wakefulness 168
worry and worry book 167–8
sleep problems 158–70
changing unhelpful sleep habits see sleep habits, changing
current sleep pattern 159–60
from chronic pain 159
hours of sleep needed 160–1
sleep diary 161–2, 163–4, 170
summary 170
step-by-step planning 109
stretch-and-strength programme(s) 59, 70
talking therapies 68–70, 73
see also cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
talking through difficulties 70
Tens (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) machines 64
unhelpful thinking/thoughts 176, 186–7, 196–7, 200–10, 217–26, 217, 236, 245
challenging thoughts worksheet 207, 209, 222–4
challenging unhelpful thoughts 203–10, 220–1
identifying styles 202
types of unhelpful thoughts 218–20
using worksheet 206–10
useful information and further reading 280–9
wordlist 290–2
work 270–9
barriers to overcome 271
help in preparation for work 276–7
help in staying at work 272–3
legal provisions for employees 272
resources 276, 277, 279
returning to work 273–6
training courses 278
volunteering/community activities 277–8
World Health Organisation (WHO) 78–9, 87, 93
X-rays 55–7
