
- •Part 1. Waste Recycling
- •Vocabulary:
- •Waste Recycling
- •Part 2. Recycling in the usa
- •Vocabulary:
- •Recycling in the usa
- •Where does the waste go?
- •Recyclable materials
- •New Ideas
- •Part 3. Alternative Sources of Energy
- •Vocabulary:
- •A lternative Sources of Energy
- •1. Wave Power, 2. Wind Power, 3. Geo-Thermal Power, 4. Solar Power
- •Part 4. Solar Energy
- •Vocabulary:
- •The Sun’s Energy
- •W hat Happens to the Sun’s Heat
- •Absorption of sunlight by different surfaces
- •Vocabulary:
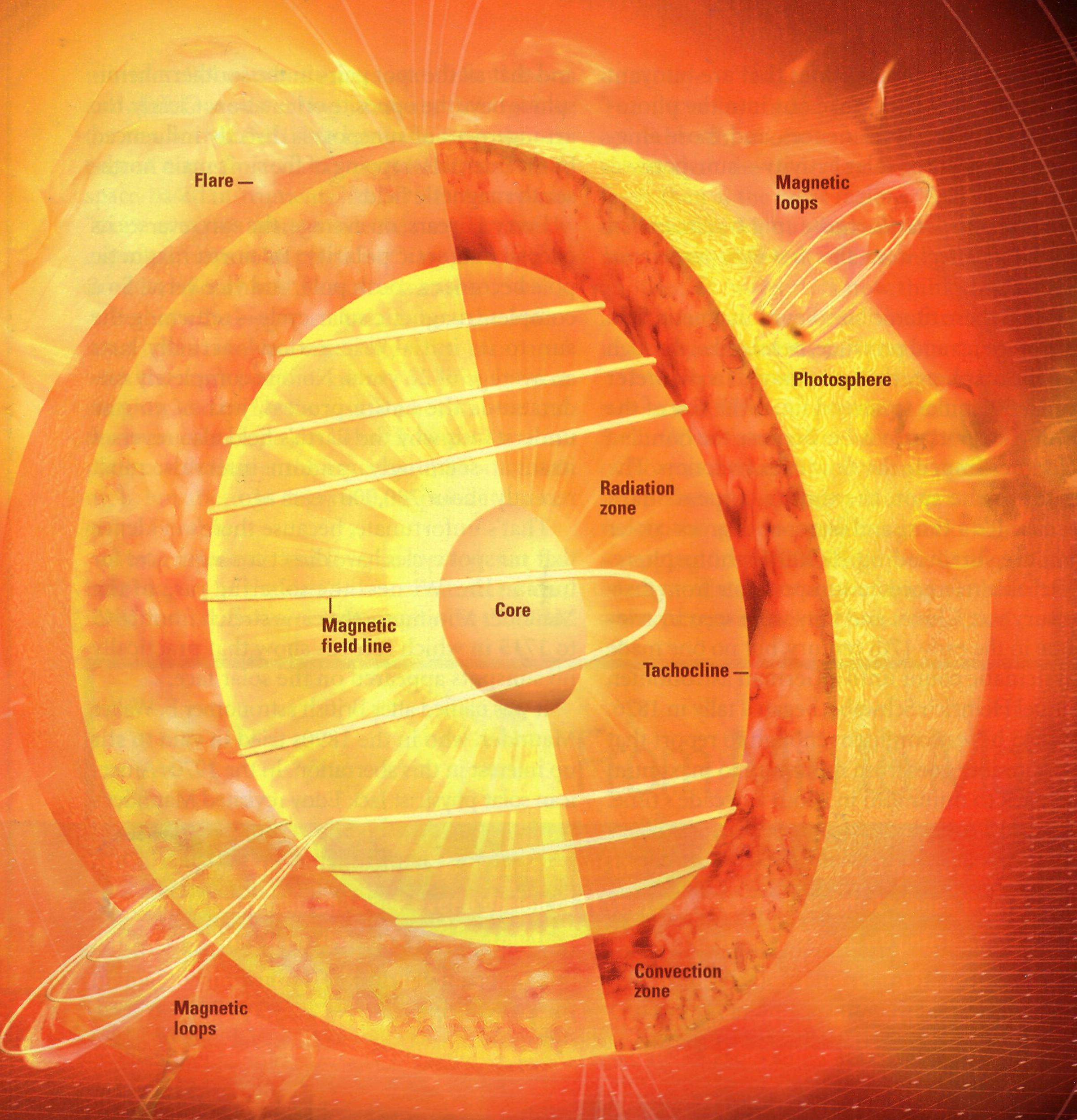
- •Hot News from Our Stormy Star
W hat Happens to the Sun’s Heat
What happens to the sun’s heat is shown in the diagram. This is for average weather — that is, 52 per cent cloudiness in the sky. A typical cloud reflects back into space 75 per cent of the sunlight striking it. On overcast days, only about 25 per cent of the sun’s energy hits the ground. Energy that does reach the ground is absorbed and reflected in varying degrees. Snow reflects about 75 per cent, absorbs only 25 per cent; this partly accounts for the cold of polar regions. In comparison with dry deserts the figures are upside down 75 per cent is absorbed and 25 per cent is reflected. And the plowed field reflects from 25 to 5 per cent of the sun’s energy. Grassy field absorbs a little bit more energy. Dark forests absorb about 95 per cent of solar energy and change it to heat. Ocean water reflects from 40 to 14 per cent depending on angle. Such differences in absorption and reflection account, in part, for regional differences in temperature and climate.
Absorption of sunlight by different surfaces
1. 25%; 2. 60-86%; 3. 80 to 96%; 4. 75%; 5. 95%; 6. 75 to 95%
A. B.


Water Dense forests
C. D.


Plowed field Dry sand
E. F.


Grassy field Snow
Exercise 7. Read the following text “The Sun” and find in it the words according to the definitions given below to fill in the crossword:
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
U |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
N |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
G |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
T |
|
|
|
||||||||||
hardened remains of a prehistoric organic matter
something that has the same function as something else
current of air
black mineral consisting mainly of carbon, used as a fuel
a straight line through the center of a circle or sphere
light flammable colourless gaseous element which combines with oxygen to form water
a unit of time measured in sixty minutes
whole, a sum of parts
The Sun
The sun is the source of almost all energy on earth. Solar heat creates most wind and also causes evaporation from the oceans and other bodies of water, resulting in precipitation. Rain fills rivers and reservoirs, and makes hydroelectric power possible. Coal and petroleum are fossil remains of plants and animals that, when living, required sunlight. In one hour the earth receives solar energy equivalent to the energy contained in more than 20 billion tons of coal, and this is only half of one billionth of the sun’s total radiation.
Just a star of average size, the sun is yet so vast that it could contain over a million earths. Its diameter, 864,000 miles, is over 100 times that of the earth. It is a gaseous mass with such high temperatures (11,000° F at the surface, perhaps 325,000,000°F at the center) that the gases are incandescent. As a huge nuclear furnace, the sun converts hydrogen to helium, simultaneously changing four million tons of matter into energy each second.
Exercise 8. Read the text above once again and decide true or false are the following statements:
Statements:
1. Precipitation is a result of wind and evaporation from the oceans and other bodies of water caused by solar heat.
2. Hydroelectric power is also created by wind and evaporation.
3. Petroleum is a form of fossil remains of plants and animals.
4. 20 billion tons of coal is extracted every hour.
5. In one hour the earth receives only half of one billionth of the sun’s total radiation.
6. The sun is the biggest star in the universe.
7. The diameter of the sun exceeds 100 times the earth’s one.
8. The sun is an incandescent gaseous mass.
9. The sun converts helium to hydrogen.
10. Four million tons of matter are changed into energy each minute.
Study the list of vocabulary and pronounce the words after the teacher:
