- •1. Phonetics as a branch of linguistics.
- •2. Phonetics and other disciplins.
- •3. The role of pronunciation in the process of communication.
- •4. The role of phonetics in foreign language teaching.
- •5. The material aspect of the phoneme
- •6. The abstract aspect of the phoneme
- •7. Phonetic transcription. What type of broad transcription is preferable for teaching pronunciation?
- •8. Which method of broad transcription do you prefer? why?
- •9. The functional aspect of the phoneme.
- •10. The conceptions of the phoneme.
- •11. Main trends in the phoneme theory
- •12. Methods of phonological analysis
- •13. Semantically-distributional method of establishing the phonemic status of speech sounds (I.E. Phonological analysis)
- •15. Degrees and position of word stress.
- •16. The definition of intonation. Components of intonation.
- •17.Intonation pattern and its components
- •18. Which component of the intonation pattern is the most important one? why? (то же самое)
- •19. View intonation on the functional level
- •20.Communicative function of intonation
- •21. The distinctive function of intonation
- •22. What kinds of meaning can be differentiated by the opposition of terminal tones?
- •23. The role of intonation in structuring the information content of the utterance.
- •24. Organizing function of intonation: delimitation and integration
- •25. Pragmatic function of intonation
- •26. Is intonation always in balance with the grammatical structure and word content?
- •27. Rhythm in english
- •28. Phonostylistics. Phonostylistic approach to the description of phonetic phenomena
- •29. Extralinguistic situation and its components
- •30. What extralinguistic factors play the leading role in phonetic styles formation?
- •31. Stylistic modifications of speech sounds
- •32. Which classification of phonetic styles do you prefer?
- •33. In which spheres of communication is informational style used? what are its main prosodic characteristics?
- •34. In which spheres of communication is academic style used? what are its main prosodic characteristics?
- •35. Rp as a pronunciation standard and teaching norm
- •New tendencies in the pronunciation of present day english
- •Intrusive “r”, inserted before a following vowel even though there is no “r” in spelling. (idea of, China and)
- •37. Principle types of pronunciation in britain
- •General american
7. Phonetic transcription. What type of broad transcription is preferable for teaching pronunciation?
8. Which method of broad transcription do you prefer? why?
Transcription – a set of symbols representing speech sounds. The symbols are accepted by the International Phonetic Association. Transcriptions differ according to whether the aim is to indicate the phoneme or to reflect the modifications of its allophones as well:
The broad (phonemic) transcription – a transcription that provides special symbols for all the phonemes of the language (it indicates the phoneme as a functional unit). This type of transcription is mainly used for practical purposes (for example, in EFL (English as a foreign language) teaching and learning). Phonetic transcription is a good basis for teaching the pronunciation of a foreign language as it is a powerful visual aid.
The narrow (allophonic) transcription – a transcription that suggests special symbols for speech sounds, representing particular allophonic features. This type of transcription serves the purposes of research work.
The striking difference among modern broad transcriptions of British English is the varying significance which is attached to vowel quality and quantity.
Two kinds of broad transcription of English which are used in Russia for practical purposes:
Broad transcription by D. Jones |
Broad transcription by V.A. Vasilyev |
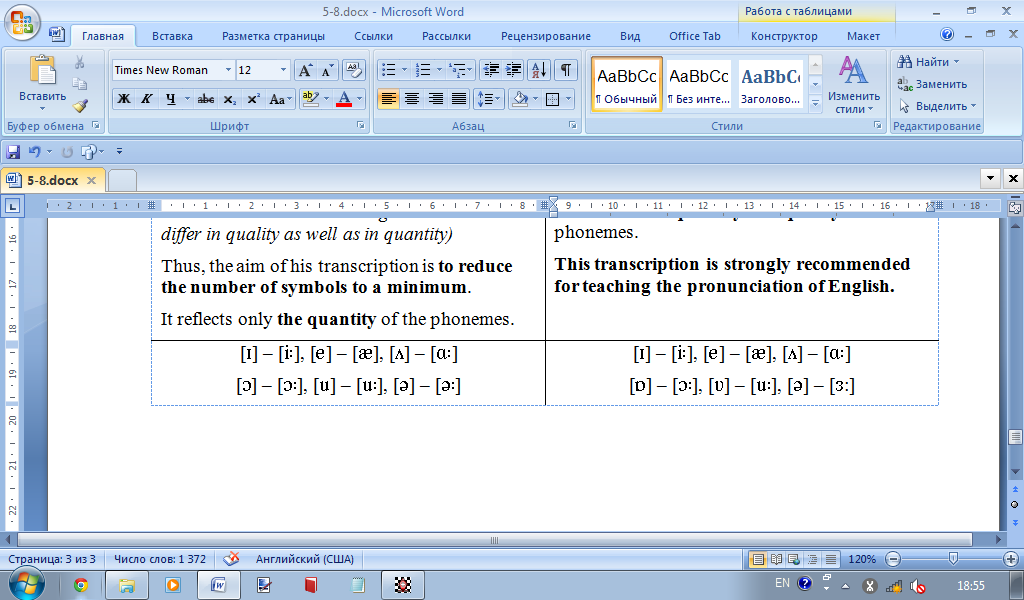
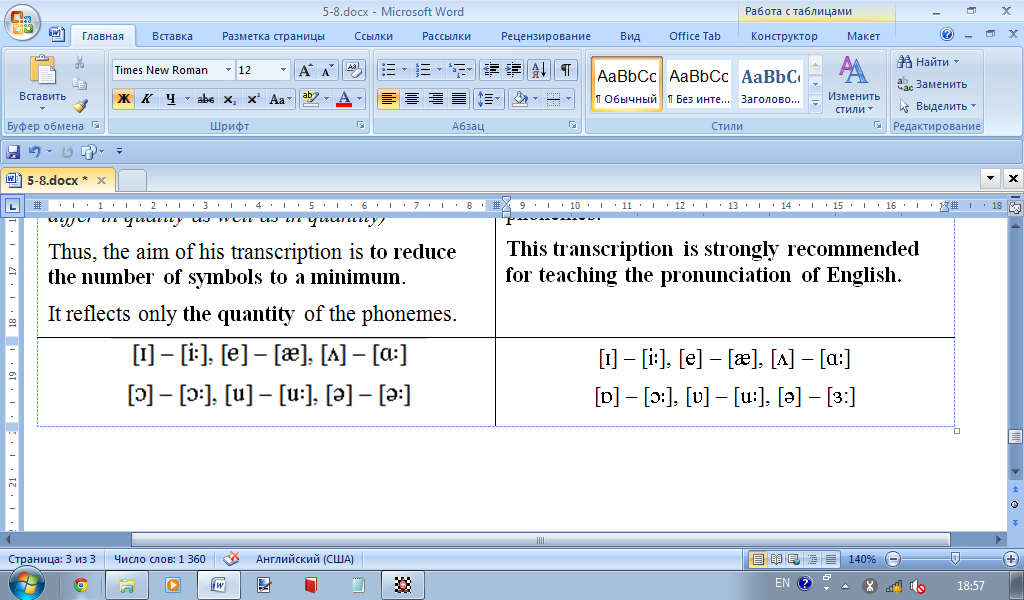
Jones realized the difference in quality as well as in quantity between the vowel sounds (sit – seat, pot – port), the neutral sound and the vowel in the word earn. He insisted that certain conventions should be stated once for all so that to relieve us from numerous transcription symbols. (One of the conventions was that the long and short vowels differ in quality as well as in quantity) Thus, the aim of his transcription is to reduce the number of symbols to a minimum. It reflects visually only the quantity of the phonemes. |
Vasilyev was the first who used this transcription. It provides special symbols for all vowel phonemes, thus causing no phonological misunderstanding. It reflects visually both quantity and quality of the phonemes. This transcription is strongly recommended for teaching the pronunciation of English. |
|
|
9. The functional aspect of the phoneme.
The Functional Aspect
It is reflected in the following part of the definition: “the phoneme is opposable to other phonemes of the same language to distinguish the meaning of morphemes and words”.
This is the main aspect of the phoneme. The phonemes are capable of differentiating the meaning of morphemes, words and even sentences.
The phoneme can perform the distinctive function when it is opposed to another phoneme in the same phonetic context. (ka:t - pa:t). Sometimes the opposition of the phonemes serves to distinguish the meaning of the whole phrases: he was heard badly - he was hurt badly.
In this case the phonemes differ in one articulatory feature – backlingual/forelingual. Such features are called relevant (distinctive).
The articulatory features that do not affect the meaning are called non-distinctive (irrelevant). A good example of such a feature is aspiration. For consonants the distinctive features are: place of articulation, manner of articulation, presence or absence of voice. For vowels – it’s quality.
If an allophone of some phoneme is replaced by an allophone of a different phoneme, the mistake is called phonological (sit – si:t). If an allophone of some phoneme is replaced by another allophone of the same phoneme, the mistake is called phonetic.