
- •Choose the correct answer:
- •Give reasons for the following:
- •Mention a difference between the pair of organisms:
- •Living organisms have different limbs to move in their environments:
- •Birds have different beak shapes & legs according to the food they eat & the environment they live in:
- •Give reasons for the following :
- •O puntia & cactus
- •Give an example (the name of an animal) which adapts to its environment using the following methods:
- •What the function of:
- •Choose the correct answer:
- •Give reasons for the following:
- •Compare elodea plant to calmagrostis plant in the following table:



Lesson
1 :
Diversity
of living organisms
&
their classification
Lesson
2:
Adaptation
of Living Organism in
diverse
environment
Lesson
3:
Adaptation
& Continuity of life





Living organisms are different. In order to study them easily & make benefit of them we put them in groups (classes).
Living organisms -you study this year – can be classified into 3 main classes: microorganisms – plants – animals.

T hey
exist in every environment. They ‘re not seen by the naked eye &
are only seen by a microscope.
hey
exist in every environment. They ‘re not seen by the naked eye &
are only seen by a microscope.
Activity 1:
Aim to : Look at the water from a potted plant through a microscope.
Materials :
S ome irrigation water from a potted plant - a dropper – glass slide – a plastic cover – some dye – a light microscope.
Procedure (steps of work)
Put a drop of water taken from a potted plant on a glass slide.
Add a drop of dye to the water on the slide.
Put the plastic cover on the water & examine the slide under the microscope.
Observation :
Many microorganisms are seen moving in the slide.
M
 icroorganisms
have different shapes.
icroorganisms
have different shapes.

Plants like corn, wheat, palm & camphor have roots, stems & leaves.
Other plant – like organisms called algae . don’t have roots, stems or leaves. Brown & red algae don’t have roots, stems or leaves. They form long threads which live in marine (related to sea) environment .
Classifying plants according to the reproductive style:
Plants which reproduce by spores |
Plants which reproduce by seeds |
||
Gymnosperms |
angiosperms |
||
Monocotyledons |
Dicotyledons |
||
Voughair Adiantum |
Pine Cycas |
Maize Wheat |
Bean Pea |
Bean
corn
Cycas
Pine

Classifying animals according to body support
Internal skeleton & back bone (Vertebrates) |
Absence of internal support (Invertebrates) |
|
|
Supported body (external skeleton) |
Soft body (without external support) |
|
|
|
Classifying arthropods according to the number of legs:
Insects |
Arachnids |
Myriapods |
|
|
|
Identifying the teeth type & number in some mammals:
Animals with teeth |
Animals without teeth (Edentates) |
|||
Animals with extended teeth |
Animals with sharp canines |
Animals with sharp incisors |
|
|
Rodents |
Lagomorphs |
|||
H |
Lion
|
Rat
S quirrel |
R |
Sloth
A |
Taxonomy is the science of classifying living organisms in groups according to similarities.
All organisms with similar shape & are able to reproduce & give birth of fertile animals form a group called species.
An example: Horses (brown, white or black) are one species because they can mate (reproduce) & give birth of ponies that grow into horses & reproduce again & thus the species doesn’t become extinct. Donkies form a species for the same reasons. When a female horse mates with a male donkey , it gives birth to a mule. The mule isn’t fertile & can’t reproduce.
The species is the base of taxonomy.
Fill in the blanks:
Class |
An organism that belongs to this class |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Octopus |
|
|
Sloth |
|
|
Wheat |
|
|
|
|
Vougheir |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Choose the correct answer:
Microorganisms are seen by……………………
(naked eyes – mirror – microscope)
……………………………don’t have roots, stem or leaves.
(adiantum – brown algae – maize)
Cycas belongs to…………………………
(angiosperms – aglae – plants)
The bodies of reptiles are …………………………………
(externally supported – soft – internally supported)
Spiders & ……………………………….are arachnids.
(scorpions – bees – files)
The basic unit of classification is the……………………….
(individual – species – microorganisms)
Write the scientific term:
Unicellular organisms present in all environments.
The group of terrestrial (on land) plants which reproduce by spores.
The class of animals with 3 pairs of jointed legs.
A group of animals with similar shape, they reproduce together & give birth to fertile individuals.
Give reasons for the following:
Tigers have sharp canines.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Scientists classify living organisms.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Jellyfish has soft body.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Spiders & ants are classified in 2 different classes.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
The front teeth of hedgehog extend outwards.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
When a zebra mates with a donkey , their offspring is infertile.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Mention a difference between the pair of organisms:
Rabbit & squirrel
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Bean & wheat
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Pine & palm
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Jellyfish & fish
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Euglena & amoeba
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Hedgehog & sloth
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Earth worm & scorpion
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Paramecium & Julius
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..


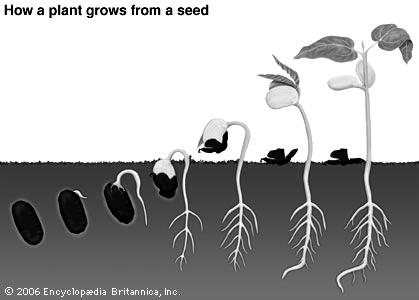
L iving organisms live in different environments. The conditions of these environments are diverse. The desert is hot & its soil is sandy. Camels’ feet are thick flat pads to walk on the sand. The mountain has rocky surface. Horses’ hooves are hard to walk on the rocks.

The modification in the living organisms that enable them to adapt to the environment is called adaptation.
A
 daptation
has 3 types:
daptation
has 3 types:
Modification of structure |
Modification of function |
Modification of behavior |
Examples: The structure of camel’s pad & horse’s hooves is suitable to their environment. |
Examples:
|
Examples:
|
Structural adaptation :

 nail
nail ussel
ussel ellyfish
ellyfish
 ly
ly
 pider
pider corpion
corpion colopendra
colopendra ulius
ulius edgehog
edgehog
 Tiger
Tiger
 abbit
abbit
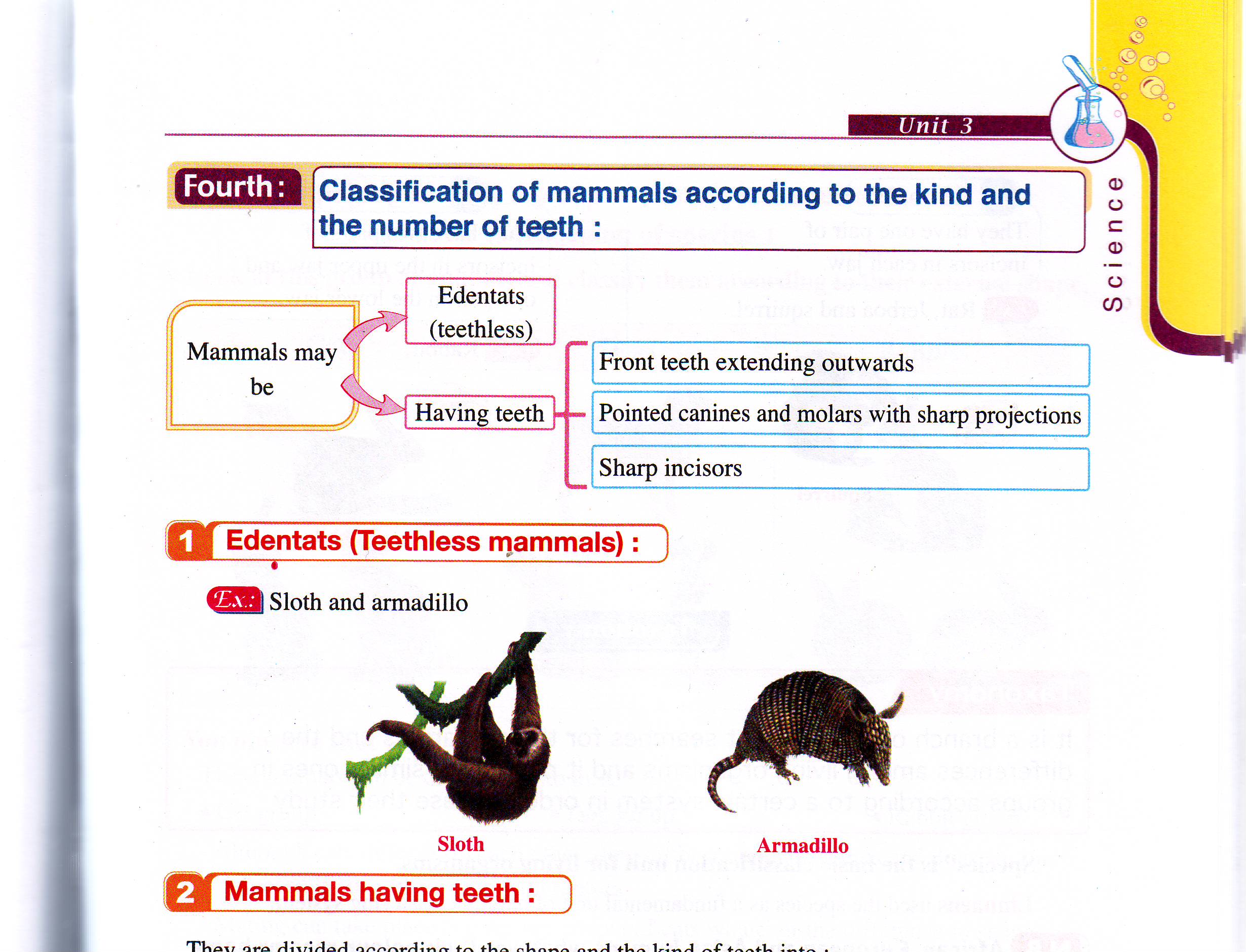 rmadillo
rmadillo