
- •Classification of pollutants
- •Air pollution
- •1. Nuclear wastes are stored in thick steel containers mixed with cement and buried deeply in the ground.
- •3. Freon is a harmful air pollutant.
- •S ources
- •Birth control.
- •Economic reform.
- •4. Desertification
- •5 .Coastal decay and dam problems
- •Variation of living organisms & their classification
- •Viruses
- •1. Virus are links between living and non living things.
- •2. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites.
- •3. Viruses are highly specific.
- •Kingdom Monera
- •3. The absence of the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, golgi bodies, plastids ..
- •4. Chromosomes spread in the cytoplasm.
- •Kingdom Protista
- •Kingdom Fungi
- •Kingdom Plantae
- •Phylum Tracheophyta
- •Angiosperms
- •Kingdom Animalia
- •1. Most developed animals
- •Interaction Among living organisms
- •Predation
- •Importance of predation to man:
- •1. According to site of attack
- •2. According to the period of parasitism in the host body.
- •Importance of saprophytes to the environment:
- •Saprophytic plants:
- •Saprophytic fungi:
- •Bacteria Dolphins big fish
- •Bacteria Hawk
- •2 . Pyramid of Mass
- •3.Pyramid of energy
- •E xamples of Intermediate link
- •Isolation & speciation (species formation): There're two types of speciation:
- •Sheet 1
- •Sheet 2
- •VIII-Give reasons for:
- •Sheet 3
- •Sheet 4
- •Sheet 5
- •Sheet 6
- •Sheet 7
- •Sheet 8
- •Sheet 9
- •2. Compare autotrophic nutrition & heterotrophic nutrition Sheet 10
- •Sheet 11
- •Biology practical revision
- •12.Tapeworm
- •In order for this scenario to take place
- •Vestigial structures
- •4. Embryology
- •5. Comparing the anatomy of organisms.
- •6.Physiological resemblance:
Angiosperms
|
Subclass: Monocotyledon |
Subclass: Dicotyledon |
Examples |
Wheat, maize, palm, onion & cactus |
Peas, cotton, roses |
Roots |
Fibrous root |
Tap roots |
Leaves |
Parallel veined |
Pinnate or palmate |
Flowers |
Trimerous or their multiplate |
Tetramerous or pentamerous |
Seeds |
O |
T |
P.O.C
|
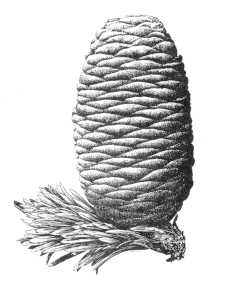
Gymnosperms
|
Angiosperms
|
Examples
|
Pines
|
Palm , bean, roses
|
R |
Cones |
Flower (carpel , anther)
|
Seeds
|
Naked seeds
|
Covered seeds |

Kingdom Animalia
Phylum |
Class |
Order |
1. Porifera |
|
|
2. Colenterata |
|
|
3. Platyhelminthes |
|
|
4.Nematohelminthes |
|
|
5. Annelida |
|
|
6. Arthropoda |
Crustacea, Archanida, Insecta, Myriopoda |
|
7. Mollusca |
|
|
8. Echinodermata |
|
|
9. Chordata |
Chondichthyes, Osteichthyes Amphibia Reptilia Aves
|
Edentata Insectivora Carnivora Cetacea Ungulata Rodenta Chiroptera Lagomorpha Primates |
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum |
Porefera |
Colenterata |
Examples |
S |
H jelly fish, corals |
Environment |
Aquatic animals which attach themselves to the base of rocks. |
Aquatic animals which attach themselves to t |
Description |
The body wall has many lateral pores & canals. Skeleton of calcareous, siliceous spicules, fibers. |
H
|
Reproduction |
Asexually (by budding) |
|
Sexually (by fusion of gametes) |
||
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Flat worms:
Most are endoparasites causing serious diseases to man and animals.
They have limited or no respiratory, locomotry and sensory organs.
The alimentary canal is simple.
Most of them are Hermaphrodite.
Reproduce sexually and asexually.
Subdivided into three classes
|
Class Turbellaria
|
Class Trematodes
|
Class Cestoda
|
Examples |
P |
T |
L |
Host |
|
Cow, pig then man Causing digestive disturbances & anemia. |
Cow and man |
|
Phylum Nematohelmnthes (Nematodes) |
Phylum Annelida (Ring worms) |
Examples |
|
E |
Feeding
|
Some worms are free-living |
Free living |
environment |
In water or mud. while other live as parasites on man & animals |
Sea, fresh water & moist soil Few are ectoparasites (medical leech). |
Body shape |
The body is cylindrical. |
Segmented body |
Structure |
No locomotary, respiratory or sensory systems. (unisexual). |
Closed circulatory system, have excretory and nervous system. |
Reproduction |
Female is bigger than male & lays a huge number of eggs. |
|
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Arthropoda
1. The most widely spread invertebrates
2. Their bodies are divided into identical segments.
3. They have jointed legs
|
Class Crustacea |
Class insecta |
Class Myriopoda |
Class Arachnida
|
Examples |
Cray fish Prawn C |
locust, cockroach, h |
Millipede C |
Spider,Scorpion T |
Structure of the body |
Body is covered by a Chitnous cuticle. |
Body is divided into head, thorax & abdomen. Some have wings others don't . |
|
Body is divided into thorax and abdomen, they have 4 pairs of legs. |
Respiration |
by Gills |
Trachea |
|
Trachea and lungbooks |
Eyes |
|
Compound eyes |
|
Simple eyes |
Kingdom Animalia
|
Phylum Mollusca |
Phylum Echinodermata |
Examples |
Desert snail, octopus, anodonta & mussel.
|
S |
Body |
Soft mass with an exoskeleton in the form of a calcareous shell. |
wall has prickles and calcereous plates. Some species have arms. |
Structure |
Has a circulatory , a sensory & a digestive system. |
Separate sexes & external fertilization. |
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Chordata

 ne
cotyledon
ne
cotyledon wo
cotyledons
wo
cotyledons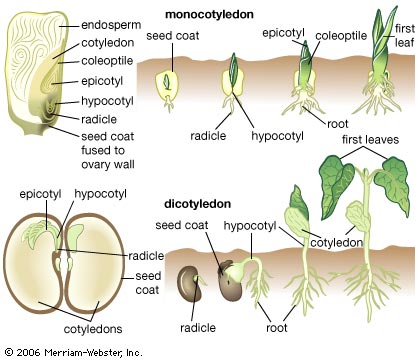
 eproductive
organs
eproductive
organs Mammalia
Mammalia
 ponges
ponges
 ydra,
ydra,
 he
base of rocks.
he
base of rocks. ave
stinging cells.
ave
stinging cells. lanaria
lanaria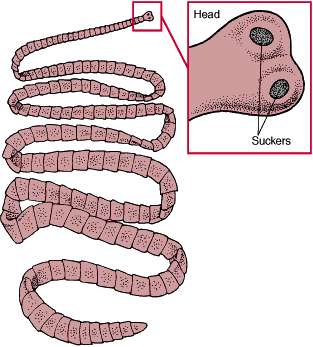 apeworm
(Taenia)
apeworm
(Taenia) iver
Fluke (Fasciola) Bilharzia
iver
Fluke (Fasciola) Bilharzia
 Ascaris,
Anklystoma
Ascaris,
Anklystoma

 art
h worm, Medical leech
art
h worm, Medical leech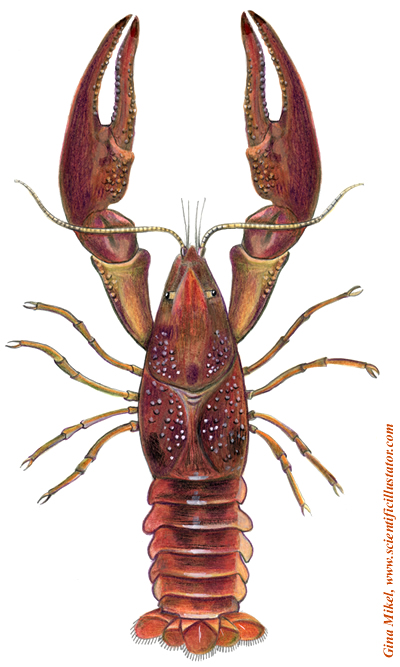 rab
rab
 oney
bee, ants, housefly, flea, mosquito
silk worm
oney
bee, ants, housefly, flea, mosquito
silk worm
 entipede
entipede
 ick,Mite
ick,Mite


 tar
fish, sea cucumber & brittle star.
tar
fish, sea cucumber & brittle star.