
- •The material - ionizing corpuscular radiation intereffect
- •Qessions for self-control:
- •Section 2. Types of the radiations used in medical practice. The biological effect|act| of ionizing radiation on a healthy and pathologically changed cell|cell|.
- •Principles and methods of the radiotherapy. Bases of the radiotherapy tumours and non-tumours diseases.
- •Classification of methods of radio therapy
- •I. Remote methods of long-focus radiotherapy:
- •II. Contact methods of an radiation exposure:
- •IV. The Combined methods of treatment of malignant tumours:
- •Bases of radio therapy of tumour and non-tumour diseases
- •Significance of volume of irradiated tissues
- •Value of a rhythm and fractionation radiation exposures
- •Qessions for self-control:
Value of a rhythm and fractionation radiation exposures
A. In unitary radiation exposure tumour cells are not at all damaged.
Fractional radiation exposure in smaller doses keeps the stroma and selectively amazes a tumour.
Fractionate and protragivity doses increase probability of an radiation exposure of a tumour at the stages sensitive to an ionizing radiation. At a stage of mitosis the cell is most sensitive to radiation exposure
Mechanism ofcontrainflammatory, desensibilising, antispastic and anaesthetic action of ionizing radiations.
As a result of action of ionizing radiations there is reduction of edema of tissues, the function of organ gets better, circulation of blood rises. In the first clock after the radiation exposure there is expansion of capillaries, rise of permeability of vascular wall, exudation growth , migration in tissue of elements of blood with subsequent their disintegration and formation biologically of active matters. Lymphatic capillaries broaden that is instrumental in strengthening of outflow from an inflammatory hearth, as a result interstitial pressure goes down and diminishes pain. Fagocitar activity of leucocytes rises, acydosis will be replaced by alkalosis and is instrumental in reduction of pain syndrome. Hyperemia and edema diminishes after brief expansion of road clearance of vessels.
Structure of a rate of radio therapy
The rate of radio therapy is the period of radio treatment during which the patient receives total dose distributed in days with disposable local dose.
Scheduling radio therapy is spent personally by three experts (the oncologist, the radio therapist and chemotherapist) according to existing structure of a rate of radio therapy.
Course of treatment divide into 3 periods: preradio-, radio- and postradio.
The preradio period:
Detailed inspection of the patient (clinic, laboratory, US, radiological, CT, МRI and other evalvulationes).
Definition of the histological form (biopsy).
The Establishment of indications to radio treatment.
Exception of contra-indications to radio treatment.
The Choice and kind of method of radiotherapy and additional non-radio medical actions.
Definition of topographical-anatomic mutual relations of a tumour with surrounding healthy bodies and tissues (topometry preparation of the patient) is carried out by manufacturing an personal cross-section body of the patient in the field of arrangement of tumour on projective labels preliminary then on skin in which the center of tumour lies. The contour of cross-section of the body and arrangement of a tumour and surrounding bodies is taken on the paper (see fig..5.1.).
The Choice of optimum single and total doses of an radiation exposure (see above)
Definition of quantity and the sizes of skin fields. Technology of radiation exposure.
The Choice of optimum mode of radiation exposure (unitary, fractional, continuous).
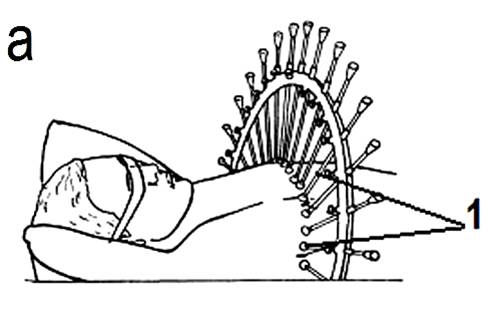
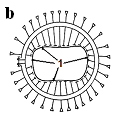
Fig. 5.1. The scheme of manufacturing of an personal contour of cross-section section of the body of patient. Removal of contour of cross-section section of the body of patient at the level of projection (1) by the means of copy device; transferring of the received contour on a paper with a designation of labels (1) projections of a tumour.
The radio period:
1. Carrying out of radiation exposure.
2. Application of additional non-radio methods of treatment.
3. Supervision of the patients, need of the correction of the plan of treatment.
Postradio the period:
Supervision of the patient, the periodic control of the radio therapist, estimation of efficiency of results of treatment, supervision of the patients 2 times a year. If in 10 years there was no relapse, the patient is removed from the oncological register.
