
- •Unit 1 semiconductors
- •What is a semiconductor?
- •Types of semiconductors
- •Vocabulary
- •How semiconductors work
- •Doping of semiconductors
- •Vocabulary
- •Unit 2 diode
- •What is a diode?
- •Vocabulary
- •Creating a p-n junction
- •Types of diodes
- •Diode applications
- •Ionizing radiation detectors
- •Vocabulary
- •Unit 3 transistor
- •What does a transistor actually do?
- •Types of transistors and how they work
- •Vocabulary
- •Transistors in computers who invented the transistror?
- •Who Invented the Transistor?
- •Integrated circuit
- •What is an integrated circuit?
- •Vocabulary
- •How are integrated circuits made? who invented the integrated circuit?
- •Inside a Chip Plant
- •Vocabulary
- •Verbs with vowel changes
- •Verbs with 3 different vowels!
- •The really Irregular Verbs
- •Semiconductor glossary of terms
- •Unit 1 semiconductors
- •What is a semiconductor?
- •Types of semiconductors
- •Vocabulary
- •How semiconductors work
- •Doping of semiconductors
- •Unit 2 diode
- •What is a diode?
- •Vocabulary
- •Creating a p-n junction
- •Types of diodes
- •Vocabulary
- •Transistors in computers who invented the transistror?
- •Integrated circuit
- •What is an integrated circuit?
- •Vocabulary
- •How are integrated circuits made? who invented the integrated circuit?
- •Vocabulary
- •Bibliography
Vocabulary
Choose the correct spelling of these words and translate them:
-
diode
diod
p-n juction
p-n junction
anod
anode
foward bais
forward bias
reverse voltage
revers voltag
cathode
catode
curent ratin
current rating
lead
laed
cercuit
circuit
threshold
treshold
Speaking
Work in pairs, choose one of the following questions and discuss it.
What is the connection between diodes and semiconductors?
How would you assess the importance of diodes?
Are vacuum tube diodes still used or are they totally replaced by semiconductors?
Creating a p-n junction
Start here
Read the text below. Match the descriptions 1- 3 with the diagrams a-c in Fig. 2.5. Put the descriptions 1-3 in logical order. Indicate the n-type and p-type regions, holes and electrons, reverse and forward bias.
 a)
a)
 b)
b)
 c)
c)
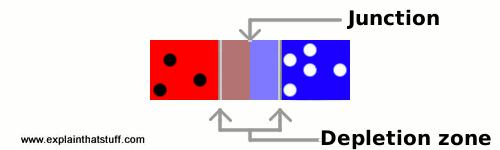
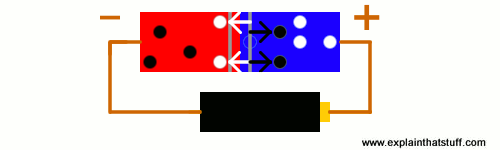
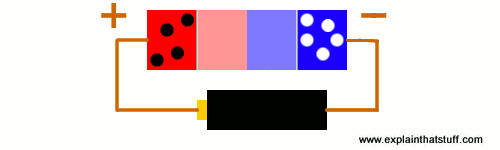
Fig. 2.5. How a p-n junction works.
A diode is a two-terminal device, having two active electrodes, between which it allows the transfer of current in one direction only. Diodes are known for their unidirectional current property, wherein, the electric current is allowed to flow in one direction.
Suppose you connect a battery to this little p-type/n-type junction. What will happen? It depends which way the battery is connected. If you put it so that the battery's negative terminal joins the n-type silicon, and the battery's positive terminal joins the p-type silicon, the depletion zone shrinks drastically. Electrons and holes move across the junction in opposite directions and current flows. This is called forward-bias.
However, if you reverse the current, all that happens is that the depletion zone gets wider. All the holes push up toward one end, all the electrons push up to the other end, and no current flows at all. This is called reverse-bias.
Interesting things happen when you start putting p-type and n-type silicon together. Suppose you join a piece of n-type silicon (with slightly too many electrons) to a piece of p-type silicon (with slightly too few). What will happen? Some of the extra electrons in the n-type will nip across the join (which is called a junction) into the holes in the p-type so, either side of the junction, we'll get normal silicon forming again with neither too many nor too few electrons in it. Since ordinary silicon doesn't conduct electricity, nor does this junction. Effectively it becomes a barrier between the n-type and p-type silicon and we call it a depletion zone because it contains no free electrons or holes.
That's how an ordinary diode works and why it allows an electric current to flow through it only one way. Think of a diode as an electrical one-way street.
Grammar
Study the sentences below and pay attention to the underlined verb forms in italics.
I am an English teacher. I am teaching English now. |
What are you? What are you doing now? |
You are students. You are studying English now. You are listening to me. |
Aren’t you? |
This is Andrew. He is a future electronics engineer. He is learning about diodes at this moment. |
That is Helen. She is learning English Grammar. |
What are we doing? What are they doing? |
Answer the following questions:
What are these verb forms?
am, is, are. What verb has such forms?
teaching, doing, studying, listening, learning. What do these verb forms have in common?
What grammatical notion is it? Is it a tense? What tense is it?
It is the Present Continuous or Present Progressive Tense.
How do we form sentences in the Present Continuous? Complete the table.
Positive
Negative
Interrogative
Subject + am, is, are+ Verb + ing.
Subject + am, is, are+ not Verb + ing.
Am, is, are + Subject+Verb + ing?
I am teaching.
You are studying.
He
She
It
We
They
I am not studying.
You are not teaching.
Am I studying?
Are you teaching?
So, now we can form the Present Continuous. But when do we use the Present Continuous? Study the following table and give your own examples.
Actions are happening… |
Examples |
now right now at the moment of speaking at this very moment |
|
around now around the moment of speaking currently, for longer actions in progress
|
|
this week, month, year these days, for temporary actions |
|
tonight tomorrow next week, month, year, for future arrangements and plans |
|
always constatly continually, for irritating repeated actions |
|
Make a presentation on the topic: “Types of diodes”. You may present all types of diodes, or two of them to compare, or just the only one. Use the information in the table to help you.
How do I start? |
So, how much do you know about ...? Have you ever asked yourself why ...? What I'm going to tell you about today will change the way you think about... Pass around the picture/object. What do you think it is? |
How do I organize the presentation? |
Introduce each point with an expression from the list below. The first/key thing to say about _________ is... The main point to make about _________ is… What you really need to know about__________ is ... Now let's look at... Let's turn to/move on to ... Another interesting thing to say about__________ is ... Finally, I'd like to say a few words about... |
What do I say? |
Anyway ...; Naturally ...; Of course ... Similarly ... ; Surprisingly …; Remarkably ... Despite ...; However ...; Although ...; Whereas ... Consequently ...; In addition ...; Moreover...; Furthermore ... Incidentally...; By the way...; It's worth noting that... |
How do I finish? |
In conclusion...; To sum up... So, remember that……..is all about ……., and... So, there are three things to remember about… Does anybody have any questions? |




