
- •Г. Д. Малик
- •Information Challenges
- •Contents
- •Information Age Text 1 understanding data, information, knowledge and their interrelationships
- •Text 2 how to build wisdom and prosper in an ‘information age’
- •5 Myths About the 'Information Age'
- •Brief Overview of Document Management
- •Introduction
- •Text 5 Understanding documents and documentation
- •Typical digital and traditional libraries compared
- •Text 6 The Transformation of Document Storage into Records Management
- •Text 7 problems and challenges of the information age
- •Industrial vs. Information Age
- •Text 8 Hidden-Information Agency
- •Introduction
- •Information Professionals Text 1 The Role of Information Professionals in Global Economic Crisis
- •Introduction: the causes and evolution of the global economic crisis
- •Information Professionals in the Information Age:
- •Vital Skills and Competencies
- •Intellectual Capital And Intangible Assets
- •Text 3 Entrepreneurship Education and Information Professionals
- •Text 4 The Information Professional facing the impact of Search Technology
- •Information Professional in news organizations
- •Knowledge Experts in the Intelligent Organization
- •Text 5 The Changing Role of the Information Professional
- •Implications for Education
- •Text 6 Challenges in Educating 21st-Century Information Professionals
- •Information Professionals in the Corporate World
- •Text 8 The Future of the Information Professional
- •Text 1 The Freedom of Expression and Information
- •Text 2 mass media and its influence on society
- •Text 3 pros and cons of mass media
- •Pros and Cons of Different Types of Media
- •Text 4 seven myths about media effects
- •Classification of Media
- •Text 5 children and the media
- •Print Materials
- •Television
- •Text 6 Ten Reasons to Advertise in a Newspaper
- •Immediate
- •Pros and Cons of Advertising in Newspapers
- •Text 7
- •Interactive elements and customization
- •Text 8 are newspapers dying? yes or no?
- •Newspapers Are Dead
- •No They Aren’t – Not Yet, Anyway
- •Internet Text 1
- •Internet as an important element of the information society and e-business development
- •Text 2 The Internet Revolution: It came. It went. It's here.
- •Text 3 Consumer Benefit from Use of the Internet
- •Text 4 The Educational Advantages of Using Internet
- •Text 5 From media literacy to digital skills
- •Text 6 Social Network Sites
- •Text 7 History of e-books
- •Text 8 The future of the Internet is wired into the human brain
- •It’s all in your head
- •Text 1 Censorship, Violence & Press Freedom
- •Text 2 Censoring and Destroying Information in the Information Age
- •Text 3 Pros and Cons of CenSorship
- •Text 4 Media Censorship: Why is Censorship Good
- •Internet / Magazines
- •Text 5 Censorship and the Arts
- •Text 6 Data driven futures - censorship takes new forms
- •Freedom of speech and censorship - project
- •Surveillance and censorship intertwined
- •Who controls the internet?
- •Paradoxes of democracy
- •Big media - concentration, globalization and user data
- •Media redefined
- •Big data
- •Information regime and respect for the user
- •Text 7 Kids' Book Censorship: The Who and Why
- •Challenges Are Ongoing
- •Why Do People Want to Ban Books?
- •The First Amendment to the u.S. Constitution
- •Kids Fight Book Banning Through kidSpeak
- •Parents Against Bad Books in Schools
- •What Do You Think?
- •Why do people want to ban books?
- •Text 8 Why Not Censor?
- •Text 1 a brief history of pr
- •Text 2 the important role of public relations
- •10 Principles of Public Relations
- •Text 4 ethical public relations: not an oxymoron
- •Text 5 public relations across cultures: building international communication bridges
- •Text 6 pr and blogging – how to think about it?
- •Text 7 how to choose between pr and advertising
- •Text 8 how to run ethically sound pr campaigns
- •Text 1 deal or no deal? resolving conflict through negotiation
- •Importance of good communication skills in negotiation
- •Text 3 a Buyers’ and Sellers’ Guide to Multiple Offer Negotiations
- •Information for Buyers
- •Information for Sellers
- •Information for Buyers and Sellers
- •Text 4 Deception in Negotiations: The Role of Emotions
- •Text 5 Differences in Business Negotiations between Different Cultures
- •Text 6 negotiation conflict styles
- •When to use?
- •What's the Danger?
- •Self Defense
- •When to use?
- •What's the Danger?
- •Self Defense
- •Avoid (I Lose - You Lose)
- •When to use?
- •What's the Danger?
- •Self Defense
- •Compromise (I Lose / Win Some - You Lose / Win Some)
- •When to use?
- •What's the Danger?
- •Self Defense
- •When to use?
- •What's the Danger?
- •Self Defense
- •Text 7
- •Text 8 ten tips for negotiating in 2013
- •Information Challenges
- •38 Karhula p. Data driven futures - censorship takes new forms / p. Kashula. – Available at: http://www.Ifla.Org/publications/data-driven-futures-censorship-takes-new-forms.
Text 8 The Future of the Information Professional
By Jan Sykes,
Richard Fletcher 16
The number of participants in the study was by no means statistically representative of the information professional community in the study countries. However, the insights and frank observations about the profession shared by interviewees provide a framework that allows inferences to be made about the state of the profession globally. The future appears to be characterized by continuing dynamic changes in terms of content resources, technology, and information service/management models. Further study is needed to validate these observations as actual trends, but the credentials of individuals and organizations represented in this study indicate that companies doing business with information professionals must be aware of and pay attention to the following:
• Successful information professionals are moving closer to information consumers in two ways. First, as information professionals are integrated into business units or teams, adding value means being credible. In order to be credible, information professionals must possess or add specialized subject knowledge to their information management skills. Second, in some cases, information professionals are themselves the information consumers, responsible for analysis and presentation of information to their colleagues. In both cases, it is critical that information professionals understand their roles and the decision-making processes within their organizations. Failure to “step up to the plate” in such a dynamic business environment means being relegated to a back office function that will likely disappear.
• Information professionals who embrace knowledge management and the development of corporate intranets are forced into intensive interaction with other parts of their organizations. Most see this involvement as an opportunity to leverage their skills in organizing information and selecting content appropriate to user information needs. Evaluating and selecting content for deployment to the desktop (and in some cases abstracting and indexing that content)—whether for business professionals in corporations or students/professors in academic communities—are key tasks and areas of growth for the profession.
• Concomitant with the deployment of information resources are the dual challenges of negotiating licenses and managing copyright compliance—issues of major concern to information professionals.
• Information professionals are anxious to demonstrate the value of their contribution and to have models, case studies, and tools that increase their effectiveness in negotiating with senior management for budgets, staff and technology resources.
• Managing internal and external documents in document warehouses with consistent indexing schemes and uniform interfaces for optimum retrieval is another growth area for information professionals.
• In many of our study countries, critical local content resources may need to be included in information product offerings.
• Increasingly, some companies are using vendors to combine internal proprietary content with external content to produce customized information products.
• Eventual outsourcing or elimination of back office functions, like corporate libraries, is likely to continue though shared services models which offer opportunities for corporate libraries to evolve and keep pace with their rapidly changing organizations.
Assignments
When do successful information professionals move closer to information consumers?
Do you agree that information professionals will not be useful in the future?
What are the main growth areas for information professionals?
What do shared services models offer for corporate libraries?
What is meant by knowledge management? Use the figure below.
Fig. 2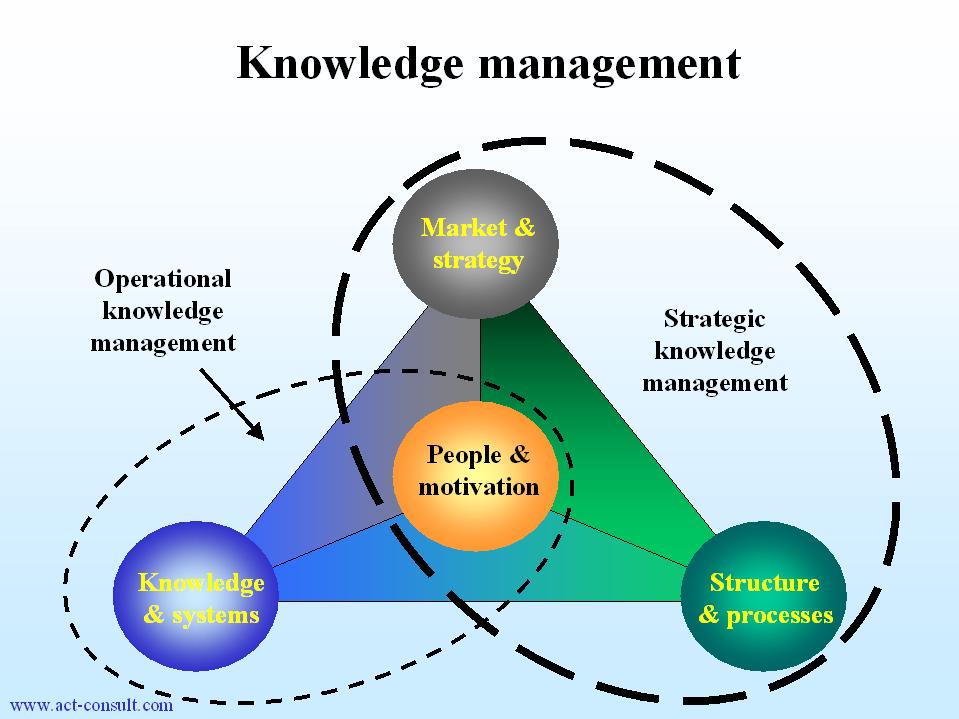 .16
Knowledge Management
.16
Knowledge Management
What are the key tasks of growth for the information professions?
How can information professional be successful in the future?
What does failure to “step up to the plate” mean?
How can information professions be transformed in the future?
Summarize the text.
Mass media
