
- •Section I Control of the initial level of knowledge. Biochemical constituents of the cell. Methods of biochemical investigations.
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •77. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •78. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •Section іі Enzymes, structure and classification. Regulation of metabolism
- •Е. Whatever part of polypeptide chain of enzyme molecule.
- •Substrate concentration at which reaction rate is half maximal
- •The second enzyme has higher affinity to substrate
- •Competitive
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Cysteine
- •B. Amylase
- •Peptidases
- •Enteropeptidase
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section ііi Metabolic pathways and bioenergetics. Tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation and oxidative phopshorylation
- •1. When atp forms amp:
- •B. Protons
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of carbohydrates
- •19. Chose the reaction of glycolysis catalyzed by an enzyme phosphofructokinase:
- •A. Liver
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Acetoacetate, β-hydroxybulyrate, and acetone
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of lipids
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •143. A patient with high rate of obesity was advised to use carnitine as a food additive in order to enhance "fat burning". What is the role of carnitine in the process of fat oxidation?
- •144. Lipids are obvious energetic material for the body. What is the main pathway of fatty acids metabolism in mitochondria?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks Situational tasks
- •179. The patient is observed an allocation of undigested fat in the faeces. What are the possible causes for this?
- •184. Free cholesterol can affect cholesterol metabolism in the body by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis. By which step free cholesterol can inhibit its biosynthesis?
- •186. Explain the mechanism of phospholipids breakdown, shown at the scheme below:
- •Section VI Structure and metabolism of amino acids
- •B. Amylase
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •112. According to clinical indications a patient was administered pyridoxal phosphate. What processes is this medication intended to correct?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •145. In a patient 10 g of urine per day is excreted. Evaluate this result.
- •151. Skin color is the aggregate result of the expression of a number of genes modified by ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. What can cause the hypopigmentation?
- •Section VII Principles of molecular biology and molecular genetics
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •108. List and describe properties of the genetic code.
- •113. Fill in the blanks.
- •114. Put the numbers of the enzymes on their place in the picture. Using arrows indicate the direction of replication and direction of synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
- •Section VIII Molecular mechanisms of hormone action on target cells. Biochemistry of hormonal regulation
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •78. For analgesia, a certain substance which imitates the physiological properties of morphine but is synthesized inside the human brain can be used. Name this substance.
- •80. A patient suffering from rheumatism was administered glucocorticoid therapy. What changes in carbohydrate metabolism in liver can be expected?
- •88. In blood of a patient a hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, in urine – hyperphosphaturia is observed. What is a possible cause of this state?
- •90. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. It is caused by deficiency of:
- •93. Signaling via prostanoids begins by interaction of the prostanoid with its receptor. The receptor involved is usually located in which part of the cell?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •97. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. Which hormone deficiency can cause this disease?
- •99. The thyroid hormones t3 and t4 are synthesized in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. From which of the following essential amino acids are the thyroid hormones synthesized?
- •101. Name types of signalling:
- •Section IX Biochemistry of the nervous tissue
- •С. Ketone bodies
- •24. What compound may be used by the cns cells after extensive physical exercises and prolonged starvation?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •114. Describe the structure of a synapse and explain how it operates?
- •Section X Biochemistry of the Muscular tissue
- •D. Glycogenolysis in muscles
- •С. Fatigue faster compared to the red fibers
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XI Biochemistry of nutrition
- •1. Note substance, which activates pepsinogen to pepsin:
- •2. Chose the enzyme which plays an important role in production of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells of gastric mucosa glands:
- •3. Which of the following is not a function of the pancreas?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •62. The clinical and laboratory examination of the patient evaluated the presence of the lactic acid in his gastric juice. What does it indicate? What should be recommended to the patient?
- •69. Discribe the mechanism of hydrochloric acid production shown at the picture:
- •Section XII Functional role of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins in metabolism and providement of cell functions
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •100. A deficiency in thiamine (vitamin b1) would most likely lead to which clinical manifestations?
- •Section XIII Biochemistry and pathobiochemistry of blood
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •89. The blood clotting cascade in humans is represented in the picture below. Using this scheme answer the following questions:
- •Section XIV Functional and clinical biochemistry of liver tissue. Biotransformation of xenobiotics and endogenous toxic compounds
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XV Water and mineral metabolism
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVI Functional role of kidneys in urinogenesis. Normal and pathological constituents of urine
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVII Biochemical constituents of connective tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 Tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •34. Patient with burn disease is at the risk of formation of blood clots in blood vessels. What glycosaminoglycan may be used to prevent formation of blood clots?
- •Section XVIII Biochemistry of saliva and tooth tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XIX. Biochemical reactions
- •References:
69. Discribe the mechanism of hydrochloric acid production shown at the picture:
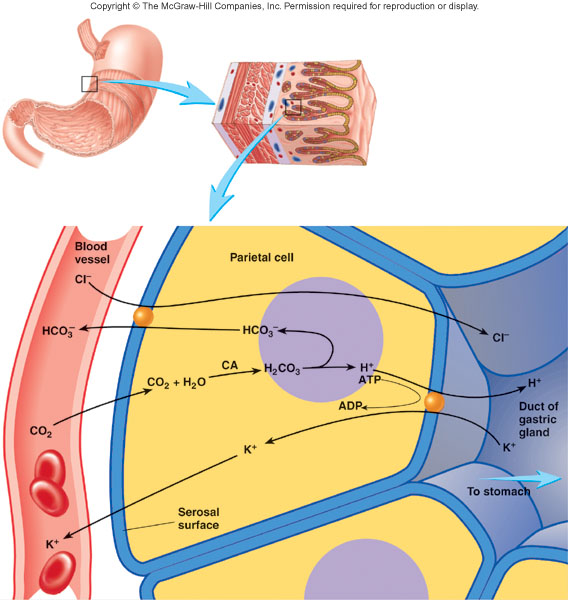
Answer: 1. CO2 and Cl- diffuse from the blood into the stomach cell.
2. CO2 combines with H2O to form H2CO3.
3. H2CO3 dissociates into bicarbonate (HCO3-) and H+.
4. H+ combines with Cl- in duct of gastric gland to form HCl-.
5. An ATP pump is necessary to pump the HCl- into the duct since the concentration of HCl- is about a million times more concentrated in the duct than in the cytosol of the cell.
Section XII Functional role of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins in metabolism and providement of cell functions
1. Vitamins are:
Accessory food factors
Generally synthesized in the body
Produced in endocrine glands
Proteins in nature
2. A severe deficiency in nicotinic acid is the cause of the next disease:
Pellagra
Rickets
Polyneuritis
Scurvy
Hemorrhagic diathesis
3. Select the metabolic process with which is most likely associated vitamin C:
Biosynthesis of collagen
Intestinal calcium absorption
Biosynthesis of DNA
Biosynthesis of glycogen
Oxidative decarboxylation of α-ketoacids
4. Select the metabolic process with which thiamine is mostly associated:
Decarboxylation of α-ketoacids
Biosynthesis of collagen
Biosynthesis of amino acids
Oxidation of fatty acids
Biosynthesis of prothrombin
5. Beri-beri is a disease caused by deficiency of the next nutritional factor:
Thiamine
Carotene
Linolenic acid
Nicotinic acid
Tocoferol
6. Biotin as a cofactor participates in the next metabolic reactions:
Incorporation of CO2 into molecules of metabolites (carboxylation)
Decarboxylation of pyruvate
Oxidation of fatty acids
Transfer of phosphate groups (kinase reaction)
Production of H2O2 (oxidase reaction)
7. Chose from the following vitamins one which is considered as antianemic factor.
Folic acid
Thiamine
Pantothenic acid
Ascorbic acid
Pyridoxine
8. Biochemical functions of water soluble vitamins are realized due to their transformation to coenzymes. What coenzyme is formed by vitamin PP?
NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide)
Pyridoxalphosphate
FMN (flavinmononucleotide)
Thiamine pyrophosphate
9. Which of the following symptoms would be seen in a patient with a severe deficiency of thiamine?
A decreased level of transketolase activity in red blood cells
An increased clotting time of blood
A low level of cell transaminase activity
Xerophthalmia
A decrease in blood level of pyruvate and lactate
10. A prolong deficiency in cobalamine supply leads to development of the next disease:
Pernicious anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Hemorrhagic diathesis
Scurvy
Rickets
11. Thiamine pyrophosphate is a cofactor of which of the following enzymes?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
Aminotransferase
Citrate synthase
Arginase
Succinate dehydrogenase
12. Pantothenic acid is a precursor of the next coenzyme:
Coenzyme A
FAD
NADP
Coenzyme Q
SAM (S-adenosylmethionine)
13. Para-aminobenzoic acid is believed to be an inhibitor in biosynthesis of the next vitamin in: bacteria:
Folic acid
Biotin
Pantothenic acid
Cobalamin
Pyridoxine
14. Both Wernicke’s disease and beriberi can be reversed by administrating:
Thiamin
Retinol
Pyridoxine
Biotin
Vitamin B12
15. The Vitamin B1 deficiency causes:
Beri-beri
Ricket
Nyctalopia
Pellagra
Osteoporosis
16. Concentration of pyruvic acid and lactic acid in blood is increased due to deficiency of the vitamin:
Thiamin
Riboflavin
Niacin
Pantothenic acid
Biotin
17. Vitamin B1 coenzyme (TPP) is involved in:
Oxidative decarboxylation
Hydroxylation
Transamination
Carboxylation
18. Increased glucose consumption increase the dietary requirement for:
Thiamin
Pyridoxine
Niacin
Biotin
Riboflavin
19. Riboflavin is a coenzyme in the reaction catalysed by the enzyme:
Acyl CoA synthetase
Acyl CoA dehydrogenase
-Hydroxy acyl CoA
Enoyl CoA dehydrogenase
Enoyl CoA synthetase
20. The daily requirement of riboflavin for adult in mg is:
2.0–3.5
0–1.0
1.2–1.7
4.0–8.0
9.0-10.5
21. The pellagra preventive factor is:
Niacin
Riboflavin
Pantothenic acid
Pyridoxine
Biotin
22. Niacin is synthesized in the body from:
Tryptophan
Tyrosine
Glutamate
Aspartate
Valine
23. The enzymes with which nicotinamide act as coenzyme are:
Dehydrogenases
Transaminases
Decarboxylases
Carboxylases
Oxidases
24. Pantothenic acid is a constituent of the coenzyme involved in:
Acetylation
Decarboxylation
Dehydrogenation
Oxidation
Carboxylation
25. The precursor of CoA is:
Pantothenate
Riboflavin
Pyridoxamine
Thiamin
Biotin
26. Pyridoxal phosphate is central to:
Transamination
Deamination
Amidation
Carboxylation
Oxidation
27. The vitamin required as coenzyme for the action of transaminases is:
Pyridoxal phosphate
Niacin
Pantothenic acid
Riboflavin
Ascorbic acid
28. Vitamin B6 deficiency may occur during therapy with:
Isoniazid
Terramycin
Sulpha drugs
Aspirin
29: Biotin is a coenzyme of the enzyme:
Carboxylase
Hydroxylase
Dehydrogenase
Decarboxylase
Deaminase
30. The coenzyme required for conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate is:
Biotin
FAD
NAD+
TPP
FMN
31. Consumption of raw eggs can cause deficiency of:
Biotin
Pantothenic acid
Riboflavin
Thiamin
32. The cofactor or its derivative required for the conversion of acetyl CoA to malonyl-CoA is:
FAD
ACP
NAD+
Biotin
Pantothenic acid
33. A cofactor required in oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate is:
Biotin
Lipoate
Pantothenic acid
Para aminobenzoic acid
34. The central structure of B12 referred to as corrin ring system consists of:
Cobalt
Manganese
Magnesium
Iron
Sodium
35. Vitamin B12 has a complex ring structure (corrin ring) consisting of four:
Pyrrole rings
Purine rings
Pyrimidine rings
Pteridine rings
36. A deficiency of vitamin B12 causes:
Perniciuos anemia
Beri-Beri
Scurvy
Rickets
Pellagra
37. Folic acid or folate consists of the:
Base pteridine, p-amino benzoic acid and glutamate
Base pteridine, p-amino benzoic acid and asparate
Base purine, p-amino benzoic acid and glutamate
Base purine, p-hydroxy benzoic acid and glutamate
Base pirimidine, p-amino benzoic acid and asparate
38. Folate as a coenzyme is involved in the transfer and utilization of:
Single carbon moiety
Amino group
Hydroxyl group
Amido group
39 Folate deficiency causes:
Microcytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Iron deficiency anemia
Megaloblastic anemia
40. Coenzyme A contains a nitrogenous base which is:
A. Adenine
B. Guanine
C. Choline
D. Ethanolamine
41. Chemically, lipoic acid is:
Sulphur containing fatty acid
Saturated fatty acid
Unsaturated fatty acid
Amino acid
Nucleic acid
42. Deficiency of vitamin C causes:
Scurvy
Pellagra
Pernicious anaemia
Beriberi
43. Retinol is produced in human body from the next precursor:
β-Carotene
Xanthophyll
7-Dehydrocholeterol
Ergosterol
Tryptophan
44. The precursor of cholecalciferol in human is the following substance:
7-dehydrocholesterol
Carotene
Heme, released after degradation of hemoglobin
Ergosterol
Phylloquinone
45. Vitamin K has the next physiological significance:
Provides the synthesis of prothrombine and other coagulating factors.
Stimulates absorption of calcium in intestines
Support the maturation of mucosal epithelium
Regulates the excretion of bile in the liver.
It is a cofactor of decarboxylases
46. Vitamin K is a cofactor of carboxylase, which produce the next amino acid derivative:
γ-Carboxyglutamate
Carboxyproline
N-Carboxyhistidine
γ-Carboxyaspartic acid
ε-Hydroxylysine
47. Deficiency of ergocalciferol causes development of the next disease:
Rickets
Xerophthalmia
Scurvy
Pellagra
Pernicious anemia
48. The appearance of osteoporosis in adults may be caused by deficiency of the next vitamin:
Ergocalciferol
Tocoferol
Phylloquinon
Ubiquinon
Pantothenic acid
49. Vitamin A or retinal is a:
Polyisoprenoid compound containing cyclohexenyl ring
Steroid
Benzoquinone derivative
6-Hydroxychromane
50. -Carotene, precursor of vitamin A, is oxidatively cleaved by:
-Carotene dioxygenase
Oxygenase
Hydroxylase
Transferase
51. The molecule of vitamin A1 contains:
-Ionone ring
Benzene ring
-Carotene ring
Purine ring
52. One of the manifestation of vitamin A deficiency is:
Night blindness
Painful joints
Loss of hair
Thickening of long bones
53. Deficiency of Vitamin A causes:
Xeropthalmia
Hypoprothrombinemia
Megaloblastic anemia
Pernicious anemia
Beriberi
54. Retinal is a component of:
Rhodopsin
Cardiolipin
Glycoproteins
Iodopsin
Nucleoprotein
55. The most potent Vitamin D metabolite is:
1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
25-Hydroxycholecalciferol
24, 25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
7-Dehydrocholesterol
1- Dehydrocholesterol
56. Deficiency of vitamin D causes:
Ricket and osteomalacia
Tuberculosis of bone
Hypthyroidism
Skin cancer
Beriberi
57. Calcitriol synthesis involves:
Both liver and kidney
Intestine
Adipose tissue
Muscle
Brain
58. The most important natural antioxidant is:
Vitamin E
Vitamin D
Vitamin B12
Vitamin K
Vitamin A
59. Vitamin K is involved in posttranslational modification of the blood clotting factor by acting as cofactor for the enzyme:
Carboxylase
Decarboxylase
Hydroxylase
Oxidase
Dehydrogenase
60. Vitamin K is a cofactor for:
Gamma carboxylation of glutamic acid residue
-Oxidation of fatty acid
Formation of -amino butyrate
Synthesis of tryptophan
