
- •Section I Control of the initial level of knowledge. Biochemical constituents of the cell. Methods of biochemical investigations.
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •77. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •78. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •Section іі Enzymes, structure and classification. Regulation of metabolism
- •Е. Whatever part of polypeptide chain of enzyme molecule.
- •Substrate concentration at which reaction rate is half maximal
- •The second enzyme has higher affinity to substrate
- •Competitive
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Cysteine
- •B. Amylase
- •Peptidases
- •Enteropeptidase
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section ііi Metabolic pathways and bioenergetics. Tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation and oxidative phopshorylation
- •1. When atp forms amp:
- •B. Protons
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of carbohydrates
- •19. Chose the reaction of glycolysis catalyzed by an enzyme phosphofructokinase:
- •A. Liver
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Acetoacetate, β-hydroxybulyrate, and acetone
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of lipids
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •143. A patient with high rate of obesity was advised to use carnitine as a food additive in order to enhance "fat burning". What is the role of carnitine in the process of fat oxidation?
- •144. Lipids are obvious energetic material for the body. What is the main pathway of fatty acids metabolism in mitochondria?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks Situational tasks
- •179. The patient is observed an allocation of undigested fat in the faeces. What are the possible causes for this?
- •184. Free cholesterol can affect cholesterol metabolism in the body by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis. By which step free cholesterol can inhibit its biosynthesis?
- •186. Explain the mechanism of phospholipids breakdown, shown at the scheme below:
- •Section VI Structure and metabolism of amino acids
- •B. Amylase
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •112. According to clinical indications a patient was administered pyridoxal phosphate. What processes is this medication intended to correct?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •145. In a patient 10 g of urine per day is excreted. Evaluate this result.
- •151. Skin color is the aggregate result of the expression of a number of genes modified by ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. What can cause the hypopigmentation?
- •Section VII Principles of molecular biology and molecular genetics
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •108. List and describe properties of the genetic code.
- •113. Fill in the blanks.
- •114. Put the numbers of the enzymes on their place in the picture. Using arrows indicate the direction of replication and direction of synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
- •Section VIII Molecular mechanisms of hormone action on target cells. Biochemistry of hormonal regulation
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •78. For analgesia, a certain substance which imitates the physiological properties of morphine but is synthesized inside the human brain can be used. Name this substance.
- •80. A patient suffering from rheumatism was administered glucocorticoid therapy. What changes in carbohydrate metabolism in liver can be expected?
- •88. In blood of a patient a hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, in urine – hyperphosphaturia is observed. What is a possible cause of this state?
- •90. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. It is caused by deficiency of:
- •93. Signaling via prostanoids begins by interaction of the prostanoid with its receptor. The receptor involved is usually located in which part of the cell?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •97. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. Which hormone deficiency can cause this disease?
- •99. The thyroid hormones t3 and t4 are synthesized in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. From which of the following essential amino acids are the thyroid hormones synthesized?
- •101. Name types of signalling:
- •Section IX Biochemistry of the nervous tissue
- •С. Ketone bodies
- •24. What compound may be used by the cns cells after extensive physical exercises and prolonged starvation?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •114. Describe the structure of a synapse and explain how it operates?
- •Section X Biochemistry of the Muscular tissue
- •D. Glycogenolysis in muscles
- •С. Fatigue faster compared to the red fibers
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XI Biochemistry of nutrition
- •1. Note substance, which activates pepsinogen to pepsin:
- •2. Chose the enzyme which plays an important role in production of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells of gastric mucosa glands:
- •3. Which of the following is not a function of the pancreas?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •62. The clinical and laboratory examination of the patient evaluated the presence of the lactic acid in his gastric juice. What does it indicate? What should be recommended to the patient?
- •69. Discribe the mechanism of hydrochloric acid production shown at the picture:
- •Section XII Functional role of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins in metabolism and providement of cell functions
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •100. A deficiency in thiamine (vitamin b1) would most likely lead to which clinical manifestations?
- •Section XIII Biochemistry and pathobiochemistry of blood
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •89. The blood clotting cascade in humans is represented in the picture below. Using this scheme answer the following questions:
- •Section XIV Functional and clinical biochemistry of liver tissue. Biotransformation of xenobiotics and endogenous toxic compounds
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XV Water and mineral metabolism
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVI Functional role of kidneys in urinogenesis. Normal and pathological constituents of urine
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVII Biochemical constituents of connective tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 Tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •34. Patient with burn disease is at the risk of formation of blood clots in blood vessels. What glycosaminoglycan may be used to prevent formation of blood clots?
- •Section XVIII Biochemistry of saliva and tooth tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XIX. Biochemical reactions
- •References:
101. Name types of signalling:
a)
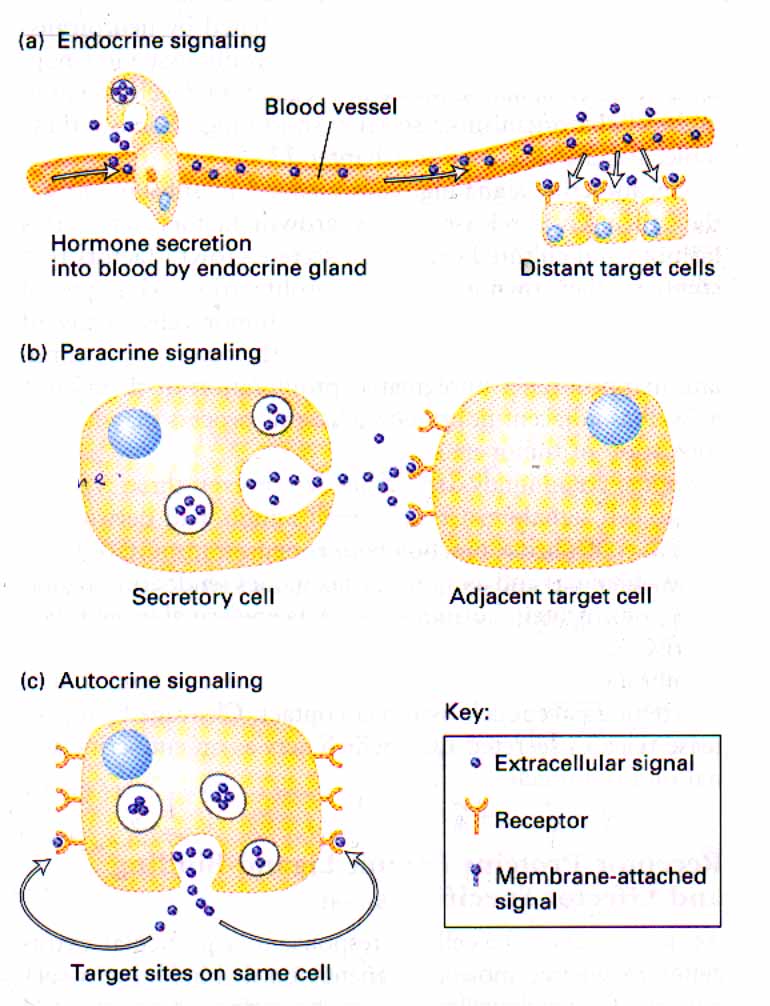
b)
c)
Answer:
a) endocrine signals are directed at distant cells through the intermediacy of the blood stream;
b) paracrine signals are directed at nearby cells;
c) autocrine signals are directed at the cell that produced them.
102. Name the enzyme, which catalyses the following raction.
?
Answer: Adenylate cyclase catalyzes the conversion of ATP to 3’,5’-cyclicAMP (cAMP) and pyrophosphte.
Section IX Biochemistry of the nervous tissue
1. Which compound is the main source of energy for the brain tissue?
А. Glucose
В. Lactic acid
С. Ketone bodies
D. Fatty acids
Е. Amino acids
2. The tyrosine metabolism results in synthsesis of such mediator as:
A. Dopamine
B.Serotonin
C. Enkephalin
D. Histamin
E. γ –amunobutyric acid
3. For the compensatory treatment of nervous system alterations (dimentia) with simultaneous involvmentd of skin (dermatitis) and gastrointestinal tract (diarhea) a antipellagric vitamin was administered to the patient:
А. PP
B. C
C. A
D. B6
E. K
4. The peculiarity of the amino acid constituents of the brain is the large amount of monoaminodicarboxylic acids, including:
А. Glutamate, aspartate
В. Arginin, lysine
С. Glutamine, asparagine
D. Serine, histidine
Е. Valine, tyrosine
5. The neurotransmitters of the group of biogeneous amines include:
А. Norepinephrine, serotonin
В. Glycine, proline
С. Glutamate, aspartate
Е. Acetylcholine, choline
6. The amino acids, containing “excitatory amino acids” include:
А. Glutamate, aspartate
В. GABA, glycine
С. Proline, serine
D. Histidine, lysine
Е.Glutamine, asparagine
7. The neurotransmitters, containing “depressive amino acids” include:
А. GABA, glycine
В. Glutamate, glutamine
С. Aspartate, asparagine
D. Proline, lysine
Е. Histidine, tyrosine
8. The main represantatives of opioid neuropeptides are met-enkephaline and leu-enkephaline which chemical structure is typical for:
А. Pentapeptides
В. Tetrapeptides
С. Hexapeptides
D. Octapeptides
Е. Decapeptides
9. Which tissue is the most sensitive to the lack of oxygen?
A. Nervous
B. Muscular
C. Connective
D. Epithelial
E. Bone
10. Which metabolite is the main energy supplier for the brain?
A. Glucose
B. Fatty acids
C. Amino acids
D. Glycerol
E. Glycogen
11. Which types of phospholipids differently from other tissues are neurospecific?
A. Gangliosides
B. Satured fatty acids
C. Phosphatidylcholine
D. Phosphatidylserine
E. Unsatured fatty acids
12. Whch of the mentioned below amno acids are the most commonly present in the nervous tissue?
A. Glutamate and aspartate
B. Glycine,proline
C. Histamine, tyrosine
D. Valine, isoleucine
E. Phenylalanine, threonine
13. Which amino acid is used for ammonia detoxication in the nervous tissue?
A. Glutamate
B. Leucine
C. Proline
D. Valine
E. Glutamine
14. Which depressing mediator is synthesized in nervous tissue from the glutamate?
A. γ-aminobutyric acid
B. Taurine
C.Glycine
D. Glutamine
E. Enkephaline
15. The source for catecholamine biosynthesis is:
A. Tyrosine
B. Tryptophan
C. Glutamate
D. Glutamine
E. Methionine
16. Which enzyme hydrolizes the mediator in cholinergic sinapses?
A. Acethylcholinestherase
B. Monoaminoxidase
C. Histaminase
D. Ceruloplasmin
E. Xanthinoxidase
17. Which mediator is used as antistress remedue?
A. γ-aminobutyric acid
B. Glutamine
C. Norepinephrine
D. Histamine
E. Acethylcholine
18. Which of the following neuropeptides exerts morphin-like properties?
A. Enkephaine
B. Vasointestinal peptide
C. Cholecistokinine
D. Substance P
E. Neurotensine
19. Which changes of the mediators balance are induced by stress?
A. The enhancement of cathecholamines synthesis and secretion
B. Enhancement of acetylcholine synthesis
C. Inhibition of cathecholamine synthesis
D. Inhibition of endorphine synthesis
E. Inhibition of glycine synthesis
20. Which enzyme catalises the oxidative desamination of cathecholamines?
A. Monoaminoxidase
B. Glutamate dehydrogenase
C. Cholinesterase
D. Acethylcholinesterase
E. Glutaminase
21. Which monooxidase inhibitors are commonly used in clinical practice as psychopharmacologic drugs, f.i. in treatment of the depressive conditions, schzizofrenia:
А. Iprinosil, pirasidol
В. Methionine, cysteine
С. Heparin, carnosine
D. Riboflavin, retinol
Е. Epinephrine, serotonine
22. Inhibition of the release of what mediator into the synaptic cleft occurs in tetanic toxin infection?
А. Glicine
В. Norepinephrine
С. GABA
D. Acetylcholine
Е. Glutamate
23. GABA is a depressing mediator in CNS. The inhibition of GABA-involved nervous impulse transfer between the neuronal cells is caused by the increased permeability of biomembrane for the ions of:
А. СІ
В. К+
С. Са++
D. Mg++
Е. Na
