
- •Section I Control of the initial level of knowledge. Biochemical constituents of the cell. Methods of biochemical investigations.
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •77. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •78. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •Section іі Enzymes, structure and classification. Regulation of metabolism
- •Е. Whatever part of polypeptide chain of enzyme molecule.
- •Substrate concentration at which reaction rate is half maximal
- •The second enzyme has higher affinity to substrate
- •Competitive
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Cysteine
- •B. Amylase
- •Peptidases
- •Enteropeptidase
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section ііi Metabolic pathways and bioenergetics. Tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation and oxidative phopshorylation
- •1. When atp forms amp:
- •B. Protons
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of carbohydrates
- •19. Chose the reaction of glycolysis catalyzed by an enzyme phosphofructokinase:
- •A. Liver
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Acetoacetate, β-hydroxybulyrate, and acetone
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of lipids
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •143. A patient with high rate of obesity was advised to use carnitine as a food additive in order to enhance "fat burning". What is the role of carnitine in the process of fat oxidation?
- •144. Lipids are obvious energetic material for the body. What is the main pathway of fatty acids metabolism in mitochondria?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks Situational tasks
- •179. The patient is observed an allocation of undigested fat in the faeces. What are the possible causes for this?
- •184. Free cholesterol can affect cholesterol metabolism in the body by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis. By which step free cholesterol can inhibit its biosynthesis?
- •186. Explain the mechanism of phospholipids breakdown, shown at the scheme below:
- •Section VI Structure and metabolism of amino acids
- •B. Amylase
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •112. According to clinical indications a patient was administered pyridoxal phosphate. What processes is this medication intended to correct?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •145. In a patient 10 g of urine per day is excreted. Evaluate this result.
- •151. Skin color is the aggregate result of the expression of a number of genes modified by ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. What can cause the hypopigmentation?
- •Section VII Principles of molecular biology and molecular genetics
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •108. List and describe properties of the genetic code.
- •113. Fill in the blanks.
- •114. Put the numbers of the enzymes on their place in the picture. Using arrows indicate the direction of replication and direction of synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
- •Section VIII Molecular mechanisms of hormone action on target cells. Biochemistry of hormonal regulation
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •78. For analgesia, a certain substance which imitates the physiological properties of morphine but is synthesized inside the human brain can be used. Name this substance.
- •80. A patient suffering from rheumatism was administered glucocorticoid therapy. What changes in carbohydrate metabolism in liver can be expected?
- •88. In blood of a patient a hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, in urine – hyperphosphaturia is observed. What is a possible cause of this state?
- •90. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. It is caused by deficiency of:
- •93. Signaling via prostanoids begins by interaction of the prostanoid with its receptor. The receptor involved is usually located in which part of the cell?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •97. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. Which hormone deficiency can cause this disease?
- •99. The thyroid hormones t3 and t4 are synthesized in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. From which of the following essential amino acids are the thyroid hormones synthesized?
- •101. Name types of signalling:
- •Section IX Biochemistry of the nervous tissue
- •С. Ketone bodies
- •24. What compound may be used by the cns cells after extensive physical exercises and prolonged starvation?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •114. Describe the structure of a synapse and explain how it operates?
- •Section X Biochemistry of the Muscular tissue
- •D. Glycogenolysis in muscles
- •С. Fatigue faster compared to the red fibers
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XI Biochemistry of nutrition
- •1. Note substance, which activates pepsinogen to pepsin:
- •2. Chose the enzyme which plays an important role in production of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells of gastric mucosa glands:
- •3. Which of the following is not a function of the pancreas?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •62. The clinical and laboratory examination of the patient evaluated the presence of the lactic acid in his gastric juice. What does it indicate? What should be recommended to the patient?
- •69. Discribe the mechanism of hydrochloric acid production shown at the picture:
- •Section XII Functional role of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins in metabolism and providement of cell functions
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •100. A deficiency in thiamine (vitamin b1) would most likely lead to which clinical manifestations?
- •Section XIII Biochemistry and pathobiochemistry of blood
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •89. The blood clotting cascade in humans is represented in the picture below. Using this scheme answer the following questions:
- •Section XIV Functional and clinical biochemistry of liver tissue. Biotransformation of xenobiotics and endogenous toxic compounds
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XV Water and mineral metabolism
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVI Functional role of kidneys in urinogenesis. Normal and pathological constituents of urine
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVII Biochemical constituents of connective tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 Tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •34. Patient with burn disease is at the risk of formation of blood clots in blood vessels. What glycosaminoglycan may be used to prevent formation of blood clots?
- •Section XVIII Biochemistry of saliva and tooth tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XIX. Biochemical reactions
- •References:
113. Fill in the blanks.
DNA (strand 1) T G T _ _ _ _ _ _
DNA (strand 2) _ _ A C _ _ _ _ _
mRNA (from strand2) U _ _ _ C A _ _ _
tRNA anticodons _ _ _ _ _ _ G C A
Answer :
DNA (strand 1) T G T G C A C G T
DNA (strand 2) A C A C G T G C A
mRNA (from strand2) U G U G C A C G U
tRNA anticodons A C A C G U G C A
114. Put the numbers of the enzymes on their place in the picture. Using arrows indicate the direction of replication and direction of synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
1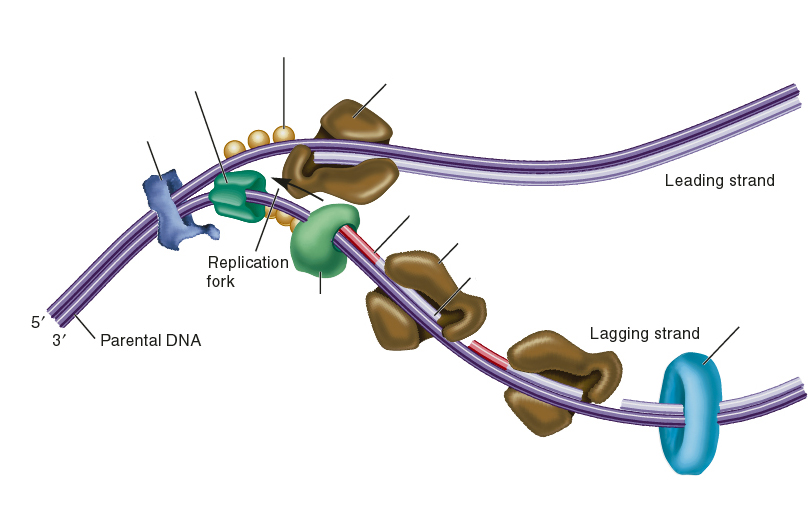 – DNA polymerase
– DNA polymerase
2 – DNA ligase
3 – SSB proteins
4 – topoisomerase
5 – Okazaki fragment
6 – RNA primer
7 - RNA primase
8 – helicase

Answer:
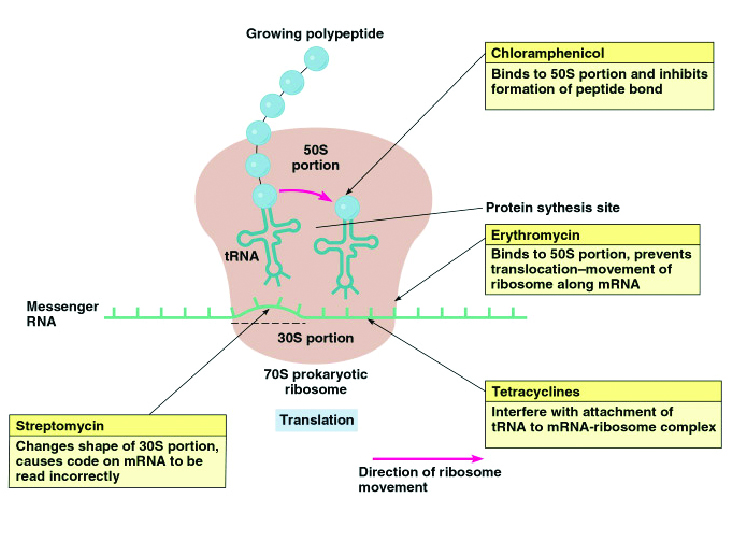
115. Many translation-inhibiting antibiotics work selectively on prokaryotic organisms because the process of translation is sufficiently different in them than it is in humans. That is why translation is a clinically important target of a variety of such drugs. Put antibiotics, inhibitors of translation chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline, streptomycin into the boxes that indicate their mechanism of action.
Answer:
116. Three possible ways in which DNA can replicate are illustrated. The two original strands of DNA are shown in dark; newly synthesized DNA is light. Choose from the above a semiconservative model of DNA replication, name the rest models.
1 2
3
Original double helix
First
round of replication
Second
round of replication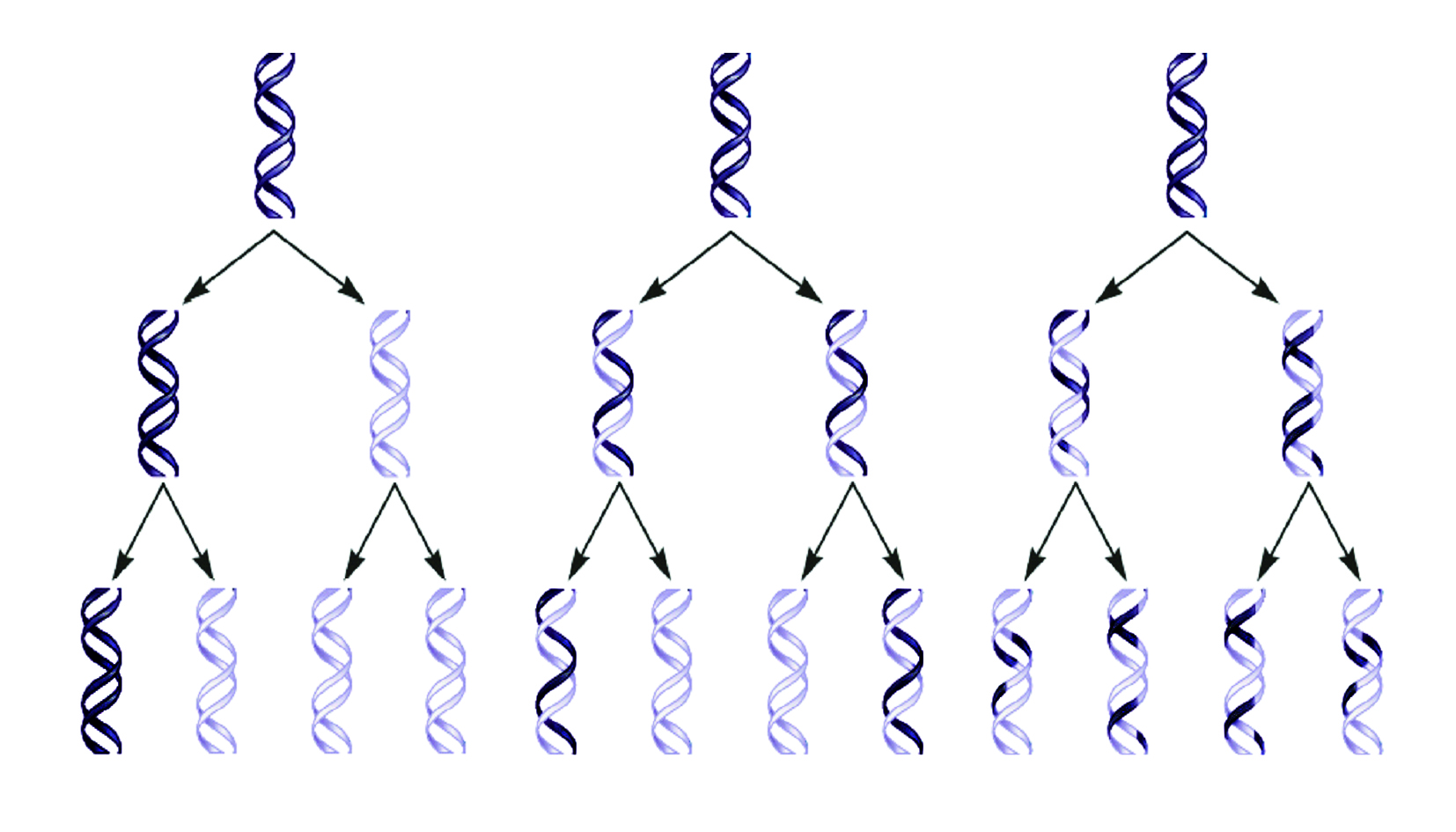
Answer: 1 – conservative, 2 – semiconservative, 3 – dispersive.
Section VIII Molecular mechanisms of hormone action on target cells. Biochemistry of hormonal regulation
l. Indicate a substance which serves as a secondary messenger and increase Ca2+ ion concentration.
Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate
Inositol-3,6-bisphosphate
Phosphatidyl-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate
Inositol-6-phosphate
Free inositol
2. A hormone secreted from anterior pituitary is:
Growth hormone
Vasopressin
Oxytocin
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
3. A hormone secreted from posterior pituitary is:
Vasopressin
Thyrotropic hormone
Prolactin
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Growth hormone
4. The number of amino acids in human growth hormone is
191
19
151
291
391
8. Acromegaly results due to excessive release of:
Growth hormone
Insulin
Glucagon
Thyroxine
Oxytocin
5. All of the following are known to be part of a signal transduction cascade EXCEPT:
Phosphorylation of fibronectin
Dissociation of the components of a heterotrimeric G-protein
Enzymatic breakdown of phosphatidyl inositol bisphosphate (PIP2 )
Elevation of intracellular [Ca2+]
Activation of cGMP phosphodiesterase
6. Ca2+ ions constitute one of the most ancient evolutionary second messengers. They are activators of glycogenolisis in case of reacting with:
Calmodulin
Calcitonin
Calciferol
Kinase of myosin light chains
Phosphorylase C
7. Secondary messengers diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate are produced from subsequent phospholipid of plasma membrane due to the activity of the following enzyme:
Phospholipase C
Phospholipase A1
Phospholipase A2
Phospholipase D
Phosphodiesterase
8. All of the following are known to be part of a signal transduction cascade EXCEPT:
Phosphorylation of fibronectin
Dissociation of the components of a heterotrimeric G-protein
Enzymatic breakdown of phosphatidyl inositol bisphosphate (PIP2 )
Elevation of intracellular [Ca2+]
Activation of cGMP phosphodiesterase
9. The receptors of which of the following hormones are not associated with G-protein?
A. Aldosterone
B. TSH
С. Epinephrine
D. Vasopressin
E. Glucagon
10. Adrenalin is water soluble hormone, its effect is mediated by secondary messengers, which are:
A. cAMP
B. NAD
C. ATP
D. Acetylcholine
E. Cytochrome c
11. There are intracellular receptors for which of the following hormones?
A. Thyroxine
B. Folllicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
C. Oxytocin
D. Insulin
E. ACTH
12. cAMP activates which of the following enzymes?
A. Protein kinase A
B. Tyrosine kinase
C. Phospholipase С
D. Phosphodiesterase
E. Adenylyl cyclase
13. Which of the following is not a steroid hormone?
ACTH
Aldosterone
Cortisol
Testosterone
Estrogen
14. A patient appealed to the doctor with complaints about tremor and hypokinesia. The biochemical analysis of blood showed the reduced amount of dopamine. Name its methabolite-precursor.
A. Tyrosine
B. Dioxyphenylalanine
C. Tyramine
D. Phenylalanine
E. Phenylpyruvate
15. Thyroxine labeled with 131I is administered to a patient for the purpose of imaging the thyroid gland. The radioactive half-life of the isotope is 8 days. The biological half-life (the time required for half of the compound to be eliminated from the body) is 2 days. The time at which 3/4 of the original radioactivity will no longer be detectable in the body is closest to
3.2 days
2.0 days
4.0 days
4.8 days
16.0 days
16. Endemic goiter is known to be widespread in certain geochemical areas. The deficiency of what chemical element causes this disease?
Iodine
Iron
Zinc
Copper
Cobalt
17. ACTH induces rise in:
Cyclic AMP
Cyclic GMP
Calcium
Magnesium
18. Tetraiodothyronine is produced in the next gland:
Follicles of thyroid gland
Cortex of adrenals
Medulla of adrenals
Parathyroid glands
Langerhans islands
19. Chose a substance from listed below which inhibits production of thyroxine:
A. 5-fluorouracil
B. Dihydrouracil
C. 5-hydroxyuracil
D. Thiouracil
E. TSH-releasing hormone
20. Calcitonin is hormone of polypeptide nature, which is produced in:
A. Thyroid gland
B. Incretory pancreas
C Parathyroid gland
D .Cortical part of adrenals
E. Hypothalamus
21. Physiological effect of calcitonin is:
A. Lowering of calcium level in blood
B. Decrease of blood glucose level
C. Stimulation of lipogenesis
D. Regulation of water balance
E. Stimulation of smooth muscle contraction
22. During operation on a thyroid gland parathyroid glands were removed by mistake. The patient got titanic cramps. The metabolism of which chemical element was disturbed?
Calcium
Magnesium
Potssium
Iron
Sodium
23. Physiological effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) is as follows:
A. Increase of calcium level in blood
B. Stimulation of protein synthesis
C. Lowering of blood glucose level
D. Decrease of calcium level in blood
E. Lipid mobilization
24. The number of amino acids in the hormoneoxytocin is:
9
7
14
18
20
25. Parathyroid hormone (PTH):
A. Is a polypeptide
B. Is a derivative of amino acid tryptophan
C. Is substance of steroid structure
D. Is derivative of N-acetyl-galactosamine
E. Exhibits properties of polysaccharide
26. Utilization of glucose occurs by means of sugar transport from the extracellular matrix through the plasma membrane membrane into the cell. What hormone stimulates this process?
Insulin
Glucagon
Thyroxine
Aldosterone
Adrenaline
27. In patient S. blood glucose level is 10 mmoles/l, polyuria, glucosuria and ketonuria are observed. What pathological state can be suggested?
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Starvation
C. Hypercorticism
D. Addison disease
E. Hyperthyreosis
28. Glucagon is produced in the next endocrine gland:
A. Langerhans islands, α cells
B. Parathyroid gland
C. Pitiutary gland
D. Thymus
E. Medullar part of adrenals
29. Adrenalin is a hormone, which is produced in:
A. Medullar part of adrenals
B. Langerhans islands, β cells
C. Cortical part of adrenals
D. Hypophysis
E. Thymus
30. Destruction of pancreatic islets of Langerhans results in the decrease of production of:
Glucagon and insulin
Parathhormone and cortisone
Thyroxyne and calcitonin
Insulin and adrenaline
Callicrein and angiotensin
31. The next enzyme is involved in the production of leukotriens from arachidonic acid:
A. Cyclooxygenase
B. Monooxygenase
C. Dioxygenase
D. Lipoxygenase
E. Catalase
32. TSH stimulates the synthesis of:
Thyroxine
Adrenocorticoids
Epinephrine
Insulin
Glucagon
33. Cyclooxygenase catalyzes the synthesis of which of the following compounds?
A. Prostaglandines
B. Cyclic AMP
C. Leucotriens
D. Porphobilinogen
E. Cyclic GMP
34. The activity of cyclooxygenase can be suppressed by some medical preparations. What preparation exhibits irreversible inhibitory action upon this enzyme?
A. Acetylsalicylic acid
B. Insulin
C. Allopurinol
D. Oligomycine
E. Aminalone
35. Leucotriens are humoral factors, produced by leukocytes using as a precursor:
A. Arachidonic acid
B. Nicotinic acid
C. Pantothenic acid
D. Homogentisic acid
E. Ascorbic acid
36. Thyroid hormones are synthesized by the iodination of the amino acid:
Glycine
Phenylalanine
Alanine
Tyrosine
Valine
37. Glucagon:
Stimulates muscle glycogenolysis
Increases protein synthesis
Inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes
Increases gluconeogenesis in liver
38. What hormone stimulates the reabsorption of water in kidney tubules?
A. Vasopressin
B. Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
C. Calcitonin
D. Aldosterone
E. Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
39. The primary action of steroid hormones is at the level of:
Transcription
RNA export from the nucleus
Pre-mRNA splicing
mRNA degradation
Gene rearrangement
40. The principal site of peptide neurohormone biosynthesis is the:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleus
Dendrite
Postsynaptic density
Synaptic vesicle
41. A hormone response element is best defined by which one of the following statements?
It is the DNA sequence to which a specific hormone-receptor complex binds
It is transmembrane protein to which steroid hormones bind
It is a DNA sequence to which steroid hormones bind
It is the region of a steroid hormone receptor to which the hormone binds
It is plasma protein that carries a specific lipophilic hormone through the bloodstream
42. What endocrine gland produces hormones regulating mineral elements turnover?
Posterior pituitary
Suprarenal glands
Pancreatic gland
Ovary
Anterior pituitary
43. Aldosteron regulates the next physiological process:
Reabsorption of sodium ions in exchange to potassium ions in renal tubules
Stimulation of gluconeogenesis
Stimulation of sodium excretion with urine
Stimulation of lipolysis and oxidation of fatty acids
Reabsorption of glucose in convoluted tubules
44. The next substance is a precursor of progesterone:
Cholesterol
Cholic acid
Cholecalciferol
Phenylalanine
Glutathion
45. G-proteins act as:
Hormone carriers
Hormone receptors
Second messengers
Signal transducers
46. During the operation on a thyroid gland parathyroid glands were removed by mistake. The patient got tetanic cramps. The metabolism of which chemical element was disturbed?
A. Calcium
B. Magnesium.
C. Potassium.
D. Iron.
E. Sodium
47. In the human organism the some amino acid are transformed into hormones. In what compound tryptophan transforms in?
A. Serotonin
B. Histamine
C. GABA
D. Corticosteron
E. -alanine
48. After a brain hemorrhage that led to the damage of hypotalamic nuclei, diabetes insipidus of a 67-year-old patient developed. What became the reason of polyuria in this case?
A. Decrease of water reabsorbtion
B. Decrease of potassium ions reabsorbtion.
C. Acceleration of glomerular filtration.
D. Hyperglycemia.
E. Hypoglycemia.
49. Graves disease is caused by dysfunction of the following endocrine gland:
Hyperthyreosis
Adrenocortex hyperfunction
Adrenocortex hypofunction
Hypothyreosis
Hyperproduction of ACTH
50. Cushing’s disease, which is characterized by obesity, hypertension and elevated blood glucose level, is caused by disorder in production and secretion of the next hormones:
ACTH and glucocorticoids overproduction
Insulin insufficiency
ACTH and glucocorticoids insufficiency
Thyroxine insufficiency
Estriol overproduction
51. Melanocyte stimulating hormone is secreted by:
A. Intermediate lobe of pituitary gland
B. Anterior lobe of pituitary gland
C. Posterior lobe of pituitary gland
D. Pineal gland
E. Thyroid gland
52. Addison’s disease is a severe disorder of sodium-potassium turnover due to failure in production of the following hormone:
Aldosterone
Thyroxine
Triiodothyronine
Testosterone
Progesterone
53. Cretinism is caused by the next inborn endocrine disorder:
Inborn and persistent hypofunction of thyroid gland
Hyperproduction of ACTH by tumor of adenohypophysis
Inborn hypofunction of adrenal cortex
Inborn hypersecretion of glucocorticoids
Underdevelopment of thymus
54. Myxoedema is manifested in adults due to the next endocrine disorder:
Severe hypoparathyroidism
Severe hypothyroidism
Insufficiency of ACTH secretion
Underproduction of corticosteroids
Hyperproduction of corticosteroids
55. Some hormone induce uncoupling of respiration and oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria and lower the efficiency of ATP production. What is this hormone?
Thyroxine
Adrenalin
ACTH
Oxytocine
Testosterone
56. Note from listed below hormones a pricipal representative of mineralocorticoids.
Aldosterone
Corticosterone
Hydrocortisone
Dihydrocorticosterone
Estradiol
57. The next compounds are the end products of steroid hormones catabolism, excreted with urine.
17-ketosteroids, conjugated with sulfuric acid
Progesterone conjugated with sulfuric acid.
Deoxycorticosterone acetate
Hydroxymandelic acid
Taurodeoxycholic acid
58. Chose from listed hormones a one with the most potent anti-inflammatory activity:
Cortisol
Aldosterone
Testosterone propionate
Megesterol
Progesterone
59. The next substance is a precursor of progesterone:
A. Cholesterol
B.Cholecalciferol
C. Cholic acid
D.Phenylalanine
E.Glutathion
60. In human body some amino acids are transformed into hormones. What compound is produced from tryptophan?
A. Serotonin
B. Histamine
C. GABA
D. Corticosteron
E. -alanine
61. How does glucocorticoids influence on the carbohydrate methabolism in a liver?
A. Stimulate gluconeogenesis
B. Stimulate glycogenesis from glucose
C. Stimulate glycogen hydrolysis
D. Stimulate glycogen phosphorolysis
E. Stimulate activity of glycogenphosphorylase
62. Cyclic AMP is formed from ATP by the enzyme adenylate cyclase which is activated by the hormone:
Insulin
Epinephrine
Testosterone
Progesterone
Aldosterone
