
- •Section I Control of the initial level of knowledge. Biochemical constituents of the cell. Methods of biochemical investigations.
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •77. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •78. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •Section іі Enzymes, structure and classification. Regulation of metabolism
- •Е. Whatever part of polypeptide chain of enzyme molecule.
- •Substrate concentration at which reaction rate is half maximal
- •The second enzyme has higher affinity to substrate
- •Competitive
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Cysteine
- •B. Amylase
- •Peptidases
- •Enteropeptidase
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section ііi Metabolic pathways and bioenergetics. Tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation and oxidative phopshorylation
- •1. When atp forms amp:
- •B. Protons
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of carbohydrates
- •19. Chose the reaction of glycolysis catalyzed by an enzyme phosphofructokinase:
- •A. Liver
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Acetoacetate, β-hydroxybulyrate, and acetone
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of lipids
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •143. A patient with high rate of obesity was advised to use carnitine as a food additive in order to enhance "fat burning". What is the role of carnitine in the process of fat oxidation?
- •144. Lipids are obvious energetic material for the body. What is the main pathway of fatty acids metabolism in mitochondria?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks Situational tasks
- •179. The patient is observed an allocation of undigested fat in the faeces. What are the possible causes for this?
- •184. Free cholesterol can affect cholesterol metabolism in the body by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis. By which step free cholesterol can inhibit its biosynthesis?
- •186. Explain the mechanism of phospholipids breakdown, shown at the scheme below:
- •Section VI Structure and metabolism of amino acids
- •B. Amylase
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •112. According to clinical indications a patient was administered pyridoxal phosphate. What processes is this medication intended to correct?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •145. In a patient 10 g of urine per day is excreted. Evaluate this result.
- •151. Skin color is the aggregate result of the expression of a number of genes modified by ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. What can cause the hypopigmentation?
- •Section VII Principles of molecular biology and molecular genetics
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •108. List and describe properties of the genetic code.
- •113. Fill in the blanks.
- •114. Put the numbers of the enzymes on their place in the picture. Using arrows indicate the direction of replication and direction of synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
- •Section VIII Molecular mechanisms of hormone action on target cells. Biochemistry of hormonal regulation
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •78. For analgesia, a certain substance which imitates the physiological properties of morphine but is synthesized inside the human brain can be used. Name this substance.
- •80. A patient suffering from rheumatism was administered glucocorticoid therapy. What changes in carbohydrate metabolism in liver can be expected?
- •88. In blood of a patient a hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, in urine – hyperphosphaturia is observed. What is a possible cause of this state?
- •90. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. It is caused by deficiency of:
- •93. Signaling via prostanoids begins by interaction of the prostanoid with its receptor. The receptor involved is usually located in which part of the cell?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •97. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. Which hormone deficiency can cause this disease?
- •99. The thyroid hormones t3 and t4 are synthesized in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. From which of the following essential amino acids are the thyroid hormones synthesized?
- •101. Name types of signalling:
- •Section IX Biochemistry of the nervous tissue
- •С. Ketone bodies
- •24. What compound may be used by the cns cells after extensive physical exercises and prolonged starvation?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •114. Describe the structure of a synapse and explain how it operates?
- •Section X Biochemistry of the Muscular tissue
- •D. Glycogenolysis in muscles
- •С. Fatigue faster compared to the red fibers
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XI Biochemistry of nutrition
- •1. Note substance, which activates pepsinogen to pepsin:
- •2. Chose the enzyme which plays an important role in production of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells of gastric mucosa glands:
- •3. Which of the following is not a function of the pancreas?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •62. The clinical and laboratory examination of the patient evaluated the presence of the lactic acid in his gastric juice. What does it indicate? What should be recommended to the patient?
- •69. Discribe the mechanism of hydrochloric acid production shown at the picture:
- •Section XII Functional role of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins in metabolism and providement of cell functions
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •100. A deficiency in thiamine (vitamin b1) would most likely lead to which clinical manifestations?
- •Section XIII Biochemistry and pathobiochemistry of blood
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •89. The blood clotting cascade in humans is represented in the picture below. Using this scheme answer the following questions:
- •Section XIV Functional and clinical biochemistry of liver tissue. Biotransformation of xenobiotics and endogenous toxic compounds
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XV Water and mineral metabolism
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVI Functional role of kidneys in urinogenesis. Normal and pathological constituents of urine
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVII Biochemical constituents of connective tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 Tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •34. Patient with burn disease is at the risk of formation of blood clots in blood vessels. What glycosaminoglycan may be used to prevent formation of blood clots?
- •Section XVIII Biochemistry of saliva and tooth tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XIX. Biochemical reactions
- •References:
151. Skin color is the aggregate result of the expression of a number of genes modified by ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. What can cause the hypopigmentation?
Answer: Excess phenylalanine inhibits tyrosinase the first step toward melanin production, thus resulting in hypopigmentation. Excess melanin leads to hyperpigmentation. Melatonin is a hormone involved in the sleep cycle. Excessive stimulation of tyrosinase would lead to more melanin and therefore hyperpigmentation. Para-hydroxyphenylpyruvate means less transamination and perhaps more tyrosine converted to melanin and hyperpigmentation.
152. Name types of deamination od amino acids:
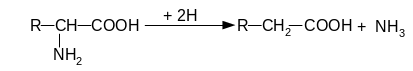
1
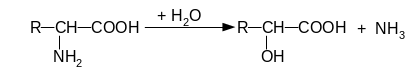
2
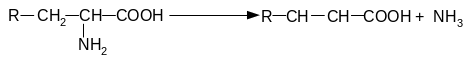
3
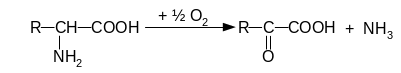
4
Answer: 1. - reductive deamination, 2 - hydrolytic deamination, 3 - reductive, 4 – oxidative.
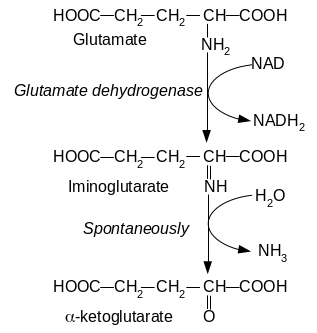
153. Complete the chemical equation of the reachtion:
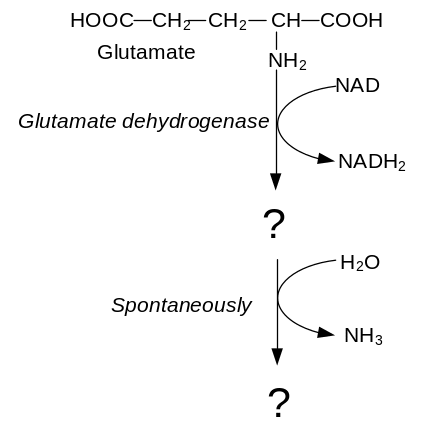
Answer:
1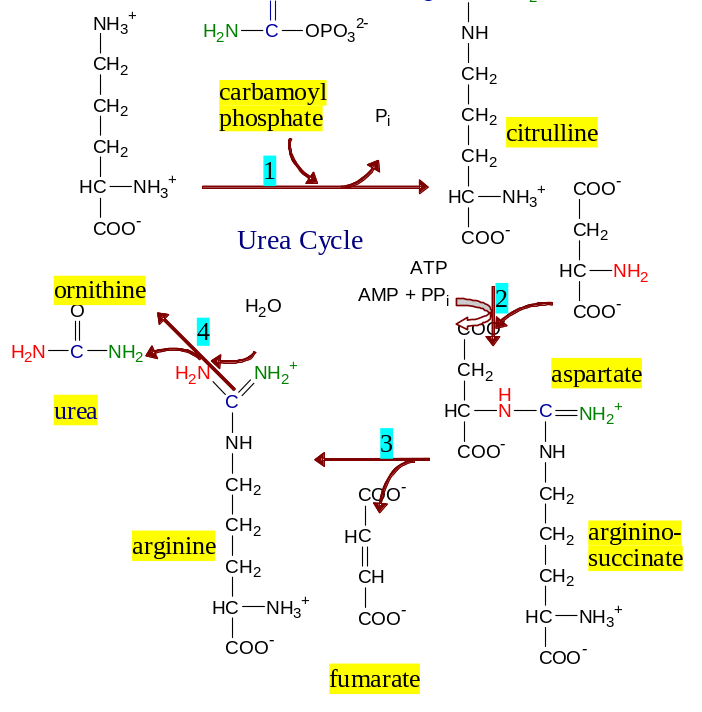 54.
Name enzymes of urea cycle :
54.
Name enzymes of urea cycle :
Answer: 1. Ornithine transcarbamylase, 2. Argininosuccinate Synthase, 3. Argininosuccinase lyase, 4. Arginase.
155. Name the enzyme, which catalises this reaction:
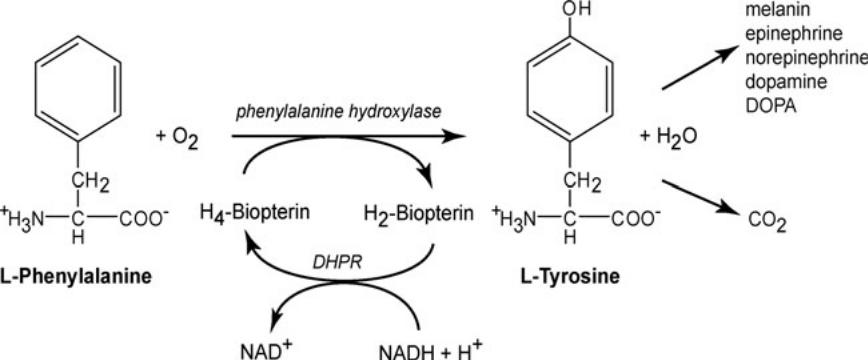

Answer: Phenylalanine hydroxylase
Section VII Principles of molecular biology and molecular genetics
1. Indicate nitrogenous base which is a specific component of ribonucleoproteins
Uracil
Adenine
Guanine
Thymine
Cytosine
2. What proteins are obvious constituents of nucleoproteins?
Histones and protamins
Albumin and globulins
Dynein and kinesin
Prolamin and glutelin
Cytochromes b5 and c
3. How is called elementary monomer of polymer chain of nucleic acids?
Mononucleotide
Nucleoside
Amino acid
Nitrogenous base
Ribosyl-3-phosphate
4. Note the complementary to cytosine nitrogenous base in DNA double helix according to Watson and Crick model
Guanine
Adenine
Uracil
Thymine
Xanthine
5. One step of DNA double helix in B-form contains the next number of base pairs:
A. 10
B. 15
C. 13
D. 7
E. 20
6. How many hydrogen bonds support a complementary base pair A-T?
A. 2
B. 1
C. 3
D. 5
E. 7
7. What type of chemical bonds joins together mononucleotides in RNA chain?
Phosphodiester bonds
Hydrogen
Ionic
Coordinative
Hydrophobic interactions
8. The base sequence of a segment of DNA is pCpApGpTpTpApGpC. Indicate a complementary sequence.
pGpTpCpApApTpCpG
pGpCpTpApApCpTpG
pCpGpApTpTpGpApC
pTpApGpCpCpApGpT
pCpApGpTpTpApGpC
9. If the cytosine content of double-helical DNA is 20 mole% of the total bases, the adenine content would be:
30 mole%
10 mole%
20 mole%
40 mole%
50 mole%
10. Which scientists first gave experimental evidence that DNA is the genetic material?
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty who repeated the transformation experiments of Griffith, and chemically characterized the transforming principle.
Garrod, who postulated that Alcaptonuria, or black urine disease, was due to a defective enzyme.
Beadle and Tatum, who used a mutational and biochemical analysis of the bread mold Neurospora to establish a direct link between genes and enzymes.
Meselson and Stahl who showed that DNA is replicated semiconservatively.
Watson and Crick who gave a model for the structure of DNA
11. The core of nucleosome is composed from the next types of histones:
H2a,H2b,H3,H4
H1,H2a, H2b, H3
H1,H3,H4
H2a,H2b,H2c,H2d
H1,H2,H3,H4
12. A sample of some substance was submitted to hydrolysis; in hydrolysate were detected organic bases of purine and pyrimidine classes, ribose and phosphates, amino acids. What substance was most probably taken for investigation?
A. Ribonucleoprotein
B. Chromoproterin
C. Phosphoproterin
D. Deoxyrybonucleoprotein
E. Glycoprotein
13. To which of the following does thymine form hydrogen bonds in DNA?
adenine
thymine
Cytosine
guanine
Uracil
14. Which of these organelles contains DNA?
Mitochondria
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
15. In a double stranded molecule of DNA, the ratio of purines: pyrimidines is:
Always 1:1
Variable
Determined by the base sequence in RNA
Genetically determined
Determined by the number of purines in the sense strand of the DNА
16. In which of the following molecules would you find an anticodon?
transfer RNA
messenger RNA
ribosomal RNA
small nuclear RNA
Heterogenous RNA
17. How many hydrogen bonds support a complementary base pair G-C?
3
7
5
1
2
18. Nucleic acids absorb ultraviolet light in 250-270 nm regions. This property is determined by the next chemical structures:
Nitrogenous bases
Hydrogen bonds
Ribose
Phosphoric acid
Phosphodiester bonds
19. Which of the following nucleotide bases is not found in iRNA?
Thymine
Adenine
Uracil
Guanine
Cytosine
20. Which of the following molecules does not form part of DNA?
Amino acid
Purine
Pyrimidine
Deoxyribose
Phosphate
21. Which of the following statements is true of double-helical DNA?
The 3’ hydroxyl groups of each chain are at opposite ends of the molecule
The planes of the bases lie parallel to the helix axis
The chains have a backbone of linked glycosides
The step of B-helix contain 12 base pairs
The duplex structure is stabilized by hydrophobic interactions between bases
22. With what mRNA codon would the tRNA in the diagram be able to form a codon-anticodon base pairing interaction?
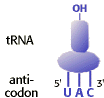
A. 3'-AUG-5'
B. 3'-GUA-5'
C. 3'-CAU-5'
D. 3'-UAC-5'
E. 3'-UAG-5'
23. Radiolabelled H3-thymidine was introduced to cell culture medium. In which cell organelles will be detected H3-label thereafter?
Nucleus
Ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum
24. Which of the following statements concerning characteristics of histones is true?
They are acidic proteins located in the nucleus
They are covalently linked to single-stranded DNA
Evolutionary they are highly conserved proteins
They are large proteins with mol weight more then 100 KDa
They have no post-translationally modified amino acids
25. Nitrosamines belong to deaminating mutagens. From what nitrogene base does uracyl appears as a result of their action?
Cytosine
Adenine
Guanine
Thymine
Methyluracil
26. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning the differences between DNA and RNA?
RNA lacks the base thymine (which is found in DNA) and has uracil instead
RNA is usually double-stranded, but DNA is usually single-stranded.
RNA has the sugar deoxyribose, but DNA has the sugar ribose.
RNA contains three different nucleotides, but DNA contains four different nucleotides.
27. Orotic acid is an intermediate in biosynthesis of the following nitrogenous base:
Cytosine
Hypoxanthine
Adenine
Guanine
Xanthine
28. The activity of xanthine oxidase is dependent from the next coenzyme:
FAD
NAD
FMN
CoA-SH
NADP
29. Which of the following contribute N to both purine and pyrimidine:
Aspartic acid.
Glutamic acid.
Glycine.
Arginine.
Ammonia.
30. Formation of thymidine nucleotides, which are used for the biosynthesis of DNA, begins from dUDP, which on the first stage is hydrolised to dUMP, and thereafter methylated. What compound serves as the donor of methyl groups?
Methylenetetrahydrofolate
Choline
Lecithin
Methionine
Carnitine
31. In reaction of transformation of ribose to deoxyribose in course of deoxyribonucleotide production for DNA biosynthesis participates a low molecular weight protein thioredoxine. It contains two SH groups, which in course of reaction are oxidized. What coenzyme is used in restoration of reduced form of thioredoxine?
A. NADP H2
B. Glutathion
C. Coenzyme Q
D. NAD H2
E.AMP
32. Biosynthesis of what mononucleotide is arrested under the influence of 5-fluorouracil?
A.dTMP
B.dUMP
C.dCMP
D.dIMP
E.dAMP
33. The smallest unit of DNA capable of coding for the synthesis of a polypeptide is:
Cistron
Operon
Repressor gene
Replicon
Terminator
34. mRNA is complementary to the nucleotide sequence of:
Coding strand
Ribosomal RNA
tRNA
Template strand
snRNA
35. All pribnow boxes are variants of the sequence:
5′–TATAAT –3′
5′–GAGCCA –3′
5′–UAACAA –3′
5′–TCCTAG –3′
5′–UCCUAG –3′
36. From nitrates, nitrites and nitrosamines in the body is produced nitrose acid, which cause oxidative deamination of nitrogeneous bases of nucleotides. This may lead to a point mutation by change of cytosine to one of the next base:
A. Uracil
B. Thymine
C. Adenine
D. Guanine
E. Inosine
37. 5’-Terminus of mRNA molecule is capped with;
7-Methylguanosine triphophate
Guanosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate
Adenosine monophosphate
38. Which of the following statements best describe the action of introns?
A. They are excised upon processing of heterogeneous nuclear RNA to messenger RNA
B. They are retained upon processing of ribosomal RNA
C. They are spacer sequences
D. They are added to mRNA during the plicing reaction.
39. Okazaki fragments are formed during the synthesis of:
DNA
mRNA
tRNA
rRNA
Proteine
40. Reverse transcriptase is capable of synthesis:
RNA → DNA
DNA → RNA
RNA → RNA
DNA → DNA
Protein → DNA
41. Synthesis of DNA is also known as:
Replication
Duplication
Transcription
Translation
42. In the treatment of infection diseases are used antibiotics streptomycine, neomycine, kanamycine. What step of protein synthesis in bacterial cell they inhibit?
Translation
Replication
Transcription
mRNA processing
Splicing
43. What enzyme is used for synthesis of genes from template RNA or DNA in gene engineering? (This enzyme was discovered in some RNA containing viruses).
A. Revertase
B. Exonuclease
C. Endonuclease
D. Topoisomerase I
E. Helicase
44. Genetic information is stored in DNA, which does not participate directly in protein synthesis in the cell. What process provides the transformation of genetic information into amino acid sequence of polypeptide chain?
Translation
Transcription
Translocation
Replication
Splicing
45. In post-translation modification of nascent protein chain are involved the next proteins:
Chaperons 60 K
Cathepsins
Caspases
Cytochrome c
Ubiquitin
46. What amino acid is coded by the triplet of bases AUG?
Methionine
serine
tyrosine
cysteine
Valine
47. Which of the following toxins inhibits eukaryotic protein synthesis through the depurination of a single adenine residue in 28 s ribosomal RNA?
Diphtheria toxin
Ricin
Sarcin
Puromycin
Cycloheximide
48. The genetic code refers to which one of the following?
The nucleotide sequences that correspond to common amino acids
The number of chromosomes in the diploid cells of the species
The amino acid sequence of cellular proteins
The ratios of Mendelian inheritance
The hierarchy of DNA, RNA and protein
49. The translation of mRNA into the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide in prokaryotes is terminated at the end of the message by one of the three stop codons in the mRNA chain. The stop codon is recognized by:
A specific protein
A specific uncharged tRNA
A specific aminoacyl-tRNA
A specific ribosomal RNA
A specific ribosomal subunit
50. The inherited information is saved in DNA, though directly in the synthesis of protein in a cell it does not participate. What process provides the realization of the inherited information in a polypeptide chain?
Translation
Transcription
Translocation
Replication
Transformation
51. Glycosylation of proteins after completion of their synthesis in ribosomes proceeds in the next cell compartment:
Golgi vesicles
Mitochondria
Lysosomes
Proteasomes
Ribosomes
52. Redundancy of the genetic code means that:
A given base triplet can code for more then one amino acid
There is no punctuation in the code sequences
The third base in codon is not important in coding
A given amino acid can be coded for by more then one base triplet
Codons are not ambiguous
53. Restrictases are enzymes of bacterial origin, which are used in recombinant DNA technology. They belong to the next class of enzymes:
Hydrolases
Oxido-reductases
Transferases,
Liases
Isomerases
54. The next technique is used for multiple amplification of distinct and selected segment of DNA:
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
DNA fingerprint analysis
Southern blot analysis
Northern blot analysis
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis
55. For the formation of the transport form of amino acid during the protein synthesis in ribosomes. is required.
A. tRNA.
B. Revertase.
C. GTP.
D. mRNA.
E. Ribosome
56. In case of poisoning by amanitine, a death-cup mushroom toxin, RNA-polymerase B (II) is blocked. This leads to the blockage of:
A. Processing of mRNA.
B. Synthesis of tRNA.
C. Reverse transcription.
D.Synthesis of primers.
E. Synthesis of mRNA.
57. Degeneration of the genetic code is the ability of more than one triplet to encode a single amino acid. Which amino acid is encoded by only one triplet?
A. Methionine.
B. Serine.
C. Alanine.
D. Leucine.
E. Lysine.
58. A human genome contains about 30000 genes, and the amount of variants of antibodies reaches millions. What mechanism is used for the formation of new genes that are responsible for the synthesis of such amount of antibodies?
A. Recombination of genes.
B. Amplification of genes.
C. Replication of DNA.
D. Reparation of DNA.
E. Formation of Okazaki fragments.
59. Choose from the following a potent inhibitor of transcription:
A. Actinomycin D
B. Steptomycin
C. Kanamycin
D. Doxorubicin
E. Actinorodin
60. Indicate a specific feature of transcription in prokaryotes:
All of the above
mRNA transcript is used directly for translation without modification.
Since prokaryotes lack a nucleus, mRNA also is translated on ribosomes before it is transcribed completely (i.e., transcription and translation are coupled).
Prokaryote mRNAs are polycistronic, they contain amino acid coding information for more than one gene.
61. What is not typical for transcription of eukaryotes?
mRNA transcript is used directly for translation without modification
mRNA transcript is not mature (pre-mRNA); must be processed.
Transcription and translation are not coupled (mRNA must first be exported to the cytoplasm before translation occurs).
Eukaryote mRNAs are monocistronic, they contain amino acid sequences for just one gene.
62. Indicate function of snRNA (small nuclear RNA):
It forms complexes with proteins used in eukaryotic RNA processing (e.g., exon splicing and intron removal).
It forms complexes called ribosomes with protein, the structure on which mRNA is translated.
It binds to 3’ UTR target mRNAs and result in silencing.
It encodes the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide.
63. The genetic code is brought by the?
mRNA
DNA
snRNA
siRNA
rRNA
64. Active translation always occurs on:
Polysomes
Lysosomes
Liposomes
Inner membrane of mitochondria
65. Escherichia coli 70S ribosome model consists from:
50S subunit and 30S subunit
50S subunit and 20S subunit
50S subunit and 40S subunit
40S subunit and 30S subunit
66. The lac operon is an example of:
Transcriptional control
Post-transcriptional control
Replicational control
Transcriptional control
67. In the lac operon, RNA polymerase:
Binds to the promoter
Binds to the operator
Binds to the regulatory gene
Is synthesized by the regulatory gene
Binds to the regulator protein
68. The promoter region of a bacterial operon:
Is a binding site for RNA polymerase
Codes for repressor proteins
Codes for inducer substances
Codes for corepressor substances
Is binding site for inducers
69. The regulatory gene of bacterial operon:
codes for repressor proteins
codes for repressor proteins
acts as an on-off swith for the structural genes
is a binding site for RNA polymerase
is a binding site for inducers
70. The sugar lactose induces synthesis of the enzyme lactase. What happens when E. coli cells run out of lactose?
Repressor protein binds to the operator.
Repressor protein binds to the promoter.
RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter.
RNA polymerase attaches to the repressor.
72. In the lactose operon system in E. coli, the repressor is:
A protein
A product of a structural gene
Bound to the promoter sequence
Lactose
A short length of DNA
73. Which of the following statements concerning the regulatory gene associated with the lac operon is correct?
mRNA is transcribed from the R gene whether lactose is present or not.
mRNA is only transcribed from the R gene when lactose is present.
mRNA is only transcribed from the R gene when lactose is not present.
Lactose inhibits the translation of R gene mRNA.
Lactose binds to the promoter of the lac operon.
74. According to the Jacob-Monod model of gene regulation, inducer substances in bacterial cells probably:
Combine with repressor proteins, inactivating them.
Combine with operator regions.
Combine with structural genes, stimulating them to synthesize messenger RNA.
Combine with promoter regions, activating RNA polymerase.
Combine with nucleoli, triggering production of more ribosomes.
75. In the tryptophan operon of E. coli the end product of biochemical pathway, tryptophan, binds to the repressor protein which then binds to the:
Operator to inhibit transcription
Promoter to accelerate transcription
Promoter to inhibit transcription
Operator to accelerate transcription
Repressor gene to accelerate transcription
76. Nucleosomes:
both D and E are correct
are composed of DNA and histones
are small particles found in only the nuclei of plant cells
disappear during transcription
play a role in coiling and uncoiling the chromosomes
77. An antibody molecule is made up of four polypeptide chains joined together by disulfide bonds. Which one of the following statements concerning these polypeptide chains is correct?
A. All four chains have variable regions
B. Only the two light chains have variable regions
C. Only the two heavy chains have constant regions
D. Only the two heavy chains have variable regions
E. All of four chains are of equal length
78. Which one of the following statements concerning antibodies is correct?
A. Antigens are bound by the variable regions of the antibody molecules.
B. Antibodies are usually proteins but sometimes they are polysaccharides.
C. Each antibody has two chains.
D. The heavy but not the light, chains of the antibody molecule have variable and constant regions.
E. The tail region is important in antigen specificity.
79. Fragments of DNA containing one or several genes and a control element that can move from one part of the genome to another are called:
A. Transposons
B. Exons.
C. Introns.
D. Plasmids.
E. Promoters
80. Genes and\or exons can be duplicated by all of the following exept:
A. mRNA processing in the nucleus.
B. Reverse transcription.
C. Transposition.
D. Unequal crossing over during meiosis.
E. Breakage and fusion during meiosis.
81. Which statement about antibodies is false?
A. Human blood contains high levels of circulating antibodies against all positive antigens.
B. Two sites on each antibody molecule can bind antigen.
C. Antibodies are globulin proteins.
D. Antibodies are found in vertebrate animals.
E. Each antibody combines with a specific antigen.
82. The enormous variety of antibodies produced by an individual is due to:
A. Excision of genetic material during fatal development and exon removal during mRNA processing.
B. Specific rearrangement of genes in developing lymphocytes induced by antigens in the nucleus.
C. Synthesis of antibodies upon exposure to an antigen using the antigen as a template for antibody formation.
D. Induction of cell division by cross-linking of the antibody molecules.
E. Mutations within the genome.
83. Restriction endonucleases are useful in recombinant DNA technique because they:
A. Cut DNA at specific sites.
B. Restrict the number of nucleotides that can be removed at one time.
C. Restore the bonds in the DNA backbone.
D. Synthesize cDNA from RNA.
E. Can be used to locate genes for mapping.
84. Which one of the following statements is false?
A. Molecules of mRNA are synthesized on the ribosomes from nucleotides brought by tRNA.
B. In base substitution mutations only a single nucleotide of a gene is altered.
C. The nucleolus is a specialized region of a chromosome where tRNA is synthesized.
D. Some amino acids are specified by several “synonymous” codons.
