
- •Section I Control of the initial level of knowledge. Biochemical constituents of the cell. Methods of biochemical investigations.
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •77. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •78. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •Section іі Enzymes, structure and classification. Regulation of metabolism
- •Е. Whatever part of polypeptide chain of enzyme molecule.
- •Substrate concentration at which reaction rate is half maximal
- •The second enzyme has higher affinity to substrate
- •Competitive
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Cysteine
- •B. Amylase
- •Peptidases
- •Enteropeptidase
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section ііi Metabolic pathways and bioenergetics. Tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation and oxidative phopshorylation
- •1. When atp forms amp:
- •B. Protons
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of carbohydrates
- •19. Chose the reaction of glycolysis catalyzed by an enzyme phosphofructokinase:
- •A. Liver
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Acetoacetate, β-hydroxybulyrate, and acetone
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of lipids
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •143. A patient with high rate of obesity was advised to use carnitine as a food additive in order to enhance "fat burning". What is the role of carnitine in the process of fat oxidation?
- •144. Lipids are obvious energetic material for the body. What is the main pathway of fatty acids metabolism in mitochondria?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks Situational tasks
- •179. The patient is observed an allocation of undigested fat in the faeces. What are the possible causes for this?
- •184. Free cholesterol can affect cholesterol metabolism in the body by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis. By which step free cholesterol can inhibit its biosynthesis?
- •186. Explain the mechanism of phospholipids breakdown, shown at the scheme below:
- •Section VI Structure and metabolism of amino acids
- •B. Amylase
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •112. According to clinical indications a patient was administered pyridoxal phosphate. What processes is this medication intended to correct?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •145. In a patient 10 g of urine per day is excreted. Evaluate this result.
- •151. Skin color is the aggregate result of the expression of a number of genes modified by ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. What can cause the hypopigmentation?
- •Section VII Principles of molecular biology and molecular genetics
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •108. List and describe properties of the genetic code.
- •113. Fill in the blanks.
- •114. Put the numbers of the enzymes on their place in the picture. Using arrows indicate the direction of replication and direction of synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
- •Section VIII Molecular mechanisms of hormone action on target cells. Biochemistry of hormonal regulation
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •78. For analgesia, a certain substance which imitates the physiological properties of morphine but is synthesized inside the human brain can be used. Name this substance.
- •80. A patient suffering from rheumatism was administered glucocorticoid therapy. What changes in carbohydrate metabolism in liver can be expected?
- •88. In blood of a patient a hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, in urine – hyperphosphaturia is observed. What is a possible cause of this state?
- •90. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. It is caused by deficiency of:
- •93. Signaling via prostanoids begins by interaction of the prostanoid with its receptor. The receptor involved is usually located in which part of the cell?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •97. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. Which hormone deficiency can cause this disease?
- •99. The thyroid hormones t3 and t4 are synthesized in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. From which of the following essential amino acids are the thyroid hormones synthesized?
- •101. Name types of signalling:
- •Section IX Biochemistry of the nervous tissue
- •С. Ketone bodies
- •24. What compound may be used by the cns cells after extensive physical exercises and prolonged starvation?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •114. Describe the structure of a synapse and explain how it operates?
- •Section X Biochemistry of the Muscular tissue
- •D. Glycogenolysis in muscles
- •С. Fatigue faster compared to the red fibers
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XI Biochemistry of nutrition
- •1. Note substance, which activates pepsinogen to pepsin:
- •2. Chose the enzyme which plays an important role in production of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells of gastric mucosa glands:
- •3. Which of the following is not a function of the pancreas?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •62. The clinical and laboratory examination of the patient evaluated the presence of the lactic acid in his gastric juice. What does it indicate? What should be recommended to the patient?
- •69. Discribe the mechanism of hydrochloric acid production shown at the picture:
- •Section XII Functional role of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins in metabolism and providement of cell functions
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •100. A deficiency in thiamine (vitamin b1) would most likely lead to which clinical manifestations?
- •Section XIII Biochemistry and pathobiochemistry of blood
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •89. The blood clotting cascade in humans is represented in the picture below. Using this scheme answer the following questions:
- •Section XIV Functional and clinical biochemistry of liver tissue. Biotransformation of xenobiotics and endogenous toxic compounds
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XV Water and mineral metabolism
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVI Functional role of kidneys in urinogenesis. Normal and pathological constituents of urine
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVII Biochemical constituents of connective tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 Tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •34. Patient with burn disease is at the risk of formation of blood clots in blood vessels. What glycosaminoglycan may be used to prevent formation of blood clots?
- •Section XVIII Biochemistry of saliva and tooth tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XIX. Biochemical reactions
- •References:
77. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
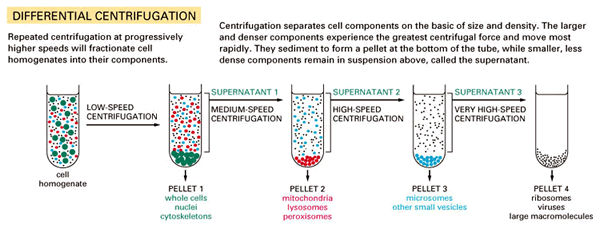
Answer: Differential centrifugation is used to separate certain organelles from whole cells for further analysis of specific parts of cells. In the process, a tissue sample is first homogenised to break the cell membranes and mix up the cell contents. The homogenate is then subjected to repeated centrifugations, each time removing the pellet and increasing the centrifugal force. Finally, purification may be done through equilibrium sedimentation, and the desired layer is extracted for further analysis.
Separation is based on size and density, with larger and denser particles pelleting at lower centrifugal forces. As an example, unbroken whole cells will pellet at low speeds and short intervals such as 1,000g for 5 minutes. Smaller cell fragments and organelles remain in the supernatant and require more force and greater times to pellet. In general, one can enrich for the following cell components, in the separating order in actual application:
Whole cells and nuclei;
Mitochondria, lysosomes and peroxisomes;
Microsomes (vesicles of disrupted endoplasmic reticulum); and
Ribosomes and cytosol.
78. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
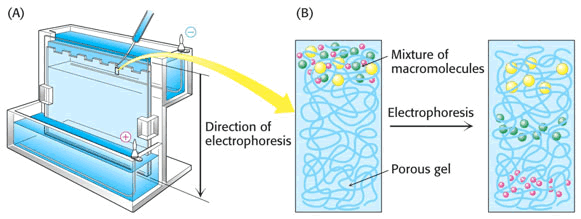
Answer: polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) - separation of molecules on the by applying an electric field. Successful separation can be accomplished by electrophoresis in various gels (semisolid suspensions in water) rather than in a liquid solution. Gels are cast between a pair of glass plates by polymerizing a solution of acrylamide monomers into polyacrylamide chains and simultaneously cross-linking the chains into a semisolid matrix. Gel pore size can be varied by adjusting the concentrations of polyacrylamide and the cross-linking reagent. Highly cross-linked polyacrylamide gel = pores are quite small. Such a gel could resolve small proteins and peptides, but large proteins would not be able to move through it smaller proteins migrate faster than larger proteins through the gel. Gel's pore size and strength of the electric field influence the rate of movement.
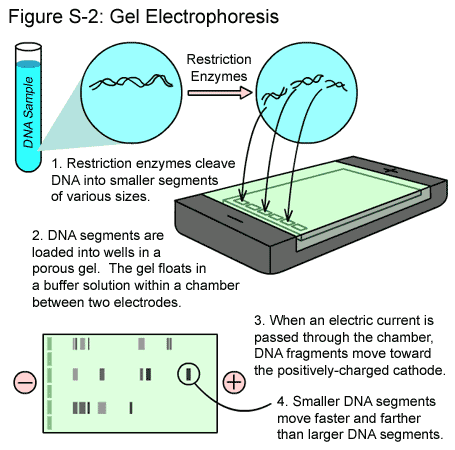
79. Discribe stages of DNA sample electrophoresis:
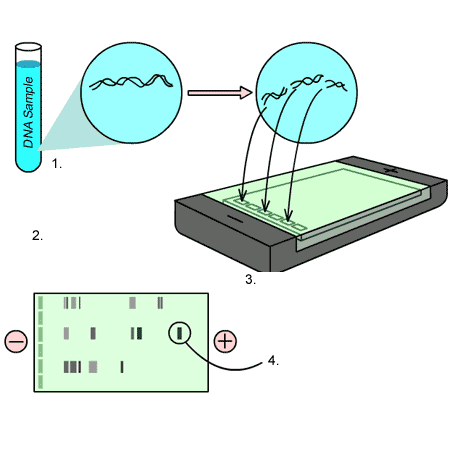
Answer:
Section іі Enzymes, structure and classification. Regulation of metabolism
1. Chose a correct statement about common feature of enzymes and inorganic catalysts:
Acceleration of thermodynamically permitted reactions
Dependence of activity on pH of medium
High selectivity to type of catalyzed reaction
Specific dependence on substrate concentration
Dependence on the presence of cofactors
2. Enzymes differ from inorganic catalysts by the next property:
Thermolability
Acceleration of reaction equilibrium achievement
Sensitivity to catalyst poisons
Thermostability
No selectivity to type of catalyzed reaction
3. Enzymes accelerate chemical reaction due the to next effect:
Enzymes lower the energetic barrier of chemical reaction
Enzymes shift the position of equilibrium of chemical reaction.
Enzymes make possible endergonic reaction without energy supply
Enzymes increase the free energy of activation
4. Enzymes accelerate the rate of reactions by:
Decreasing the energy of activation
Increasing the equilibrium constant of reactions
Increasing the energy of activation
Decreasing the free energy change of the reaction
Decreasing the equilibrium constant of reactions
5. The energy required to start an enzymatic reaction is called:
Activation energy
Chemical energy
Metabolic energy
Potential energy
Free energy
6. Chose from listed below enzymes ONE which exhibits selectivity to stereochemical epimers of substrate:
Urease
Trypsin
Aminopeptidase
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase
7. An enzyme is a:
Protein
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Nucleic acid
Amino acid
8. Which of the following is not true regarding enzymes?
They are destroyed after the completion of the reaction they catalyse
They catalyze only a particular type of reaction
They remain active even after separation from the source
They are irreversibly destroyed at high temperature
Their activity depends on the pH of the solution
9. Active center of enzyme can be defined as follows:
А. Site on the enzyme molecule, which binds substrate and provides its further transformation.
В. Part of the molecule, which easily splits from apoenzyme.
С. Nonprotein component of enzyme molecule
D. Site for binding of allosteric effector.
