
- •Section I Control of the initial level of knowledge. Biochemical constituents of the cell. Methods of biochemical investigations.
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •77. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •78. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •Section іі Enzymes, structure and classification. Regulation of metabolism
- •Е. Whatever part of polypeptide chain of enzyme molecule.
- •Substrate concentration at which reaction rate is half maximal
- •The second enzyme has higher affinity to substrate
- •Competitive
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Cysteine
- •B. Amylase
- •Peptidases
- •Enteropeptidase
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section ііi Metabolic pathways and bioenergetics. Tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation and oxidative phopshorylation
- •1. When atp forms amp:
- •B. Protons
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of carbohydrates
- •19. Chose the reaction of glycolysis catalyzed by an enzyme phosphofructokinase:
- •A. Liver
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
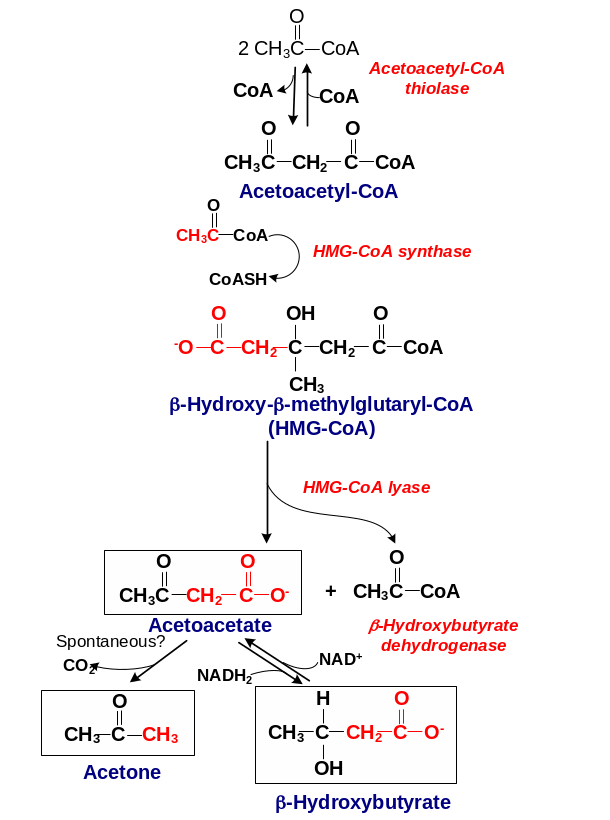
- •Acetoacetate, β-hydroxybulyrate, and acetone
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of lipids
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •143. A patient with high rate of obesity was advised to use carnitine as a food additive in order to enhance "fat burning". What is the role of carnitine in the process of fat oxidation?
- •144. Lipids are obvious energetic material for the body. What is the main pathway of fatty acids metabolism in mitochondria?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks Situational tasks
- •179. The patient is observed an allocation of undigested fat in the faeces. What are the possible causes for this?
- •184. Free cholesterol can affect cholesterol metabolism in the body by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis. By which step free cholesterol can inhibit its biosynthesis?
- •186. Explain the mechanism of phospholipids breakdown, shown at the scheme below:
- •Section VI Structure and metabolism of amino acids
- •B. Amylase
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •112. According to clinical indications a patient was administered pyridoxal phosphate. What processes is this medication intended to correct?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •145. In a patient 10 g of urine per day is excreted. Evaluate this result.
- •151. Skin color is the aggregate result of the expression of a number of genes modified by ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. What can cause the hypopigmentation?
- •Section VII Principles of molecular biology and molecular genetics
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •108. List and describe properties of the genetic code.
- •113. Fill in the blanks.
- •114. Put the numbers of the enzymes on their place in the picture. Using arrows indicate the direction of replication and direction of synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
- •Section VIII Molecular mechanisms of hormone action on target cells. Biochemistry of hormonal regulation
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •78. For analgesia, a certain substance which imitates the physiological properties of morphine but is synthesized inside the human brain can be used. Name this substance.
- •80. A patient suffering from rheumatism was administered glucocorticoid therapy. What changes in carbohydrate metabolism in liver can be expected?
- •88. In blood of a patient a hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, in urine – hyperphosphaturia is observed. What is a possible cause of this state?
- •90. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. It is caused by deficiency of:
- •93. Signaling via prostanoids begins by interaction of the prostanoid with its receptor. The receptor involved is usually located in which part of the cell?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •97. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. Which hormone deficiency can cause this disease?
- •99. The thyroid hormones t3 and t4 are synthesized in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. From which of the following essential amino acids are the thyroid hormones synthesized?
- •101. Name types of signalling:
- •Section IX Biochemistry of the nervous tissue
- •С. Ketone bodies
- •24. What compound may be used by the cns cells after extensive physical exercises and prolonged starvation?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •114. Describe the structure of a synapse and explain how it operates?
- •Section X Biochemistry of the Muscular tissue
- •D. Glycogenolysis in muscles
- •С. Fatigue faster compared to the red fibers
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XI Biochemistry of nutrition
- •1. Note substance, which activates pepsinogen to pepsin:
- •2. Chose the enzyme which plays an important role in production of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells of gastric mucosa glands:
- •3. Which of the following is not a function of the pancreas?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •62. The clinical and laboratory examination of the patient evaluated the presence of the lactic acid in his gastric juice. What does it indicate? What should be recommended to the patient?
- •69. Discribe the mechanism of hydrochloric acid production shown at the picture:
- •Section XII Functional role of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins in metabolism and providement of cell functions
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •100. A deficiency in thiamine (vitamin b1) would most likely lead to which clinical manifestations?
- •Section XIII Biochemistry and pathobiochemistry of blood
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •89. The blood clotting cascade in humans is represented in the picture below. Using this scheme answer the following questions:
- •Section XIV Functional and clinical biochemistry of liver tissue. Biotransformation of xenobiotics and endogenous toxic compounds
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XV Water and mineral metabolism
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVI Functional role of kidneys in urinogenesis. Normal and pathological constituents of urine
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVII Biochemical constituents of connective tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 Tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •34. Patient with burn disease is at the risk of formation of blood clots in blood vessels. What glycosaminoglycan may be used to prevent formation of blood clots?
- •Section XVIII Biochemistry of saliva and tooth tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XIX. Biochemical reactions
- •References:
186. Explain the mechanism of phospholipids breakdown, shown at the scheme below:

Answer: Phospholipids are degraded by pancreatic phospholipase A2, which hydrolytically excises the fatty acid residue at C(2) to yield the corresponding lysophosopholipids, which are also powerful detergents. Indeed, the phospholipid lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) is secreted in the bile, presumably to aid in lipid digestion. Pancreatic phospholipase A2, as does pancreatic lipase, preferentially catalyzes reactions at interfaces. Phospholipase C gives a diacylglycerol, phospholipase D gives a phosphatidate
187. Fill in the blanks:

Answer:
Section VI Structure and metabolism of amino acids
1. What is the number of amino acids involved in protein biosynthesis?
Twenty
Twelve
Twenty five
Fifteen
Thirty seven
2. Chose from listed below amino acids aliphatic one:
Isoleucine
Lysine
Histidine
Proline
Phenylalanine
3. Chose from listed below amino acids two aromatic ones:
Tyrosine
Phenylalanine
Serine
Cysteine
Alanine
4. Select from listed below amino acids non proteinogenous one:
β-Alanine
Aminoacetic acid
Histidine
Leucine
Proline
5. Note from listed below amino acids an acidic one:
Glutamate
Valine
Asparagine
Alanine
Lysine
6. In protein biosynthesis are involved:
L- amino acids only
D-amino acids only
D-amino acids predominantly
L-amino acids predominantly
Both D- and L- amino acids equally well
7. A polypeptide is shown to have a high pI value (approx. at pH 8,9). What from listed below amino acids is responsible for this property?
Arginine
Valine
Serine
Tyrosine
Cysteine
8. Denaturation of proteins is caused by:
Alteration of polypeptide chain folding (conformation)
Hydrolytic cleavage of peptide bonds
Reduction and cleavage of disulphide bonds.
Formation of new peptide bonds
Dissotiation of carboxyl groups
9. Sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain is defined as the next structural level:
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Multimolecular complex
10. Note the correct value of normal protein concentration in human blood plasma:
65-85 g/l
25-40 g/l
45-60 g/l
85-100 g/l
100-150 g/l
11. Proteins of blood plasma are divided into albumin and globulins. What is normal proportion of albumin to globulins (albumin/globulin coefficient)?
2:1
1:1
5:1
1:2
1:5
12. Fibrinogen is an important protein of blood plasma. To what class of proteins belongs fibrinogen:
Glycoprotein
Albumin
Lipoprotein
Chromoprotein
Nucleoprotein
13. In proteins amino acids are linked covalently by:
Peptide bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Disulphide bonds
Hydrophobic interactions
Salt like bridges
14. Protein is a biopolymer which can be defined as:
Linear chain of L-amino acids
Branched chain of mononucleotides
Linear chain of amino sugars
Linear chain of nucleosides
Branched chain of D-amino acids
15. Domains are specific elements of the next structural level of protein molecule:
Tertiary
Secondary
Primary
Quaternary
Multimolecular complex
16. Secondary structure of proteins includes the next structural element:
β-Pleated sheets
Triple superhelix
Coplanarity of peptide bond
Disulphide bridges
Attachment of oligosaccharides to a polypeptide chain
17. The net charge of protein molecule depends from the next factors:
Amino acid composition
pH value of solution
Conformation of protein molecule
Quaternary structure of protein
Hydrophobic interactions between amino acid residues
18. Proteins can be precipitated by different agents. The precipitation with ammonium sulphate is convenient due to:
Fractional precipitation of protein mixtures and purification of selected proteins
Denaturation of precipitated protein at room temperature
Fragmentation of polypeptide chain to oligopeptides
Irreversible precipitation of protein from investigated material
Precipitation of amino acids accompanying proteins
19. The concentration of protein in blood serum of a patient was on level of 40 g/l. Such situation can be classified as follows:
Hypoproteinemia
Dysproteinemia
Hyperproteinemia
Normal state
Paraproteinemia
20. Disulphide bridge in protein molecules is formed between the next amino acids:
Cysteine-cysteine
Lysine-aspartic acid
Tyrosine - histidine
Proline-tryptophan
Histidine-arginine
22. Salt like bridges (ionic bonds) in protein molecule are formed between the next amino acids:
Lysine-glutamic acid
Leucine-alanine
Phenylalanine-tyrosine
Aspartic acid-methionine
Serine-cysteine
23. Glutathion is a tripeptide possessing reducing properties. What amino acid residue is responsible for reductive properties of glutathion?
Cysteine
Glutamic acid
Glycine
Valine
Aspartic acid
24. An amino acid that does not form an α-helix is:
Proline
Valine
Tyrosine
Tryptophan
Alanine
25. Which of the following is a dipeptide?
Anserine
Glutathione
Insulin
Glucagon
β -Lipoprotein
26. Which of the following is a tripeptide?
Glutathione
Anserine
Oxytocin
Glucagon
Kallidin
27. Each turn of α-helix contains the amino acid residues (number):
3.6
3.0
4.2
4.5
5.6
28. At the lowest energy level α-helix of polypeptide chain is stabilised:
A. By hydrogen bonds formed between the H of peptide N and the carbonyl O of the residue
B. Disulphide bonds
C. Non polar bonds
D. Ester bonds
29. In proteins the α-helix and β-pleated sheet are examples of:
A. Secondary structure
B. Primary structure
C. Tertiary structure
D. Quaternary structure
30. The a-helix of proteins is:
Stabilised by hydrogen bonds between NH and CO groups of the main chain
A pleated structure
Made periodic by disulphide bridges
A non-periodic structure
31. A disulphide bond can be formed between:
Two cysteine residues
Two methionine residues
A methionine and a cysteine residue
Two serine residues
Two valine residues
32. In a child, consuming meal of plant origin for a long time growth retardation, anemia, liver and kidney impairment were observed. The cause of such state is deficiency in diet of the next nutrients:
Essential amino acids
Lipids
Carbohydrates
Mineral macroelements
Carotene
33. Pyruvic acid can be obtained by transamination of alanine with:
A. α- ketoglutaric acid
B. Acetoacetic acid
C. α- OH butyric acid
D. Phosphoenol Pyruvic acid
E. Fumaric acid
34. The product of glutamate decarboxylation is:
Gamma-amino butyrate
Putrescine
Taurine
Oxaloacetate
α-Ketoglutarate
35. A vasodilating compound is produced by the decarboxylation of the amino acid:
A. Histidine
B. Aspartic acid
C. Glutamine
D. Arginine
E. Glutamic acid
36. One of the products of amino acid deamination by amino acid oxidase is:
Hydrogen peroxide
Water
Carbone dioxide
Nitric oxide
Protons
37. An important reaction for the synthesis of amino acid from carbohydrate intermediates is transamination which requires the cofactor:
A. Pyridoxal phosphate
B. Riboflavin
C. Niacin
D. Thiamin
E. Folic acid
38. Which of the following enzymes catalyses reactions in the biosynthesis of both catecholamines and indoleamines (serotonin)?
Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase
Dopamine β-hydroxylase
Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
Tryptophan hydroxylase
Tyrosine hydroxylase
39. The main sites for oxidative deamination are:
A. Liver and kidney
B. Skin and pancreas
C. Intestine and mammary gland
D. Lung and spleen
E. Brain
40. The amino acids involved in the synthesis of creatin are:
A. Arginine, glycine, active methionine
B. Arginine, alanine, glycine
C. Glycine, lysine, methionine
D. Arginine, lysine, methionine
E. Glycine, lysine, alanine
41. Note amino acids, which are participants of creatine biosynthesis:
Arginine.
Lysine.
Methionine.
Tryptophan.
Phenylalanine.
42. The amino acid that undergoes oxidative deamination at significant rate is:
A. Glutamate
B. Aspartate
C. Alanine
D. Glutamine
E. Serine
43. Allosteric inhibitor of glutamate dehydrogenase is:
A. ATP
B. ADP
C. AMP
D. GMP
E. NAD+
44. In recognition of hepatitis the determination the following enzymes activity in blood has diagnostic significance:
A. Amino transferases
