
- •Section I Control of the initial level of knowledge. Biochemical constituents of the cell. Methods of biochemical investigations.
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •77. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •78. Discribe the method, shown at the picture below:
- •Section іі Enzymes, structure and classification. Regulation of metabolism
- •Е. Whatever part of polypeptide chain of enzyme molecule.
- •Substrate concentration at which reaction rate is half maximal
- •The second enzyme has higher affinity to substrate
- •Competitive
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Cysteine
- •B. Amylase
- •Peptidases
- •Enteropeptidase
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section ііi Metabolic pathways and bioenergetics. Tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation and oxidative phopshorylation
- •1. When atp forms amp:
- •B. Protons
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of carbohydrates
- •19. Chose the reaction of glycolysis catalyzed by an enzyme phosphofructokinase:
- •A. Liver
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Acetoacetate, β-hydroxybulyrate, and acetone
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section іv Structure and metabolism of lipids
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •143. A patient with high rate of obesity was advised to use carnitine as a food additive in order to enhance "fat burning". What is the role of carnitine in the process of fat oxidation?
- •144. Lipids are obvious energetic material for the body. What is the main pathway of fatty acids metabolism in mitochondria?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks Situational tasks
- •179. The patient is observed an allocation of undigested fat in the faeces. What are the possible causes for this?
- •184. Free cholesterol can affect cholesterol metabolism in the body by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis. By which step free cholesterol can inhibit its biosynthesis?
- •186. Explain the mechanism of phospholipids breakdown, shown at the scheme below:
- •Section VI Structure and metabolism of amino acids
- •B. Amylase
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •112. According to clinical indications a patient was administered pyridoxal phosphate. What processes is this medication intended to correct?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •145. In a patient 10 g of urine per day is excreted. Evaluate this result.
- •151. Skin color is the aggregate result of the expression of a number of genes modified by ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. What can cause the hypopigmentation?
- •Section VII Principles of molecular biology and molecular genetics
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •108. List and describe properties of the genetic code.
- •113. Fill in the blanks.
- •114. Put the numbers of the enzymes on their place in the picture. Using arrows indicate the direction of replication and direction of synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
- •Section VIII Molecular mechanisms of hormone action on target cells. Biochemistry of hormonal regulation
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •78. For analgesia, a certain substance which imitates the physiological properties of morphine but is synthesized inside the human brain can be used. Name this substance.
- •80. A patient suffering from rheumatism was administered glucocorticoid therapy. What changes in carbohydrate metabolism in liver can be expected?
- •88. In blood of a patient a hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, in urine – hyperphosphaturia is observed. What is a possible cause of this state?
- •90. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. It is caused by deficiency of:
- •93. Signaling via prostanoids begins by interaction of the prostanoid with its receptor. The receptor involved is usually located in which part of the cell?
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •97. In 13 years old girl a hypotension and polyuria is observed. Preliminary diagnosis – diabetes insipidus. Which hormone deficiency can cause this disease?
- •99. The thyroid hormones t3 and t4 are synthesized in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. From which of the following essential amino acids are the thyroid hormones synthesized?
- •101. Name types of signalling:
- •Section IX Biochemistry of the nervous tissue
- •С. Ketone bodies
- •24. What compound may be used by the cns cells after extensive physical exercises and prolonged starvation?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •114. Describe the structure of a synapse and explain how it operates?
- •Section X Biochemistry of the Muscular tissue
- •D. Glycogenolysis in muscles
- •С. Fatigue faster compared to the red fibers
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XI Biochemistry of nutrition
- •1. Note substance, which activates pepsinogen to pepsin:
- •2. Chose the enzyme which plays an important role in production of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells of gastric mucosa glands:
- •3. Which of the following is not a function of the pancreas?
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •62. The clinical and laboratory examination of the patient evaluated the presence of the lactic acid in his gastric juice. What does it indicate? What should be recommended to the patient?
- •69. Discribe the mechanism of hydrochloric acid production shown at the picture:
- •Section XII Functional role of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins in metabolism and providement of cell functions
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •100. A deficiency in thiamine (vitamin b1) would most likely lead to which clinical manifestations?
- •Section XIII Biochemistry and pathobiochemistry of blood
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •89. The blood clotting cascade in humans is represented in the picture below. Using this scheme answer the following questions:
- •Section XIV Functional and clinical biochemistry of liver tissue. Biotransformation of xenobiotics and endogenous toxic compounds
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XV Water and mineral metabolism
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVI Functional role of kidneys in urinogenesis. Normal and pathological constituents of urine
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XVII Biochemical constituents of connective tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 Tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •34. Patient with burn disease is at the risk of formation of blood clots in blood vessels. What glycosaminoglycan may be used to prevent formation of blood clots?
- •Section XVIII Biochemistry of saliva and tooth tissue
- •Examples of Krok 1 tests
- •Clinical cases and Situational tasks
- •Section XIX. Biochemical reactions
- •References:
Clinical cases and Situational tasks
134. Amital is pharmaceutical, which is used in pharmacology as a hypnotic agent. What is the mechanism of its actions on the processes of tissue respiration?
Answer: Amital (aminobarbital) – a derivative of barbituric acid, which inhibits cellular respiration by blocking electron transport ,at the level provided with the-coenzyme Q-reductase.
135. A patient with overactivity of the thyroid gland. Why biological oxidation in cells is disturbed?
Answer: Thyroid hormones (thyroxine, triiodothyronine) activate Na+, K+-ATP-ase. With their action, they observed the active absorption of O2 mitochondria without a corresponding increase in the synthesis of ATP.
136. The patient, who had been using phenobarbital to treat Gilbert’s disease, developed addiction to this drug. How can you explain the mechanism of this addiction?
Answer: The addiction to phenobarbital induction explained by the synthesis of cytochrome P-450. The phenobarbital oxidized mono-oxygenase system of endoplasmic reticulum with cytochrome P-450.
137. Why do patients with cardiovascular failure and signs of acidosis to administered the cocarboxilase (thiamine pirophosphate) drug?
Answer: Cocarboxilase (thiamine pirophosphate) is coenzyme form of vitamin B1, which is a part of enzymes involved in oxidative dekabooxydation α-ketoacids (eg pyruvate dehydrogenase). Cocarboxilase prescribed for acidosis origin of diabetes, hepatic and renal failure, respiratory acidosis, chronic pulmonary heart failure and coronary insufficiency and a number of different processes that improve energy metabolism.
138. A postoperative patient on intravenous fluids develops lesions in the mouth (angular stomatitis). Urinalysis indicates an excretion of 15 μg riboflavin/mg creatinine, which is abnormally low. Which of the following TCA cycle enzymes is most likely to be affected?
Answer: The patient has demonstrated a deficiency in riboflavin (urinary excretion of less than 30 μg/mg creatinine is considered clinically deficient). Riboflavin is a component of the cofactor FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), which is required for the conversion of succinate to fumarate by succinate dehydrogenase.
139. After excessive drinking over an extended period of time while eating poorly, a middle-aged man is admitted to the hospital with “high output” heart failure. Which of the following enzymes is most likely inhibited?
Answer: This patient has exhibited symptoms of beri beri heart disease, which is a result of a nutritional deficiency in vitamin B1 (thiamine). The active form of the vitamin, thiamine pyrophosphate, is a required cofactor for α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
140. ATP may be hydrolysed to form ADP and Pi (orthophosphate) or AMP and PPi (pyrophosphate). Pyrophosphate may be subsequently hydrolyzed to orthophosphate releasing additional free energy. Note the ΔGo values (1, 2 and 3), which are released in each reaction.
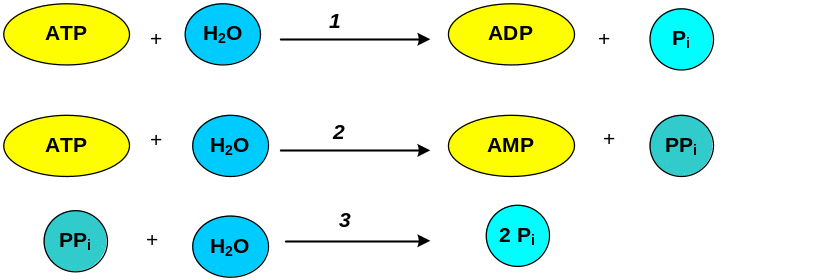
Answer: 1 - DGo=-7.3 kcal (-30.5 kJ/mol), 2 - DGo'=-7.7 kcal (-32.2 kJ/mol), 3 - DGo'=-8 kcal (-33.5 kJ/mol)
141. A 16-month-old girl was found to have ingested approimately 30 mL of an acetonitrile-based cosmetic nail remover when she vomited 15 minutes postingestion. The poison control center was contacted, but no treatment was recommended because it was confused with an acetone-based nail polish remover. The child was put to bed at her normal time, which was 2 hours postingestion. Respiratory distress developed sometime after the child was put to bed, and she was found dead the next morning. Inhibition of which of the following enzymes was the most likely cause of this child’s death?
Answer: The culprit here is cyanide produced from acetonitrile. Cyanide inhibits the electron transport chain of cytochrome oxidase.
142. Several molecules are known to specifically inhibit the electron transport process. Used in conjunction with reduction potential measurements, inhibitors have been invaluable in the determination of the correct order of electron-transport chain components. Insert the corresponding inhibitors (at the scheme) to the sites of their action.

Answer: 1- rotenone (a plant toxin used by Amazonian Indians to poison fish and is also used as an insecticide), amital (a barbiturate); 2- Antimicin A, 3- monoxide (CO), azide (N3-) and cyanide
143. Name the respiratory inhibitors, shown below:
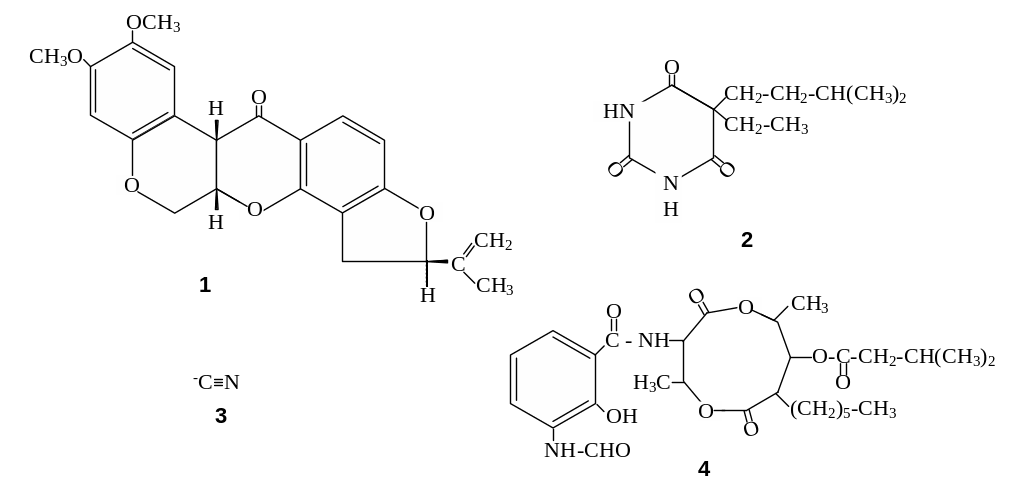
Answer:1 – rotenone, 2 – amytal, 3 – cyanide, 4 – antymycin A.
144. Explain the role of ATP-synthase components, shown below:
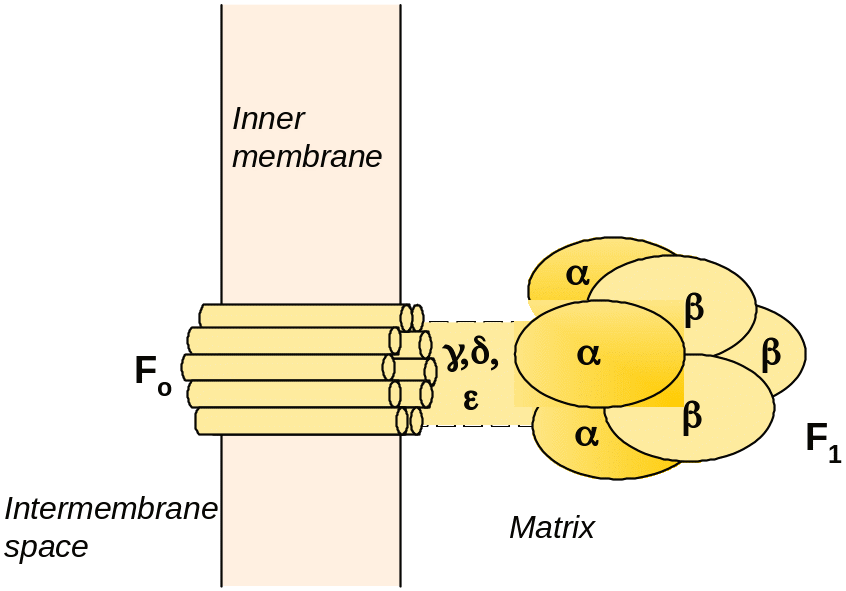
Answer: The F1 headpiece includes three α and three β subunits one copy each of three other subunits (γ, δ and ε. F0 includes a cluster of 9-12 copies of a small peptide, which appears to form a transmembrane channel for protons.
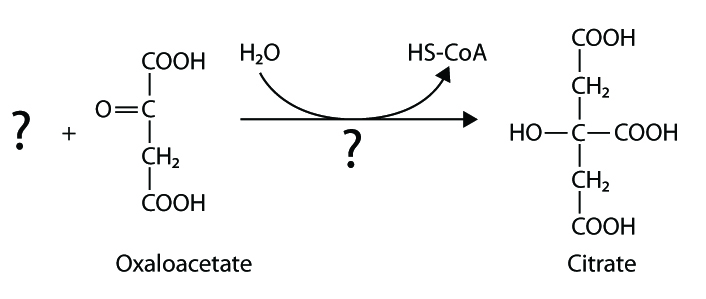
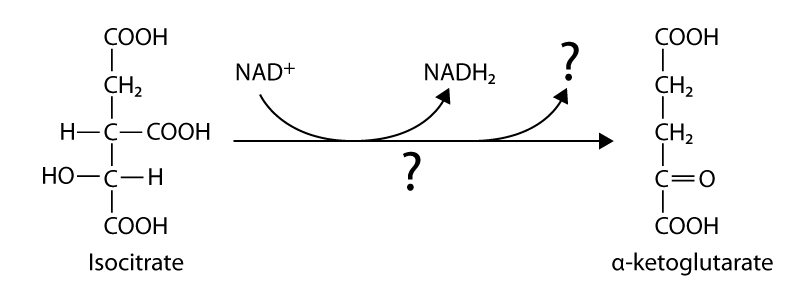
145. Name enzymes of citric acid cycle:
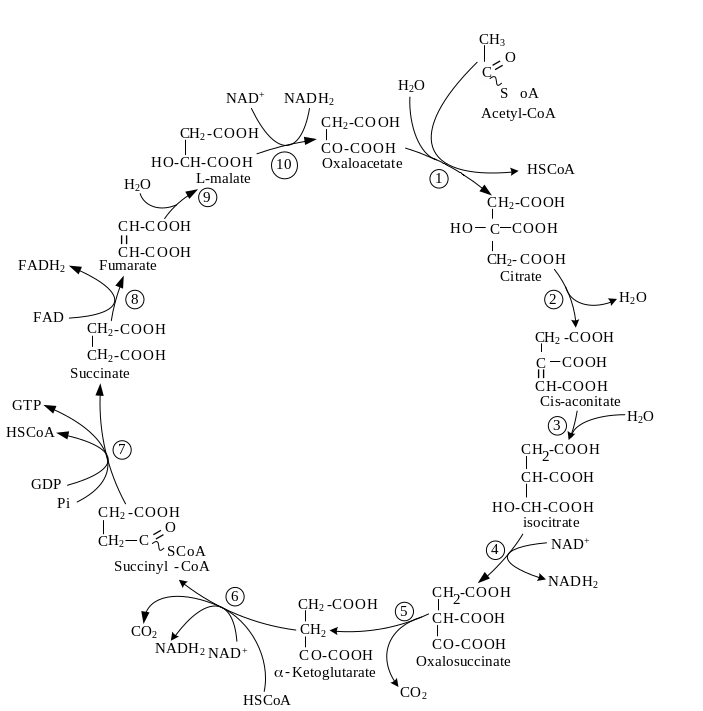
Answer:1 – Citrate synthase, 2, 3 – aconitase, 4, 5 – isocitrate dehydrogenase, 6 – a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, 7 – succinate thiokinase, 8 – succinate dehydrogenase, 9 – fumarase, 10 - malate dehydrogenase.
146. Fill in the blanks:
a
b
c
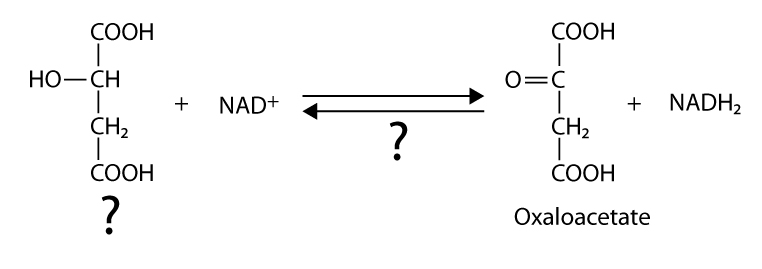
Answer: a – acetyl CoA, citrate syntase; b – isocitrate dehydrogenase, CO2 ; c – malat dehydrogenase
147. Inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation by cyanide ion leads to increases in which of processes?
Answer: Gluconeogenesis requires ATP, which is in short supply, turning up the catabolism of glucose to lactate in the absence of an intact electron transport chain. ADP cannot be transported into the mitochondrion because ATP, its antiporter partner, isn’t made by oxidative phosphorylation as a result of cyanide inhibition of cytochrome oxidase. Metabolism of fatty acids and ketone bodies requires a functional electron transport chain for their metabolism, and these possibilities are also ruled out.
148. Name the following compounds of Krebs cycle:
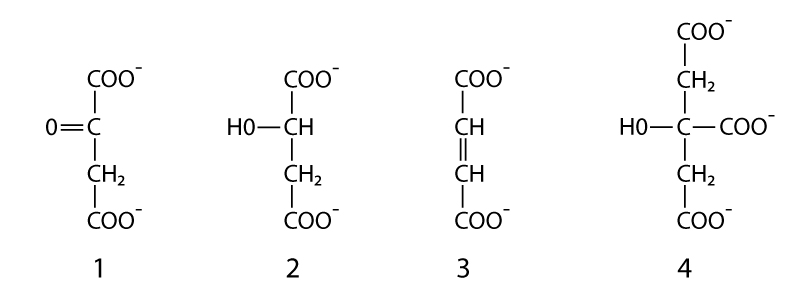
Answer: 1 – oxaloacetate, 2 – malate, 3 – fumarate, 4 – citrate
