- •Initializing with Constructor Functions . . . . .
- •Into a Web page as a separate section. Although JavaScript code can
- •Is that standard php script delimiters are guaranteed to be available
- •In the block. Any text or lines between the opening /* characters and
- •2.7541 Are not integers; they are floating-point numbers. A floating-
- •Value 300
- •Is a value of 2.5, because 6 goes into 15 exactly 2.5 times. But if you
- •IsEven.Php.
- •Ing example,
- •Ing curly brace is on its own line following the function statements.
- •In php 3 and earlier, it was necessary to put a function definition
- •Is called an iteration. When the conditional expression evaluates
- •Including Files
- •13. Close your Web browser window.
- •Including Files
- •In php, you can also use two operators to combine strings. The first
- •Xhtml source code gen-
- •Input. Php provides several functions for manipulating the case of a
- •Is uppercase. If you need the reverse of ucfirst(), the lcfirst()
- •In some situations, you will need to find and extract characters and
- •Information Interchange, or ascii, which are numeric represen-
- •In comparison, the following preg_match() function returns a value
- •In the pattern is optional. The following code demonstrates how to
- •Values; any strings you validate against a regular expression must
- •Value of 1 because the top-level domain contains a valid value of .Com.
- •Is submitted using the “post” method, the form data is embedded in
- •Validating String Data
- •Xhtml tags or character entities. The message field is a text string
- •Value of the header element. For example:
- •Xhtml code within a php script section.
- •Is typically the person who created the resource. Otherwise, the net-
- •If even a single character of the Web page is sent prior to sending
- •Variables to the file_put_contents() function.
- •Xhtml hyperlink. To download a file from outside the xhtml
- •If...Else statement to display the appropriate version of the mes-
- •Iterating Through an Array
- •Iterating Through an Array
- •In Chapter 2, you learned how to use a foreach statement to iterate
- •Iterating Through an Array
- •Iterating Through an Array
- •In comparison, the following code declares and initializes
- •If ((!file_exists("MessageBoard/messages.Txt"))
- •Values from the array to create a thumbnail gallery of images in which
- •Introduction to Databases
- •Including php, allow you to create Web pages that can read and write
- •Introduction to Databases
- •Information that can be organized into ordered sets of data, and
- •Information. Each recipe in a recipe database, for instance, is a single
- •Introduction to Databases
- •Index, which identifies records in a database to make retrievals and
- •In a single table. However, you might want to break the information
- •Into multiple tables to better organize it into logical sets. Another
- •Information in one of the tables confidential and accessible only by
- •Is the employee information table from Figure 7-1. The related table
- •Is a payroll table that contains confidential salary and compensation
- •Information. Notice that each table contains an identical number of
- •Introduction to Databases
- •Introduction to Databases
- •In a junction
- •Introduction to Databases
- •In a relational format is called a relational database management
- •Is a standard data manipulation language among many dbmSs.
- •Into the query area at the top of the screen or by dragging tables and
- •It is important to understand that even though many dbmSs sup-
- •Introduction to Databases
- •If you ever
- •Is. In comparison, the bigint data type stores integer values between
- •5 Rows in set (0.00 sec)
- •Int);[enter ]
- •Important, these two tabs can cause you to lose all of the data in the
- •Internet Explorer to export the table, click the Save button in the File
- •Ifies the table being changed and the change to make.
- •It easier for you to write php code that can be used with a variety of
- •Information about queries that match one of the following formats:
- •Various types of actions, depending on the type of query.
- •Include fields for the date and time of the flight, flight number, and
- •In the ChineseZodiac folder and upload the file to the server. Open
- •Including white space,
- •Information on a Web server. When you start a new session, the
- •Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
- •Introduction to Object-Oriented
- •Variables associated with an object are called properties or attributes.
- •In the Loan object example, a function that calculates the number of
- •Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
- •Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
- •Include instances of objects inherit the object’s functionality.
- •In this chapter, you will create the Web site for an online order form
- •In an online store application. The application includes information
- •Ity of building a working online store. Online store classes are very
- •Information and products. The OnlineStore class requires that store
- •Information is stored in a table containing six fields: storeId, name,
- •Information. Instead, the class simply uses session iDs to keep track
- •Variable and function as necessary, without bothering with all this
- •In a class
- •Is developed. Imagine what would happen if Microsoft distributed
- •Ing class is invalid because it does not include an access specifier:
- •If they will not be supported by future xhtml versions or are not
- •Xhtml standards. To review the guide of current w3c css specifi-
- •Information to remind yourself or others of what the code is doing. A
- •Xhtml document to the external style sheet. This link informa-
- •If you select Apache from the WampServer menu and select Service
- •Ing code uses the number_format() function to add comma separa-
- •In data that a user submits to a php script.
- •Value of “On” and the display_startup_errors directive is assigned
- •Instead. By looking at the source code, you could see that the value of
- •Ing engine can even help locate logic errors.
- •In Chapter 8, along with the equivalent mssql_* functions, where
- •Inline styles, 632
- •Xhtml, 620–635 (continued)
109
Figure
2-12
Output
of DiceRoll.php with foreach
statements
Short
Quiz
1.
All
loops require what feature to ensure that the looping will
eventually
end and not result in an infinite loop?
What
four looping structures are used in PHP?
Explain
the purpose of a “counter” variable when executing a
loop.
Which
type of looping structure is used to iterate through ele-
ments
of an array?
2.
3.
4.
The
include,
require,
include_once,
and require_once
statements,
much
like the echo
statement,
are not considered actual functions,
but
rather language constructs that are built into PHP. The primary
use
of the include
and
require
statements
is to reuse content onIncluding Files
13. Close your Web browser window.
Including Files
CHAPTER
2
Functions
and Control Structures
multiple
Web pages by allowing you to insert the content of an exter-
nal
file, called an include file, in your PHP scripts.
The
difference between the two statements is that the include
state-
ment
only generates a warning if the include file cannot be found,
whereas
the require
statement
halts the processing of the Web page
and
displays an error message if the include file cannot be found.
The
include_once
and
require_once
statements
are similar to the
include
and
require
statements,
except they assure that the external
file
is added to the script only once, which helps to avoid conflicts
with
variable values or function names that might occur if the file was
included
multiple times.
The
PHP scripting engine starts fresh for each include file. This
means
that if you use PHP code in the include file, it must be con-
tained
within a PHP script section. If the calling PHP file already
contains
the four basic XHTML tags (<html>,
<head>,
<title>,
and
<body>),
the include file requires only that XHTML formatting tags
be
used with XHTML content. The include file is typically saved with
a
prefix of inc_ to identify it as an include file, as opposed to a
com-
plete
.php file. An extension of .php is still used so that the file
will
be
processed by the PHP scripting engine. However, different servers
use
different configurations, so you need to verify the appropriate
file
extension
to use with your ISP.
One
common use of the include
and
require
statements
is to
display
common header and footer content at the top and bottom
of
every page of your Web site. Instead of copying and pasting the
header
and footer code into each individual page, you can simply put
your
header content in one include file and your footer content in
another
include file. Then, on each page that you want the header and
footer
to appear, you can simply refer to the include file with either an
include
or
require
statement.
Another
common use of include files is to store sensitive information
that
the program needs, but that should not be available to Web site
visitors.
Because the path of the filename passed to the include
and
require
statements
is based on the server’s file system, not the Web-
accessible
file structure, you can store include files outside of the file
structure
available to Web browsers. For example, assume that your
server
is configured so that the public_html folder in your user home
directory
is available for Web site visitors. For the user dgosselin, any
file
stored in /home/users/dgosselin/public_html/ or its subdirecto-
ries
would be browsable. However, if dgosselin created the folder /
home/users/dgosselin/php_include/,
that folder would not be brows-
able.
Any files stored in /home/users/dgosselin/php_include/ will be
110
Summing
Up
processed
by the PHP scripting engine if the files are included using
one
of the include
family
of statements.
The
include family of statements supports relative and
absolute path notation. That means you can include a file
from the parent folder by using the “../” notation, as in
include("../inc_CommonHeader.php");. Similarly,
if you were to place the included files in a folder named Includes,
you could use the notation include("Includes/inc_CommonHeader.php");
to access the files in the Includes subdirectory.
111
Short Quiz
1.
Describe the purpose of the group of include, require,
include_once, and require_once statements.
When might you want to use the require statement instead
of the include statement?
Why is it important that you add PHP script delimiters to
each PHP block in the include file?
Explain why one might want to save all include files in a sepa-
rate folder and how this folder can be accessed.
2.
3.
4.
Summing Up
• The lines of code that make up a function are called the function
definition.
• A function parameter that is passed by a value is a local copy of the
variable.
• A function parameter that is passed by a reference is a reference to
the original variable.
• A global variable is declared outside a function and is available to
all parts of your program.
• A local variable is declared inside a function and is only available
within that function.
• The process of determining the order in which statements execute
in a program is called decision making or flow control.

CHAPTER
2
Functions
and Control Structures
•
The
the evaluation of a conditional expression returns a value of TRUE.
• An
if statement that includes an else clause is called anif . . . else statement. An else clause executes when the
condition in an if . . . else statement evaluates to FALSE.
112
• When one decision-making statement is contained within
another decision-making statement, they are referred to as nested
decision-making structures.
• The
switch statement controls program flow by executing aspecific set of statements depending on the value of an expression.
• A loop statement is a control structure that repeatedly executes
a statement or a series of statements while a specific condition is
TRUE or until a specific condition becomes TRUE.
• A
while statement tests a condition prior to executing a series ofstatements at each iteration of the loop.
• The
do . . . while statement tests a condition after executing aseries of statements.
• The
for statement combines the initialization, conditional evalua-tion, and update portions of a loop into a single statement.
• The
foreach statement is used to iterate or loop through theelements in an array.
• The
include, require, include_once, and require_oncestatements insert the contents of an external file at the location
of the statement.
Comprehension Check
1.
A(n)allows you to treat a related group of
PHP commands as a single unit.
a. statement
b. variable
c. function
d. event
2.
3.
Functions must contain parameters. True or False?
Explain how to use a return statement to return a value to a
statement that calls a function.

Comprehension
Check
4.
A
variable that is declared outside a function is called
avariable.
a.
local
b.
class
c.
program
d.
global
113
5.
A
local variable must be declared
a.
before a function
b.
after a function
c.
within the braces of a function definition
d.
with the local keyword
.
6.
Explain
the difference between passing a parameter to a func-
tion
by value versus by reference.
Which
of the following is the correct syntax for an if
statement?
a.
if
($MyVariable == 10);
echo
"Your variable is equal to 10.";
7.
b.
if
$MyVariable == 10
echo
"Your variable is equal to 10.";
c.
if
($MyVariable == 10)
echo
"Your variable is equal to 10.";
d.
if
($MyVariable == 10),
echo
"Your variable is equal to 10.";
8.
An
if
statement
can include multiple statements provided
that
they.
a.
execute after the if
statement’s
closing semicolon
b.
are not contained within a command block
c.
do not include other if
statements
d.
are contained within a command block
CHAPTER
2
Functions
and Control Structures
9.
Which
is the correct syntax for an else
clause?
a.
else
(echo "Displayed from an else clause.";
b.
else
echo "Displayed from an else clause.";
c.
else
"echo 'Displayed from an else clause.'";
114
d.
else;
echo "Displayed from an else clause.";
10.
The switch
statement
controls program flow by executing a
specific
set of statements, depending on.
a. the result of an if . . . else statement
b. the version of PHP being executed
c. whether an if statement executes within a function
d. the value returned by a conditional expression
11. Decision-making structures cannot be nested. True or False?
12. When the value returned by a switch statement expression
does not match a
case label, the statements withinthelabel execute.
a. exception
b. else
c. error
d. default
13. You can exit a switch statement using a(n)
statement.
a. break
b. end
c. quit
d. complete
14. Each repetition of a looping statement is called
a(n).
a. recurrence
b. iteration
c. duplication
d. reexecution

Comprehension
Check
15.
Which of the following is the correct syntax for a while
statement?
a.
while
($i <= 5, ++$i) {
$echo
"<p>$i</p>";
}
b.
while
($i <= 5) {
$echo
"<p>$i</p>";
++$i;
}
115
c.
while
($i <= 5);
$echo
"<p>$i</p>";
++$i;
d.
while
($i <= 5; $echo "<p>$i</p>") {
++$i;
}
16.
Counter variables
a.
can only be incremented
b.
can only be decremented
.
(Choose all that apply.)
c.
can be incremented or decremented
d.
do not change
17.
Explain how an infinite loop is caused.
18.
Which of the following is the correct syntax for a for
statement?
a.
for
($i = 0; $i < 10; ++$i)
echo
"Displayed from a for statement.";
b.
for
($i = 0, $i < 10, ++$i)
echo
"Displayed from a for statement.";
c.
for
{
echo
"Displayed from a for statement.";
} while ($i = 0; $i < 10; ++$i)
d. for ($i = 0; $i < 10);
echo "Displayed from a for statement.";
++$i;

CHAPTER
2
Functions
and Control Structures
19.
When is a for
statement
initialization expression executed?
a.
when the for
statement
begins executing
b.
with each repetition of the for
statement
c.
when the counter variable increments
116
d.
when the for
statement
ends
20.
The foreach
statement
can only be used with arrays. True
or
False?
Reinforcement Exercises
Exercise 2-1
In this project, you will create a simple document that contains a con-
ditional operator you will rewrite into an if . . . else statement.
1.
2.
Create a new document in your text editor.
Type the <!DOCTYPE> declaration, <html> element, docu-
ment head, and <body> element. Use the strict DTD and
“Conditional Script” as the content of the
<title> element.Create a script section in the document body that includes
the following code, but replace the conditional expression
statement with an if . . . else statement. Note that the
strings are enclosed in single quotation marks so that the
name of the variable will be displayed, not the value.
<?php
$IntVariable = 75;
($IntVariable > 100) ? $Result = '$IntVariable is
greater than 100'
: $Result = '$IntVariable is less than or equal
to 100';
echo "<p>$Result</p>";
?>
3.
4.
Save the document as ConditionalScript.php in the Projects
directory for Chapter 2, and then upload the document to the
server.
Open the ConditionalScript.php file in your Web browser
by entering the following URL: http://<yourserver>/PHP_
Projects/Chapter.02/Projects/ConditionalScript.php.
Close your Web browser window.
5.
6.

Reinforcement
Exercises
Exercise
2-2
In
this project, you will write a while
statement
that displays all odd
numbers
between 1 and 100 on the screen.
117
1.
2.
Create
a new document in your text editor.
Type
the <!DOCTYPE>
declaration,
<html>
element,
document
head,
and <body>
element.
Use the strict DTD and “Odd
Numbers”
as the content of the <title>
element.
Create
a script section in the document body with a while
statement
that displays all odd numbers between 1 and 100
on
the screen.
Save
the document as OddNumbers.php in the Projects
directory
for Chapter 2, and then upload the document to the
server.
Open
the OddNumbers.php file in your Web browser by
entering
the following URL: http://<yourserver>/PHP_
Projects/Chapter.02/Projects/OddNumbers.php.
Close
your Web browser window.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Exercise
2-3
In
this project, you will identify and correct the logic flaws in a
while
statement.
1.
2.
Create
a new document in your text editor.
Type
the <!DOCTYPE>
declaration,
<html>
element,
document
head,
and <body>
element.
Use the strict DTD and “While
Logic”
as the content of the <title>
element.
CHAPTER
2
Functions
and Control Structures
3.
Create
a script section in the document body that includes
the
following code:
<?php
$Count
= 0;
while
($Count > 100) {
$Numbers[]
= $Count;
++$Count;
foreach ($Count as $CurNum)
echo "<p>$CurNum</p>";
}
?>
118
4.
The code you typed in the preceding step should fill the array
with the numbers 1 through 100 and then display them on the
screen. However, the code contains several logic flaws that
prevent it from running correctly. Identify and correct the
logic flaws.
Save the document as WhileLogic.php in the Projects direc-
tory for Chapter 2, and then upload the document to the
server.
Open the WhileLogic.php file in your Web browser by enter-
ing the following URL: http://<yourserver>/PHP_Projects/
Chapter.02/Projects/WhileLogic.php.
Close your Web browser window.
5.
6.
7.
Exercise 2-4
In this project, you will modify a nested if statement so it instead
uses a compound conditional expression. You will use logical opera-
tors such as || (or) and && (and) to execute a conditional or looping
statement based on multiple criteria.
1.
2.
Create a new document in your text editor.
Type the <!DOCTYPE> declaration, <html> element, docu-
ment head, and <body> element. Use the strict DTD and “Gas
Prices” as the content of the <title> element.

Reinforcement
Exercises
3.
Create
a script section in the document body that includes
the
following variable declaration and nested if
statement:
<?php
$GasPrice
= 2.57;
if
($GasPrice >= 2) {
if
($GasPrice <=3)
echo "<p>Gas prices are between
$2.00 and $3.00.</p>";
}
?>
119
4.
Modify the nested if statement you created in the previ-
ous step so it uses a single if statement with a compound
conditional expression. You need to use the && (and) logical
operator.
Add an else clause to the if statement that displays “Gas
prices are not between $2.00 and $3.00” if the compound con-
ditional expression returns FALSE.
Save the document as GasPrices.php in the Projects direc-
tory for Chapter 2 and upload the document to the server.
Open the GasPrices.php file in your Web browser by enter-
ing the following URL: http://<yourserver>/PHP_Projects/
Chapter.02/Projects/GasPrices.php.
Close your Web browser window.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Exercise 2-5
In this project, you will create header and footer pages that you will
add to a Web page with the include statement.
1.
Create a new document in your text editor and type the
<!DOCTYPE> declaration, <html> element, document head,
and <body> element. Use the strict DTD and “Coast City
Computers” as the content of the <title> element.
CHAPTER
2
Functions
and Control Structures
2.
Add
the following text and elements to the document body:
<h2>Memorial
Day Sale</h2>
<ul>
<li>Compaq
Presario m2007us Notebook:
<strong>$799.99</strong></li>
<li>Epson
Stylus CX6600 Color All-In-One Printer,
Print/Copy/Scan:
<strong>$699.99</strong></li>
<li>Proview
Technology Inc. KDS K715s 17-inch LCD
Monitor,
Silver/Black:
<strong>$199.99</strong></li>
<li>Hawking
Technology Hi-Speed Wireless-G Cardbus
Card:
<strong>$9.99</strong></li>
</ul>
120
3.
Add
the following PHP code section and include
state-
ment
to the beginning of the document body. This statement
includes
an external file named inc_header.php at the start of
the
Web page.
<?php
include("inc_header.php"); ?>
4.
Add
the following PHP code section and include
statement
to
the end of the document body. This statement includes an
external
file named inc_footer.php at the end of the Web page.
<?php
include("inc_footer.php"); ?>
5.
Save
the document as CoastCityComputers.php in the
Projects
directory for Chapter 2.
Create
a new document in your text editor and add the fol-
lowing
text and elements:
<table
width="100%" style="border: 0">
<tr><td><h1>Coast
City Computers</h1></td>
<td
style="text-align: right"><strong>Buy Online or
Call
1-800-555-1212</strong></td></tr></table><hr
/>
6.
7.
Save
the document as inc_header.php in the Projects direc-
tory
for Chapter 2.
Reinforcement
Exercises
8.
Create
a new document in your text editor and add the fol-
lowing
text and elements:
<hr
/>
<table
width="100%" style="border: 0">
<tr><td><strong>Updated</strong> 06
January,
2010</td>
<td
style="text-align: right">© 2003 by Coast
City
Computers.</td>
</tr>
<tr><td>
<a
href="http://validator.w3.org/check/
referer"><img
src="http://www.w3.org/Icons/valid-xhtml10"
alt="Valid XHTML 1.0!" height="31"
width="88" /></a>
</td>
<td style="text-align: right; vertical-align:
top">All Rights Reserved.</td></tr>
</table>
121
9.
Save the document as inc_footer.php in the Projects direc-
tory for Chapter 2.
10. Upload the CoastCityComputers.php, inc_header.php, and
inc_footer.php files to the server.
11. Open the CoastCityComputers.php file in your Web browser
by entering the following URL: http://<yourserver>/PHP_
Projects/Chapter.02/Projects/CoastCityComputers.php. The
contents of the header and footer documents should appear
on the Web page.
12. Close your Web browser window and text editor.
Exercise 2-6
You will use an appropriate looping statement to write a script that
displays a list of the Celsius equivalents of zero degrees Fahrenheit
through 100 degrees Fahrenheit. To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius,
subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature, and then multiply
the remainder by (5/9). To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, multiply
the Celsius temperature by (9/5), and then add 32. Use the round()
function you learned in Chapter 1 to display the Celsius tempera-
ture to one place after the decimal point. Save the document as
TempConversion.php.
CHAPTER
2
The
index
page is the
default page
that a Web
server dis-
plays in the
browser if a specific
filename is not part
of the requested
URL. If you enter
http://<yourserver>/
ChineseZodiac/ in the
browser, by default the
Web server will search
the ChineseZodiac Web
folder for an index page
using a list of filenames
defined in the server
configuration. A standard
list of filenames would
likely include the follow-
ing: index.html, index.
php, index.shtml, and
index.htm. The first file-
name from the list that
the server encounters
(from left to right) will be
opened in the browser.
Functions and Control Structures
Discovery Projects
The Chinese zodiac site is a comprehensive project that will be
updated in the Discovery Projects section at the end of each chapter.
All files for the site will be saved in a directory named ChineseZodiac
in the base Web folder on the server.
122
Discovery Project 2-1
In your text editor, use XHTML scripting to develop the Chinese
zodiac template page, which will include five sections: Header,
Footer, Text Navigation, Button Navigation, and Dynamic Content.
These sections will be populated with five include files. Use a table
layout with CSS formatting or lay out the entire site with CSS. For
this initial layout page, insert a placeholder in each section (i.e.,
[This is the header placeholder]) to identify the content that
will be included later. Save the file as index.php, upload it to the
ChineseZodiac folder, and view the file in the Web browser to verify
that it displays as intended.
Discovery Project 2-2
For each of the template sections in the index.php page, create an
include file. Remember that an include file requires only the XHTML
tags to format the content, not the entire XHTML skeleton tags
(<html>, <head>, <title>, and <body>).
Description
Inserts the banner image created in Discovery Project 1-1.
Inserts the nine buttons created in Discovery Project 1-2. Code to submit the
buttons will be inserted in a later project.
Inserts the code for a text links bar. Code to turn the text links into hyperlinks
will be inserted in a later project.
Inserts a copyright symbol and the current year.
Inserts a placeholder [Insert home page content here].
Include Filenames
inc_header.php
inc_button_nav.php
inc_text_links.php
inc_footer.php
inc_home.php
Table 2-1
Include files for the Chinese zodiac Web site
Create an Includes folder within the ChineseZodiac folder. Save each
of the include files (with the names listed in Table 2-1) and upload
the files to the Includes folder in the ChineseZodiac folder in the root
Web directory on the server.

Discovery
Projects
Because
directory
precedence
is set in the
server con-
figuration file, it is impor-
tant to test your server’s
order of precedence.
Discovery Project 2-3
In index.php, replace the [Placeholders] with include statements to
include the five include files created in Discovery Project 2-2, passing
the name of the respective include file to the include statement. Save
the index.php file and upload the document to the ChineseZodiac
folder on the server. View index.php in the browser to verify that each
of the template sections displays the correct include file.
123
Discovery Project 2-4
Write a for loop that displays a table with the 12 Chinese zodiac
signs as column headers, and with the years displayed below the
appropriate column heading. Begin the table with the year 1912 and
end with the current year. You may want to use the modulus operator
to determine the number of columns in each row of the table.
Use an array to store and display a picture of the appropriate sign
below the text header in each column. Use the pictures that you
found and uploaded in Discovery Project 1-4.
Save the script as Chinese_Zodiac_for_loop.php in the
ChineseZodiac folder and upload the document to the Web server.
Discovery Project 2-5
Modify the previous script to display the same table using a while
loop. Save the script as Chinese_Zodiac_while_loop.php in the
ChineseZodiac folder and upload the document to the Web server.

CHAPTER
Manipulating
Strings
In
this chapter you will:
Construct
text strings
Work
with single strings
Work
with multiple strings and parse strings
Compare
strings
Use
regular expressions
3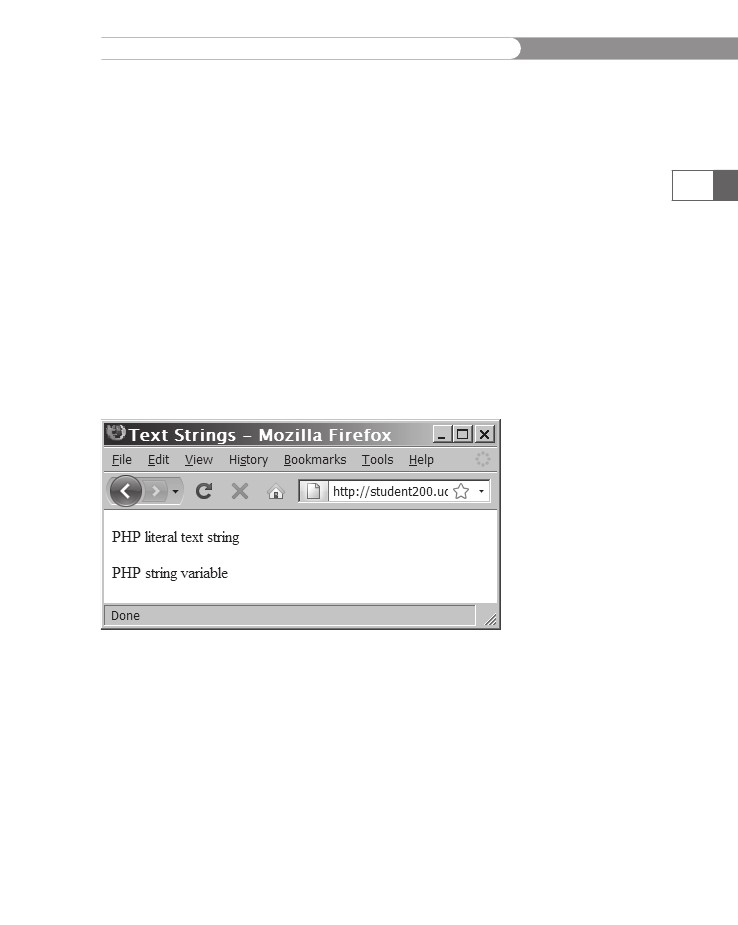
Constructing
Text Strings
PHP
is most commonly used for producing valid XHTML code and
for
processing form data submitted by users. Because all XHTML
code
and form data are strings, a good PHP programmer must be
adept
at dealing with strings. This chapter discusses techniques for
manipulating
strings.
125
Constructing
Text Strings
As
you learned in Chapter 1, a text string contains zero or more char-
acters
surrounded by double or single quotation marks. You can use
text
strings as literal values or assign them to a variable. For example,
the
first statement in the following code displays a literal text
string,
whereas
the second statement assigns a text string to a variable. The
third
statement then uses the echo
statement
to display the text string
assigned
to the variable. Figure 3-1 shows the output of this code.
echo
"<p>PHP literal text string</p>";
$StringVariable
= "<p>PHP string variable</p>";
echo
$StringVariable;
Figure
3-1
Different
ways of displaying text strings
You
can also surround a text string with single quotation
marks.
Regardless of the method you use, a string must begin
and
end with the same type of quotation mark. For example,
echo
"<p>This is a text string.</p>"; is
valid because
it
starts and ends with double quotation marks. Likewise,
echo
'<p>This is a text string.</p>'; is
valid because it begins
and
ends with single quotation marks. By contrast, the statement
echo
"<p>This is a text string.</p>'; is
invalid because it starts
with
a double quotation mark and ends with a single quotation mark.
In
this case, the string would display incorrectly because the PHP
scripting
engine cannot tell where the literal string begins and ends.