- •Методичні рекомендації
- •Вступ до методичних рекомендацій
- •Unit I Painting
- •II Reading
- •III. Language
- •IV. Text understanding
- •VII Language
- •VIII Text understanding
- •Exercise 19. Define the type of technique of paintings. What techniques were not mentioned in this text?
- •XI. Oral Practice
- •I. Vocabulary
- •II Reading
- •III. Language
- •IV. Text understanding
- •V. Oral practice.
- •VI Reading and Comprehension
- •Text b Tone, form and proportion, perspective
- •VII. Language
- •VIII Text understanding
- •IX Oral Practice
- •X Reading and Comprehension
- •XI Oral Practice
- •II Reading
- •III. Language
- •IV. Text understanding
- •Guideline – керівний принцип
- •Text b Rule of thirds
- •Rule of odds
- •VII Language
- •VIII Text understanding
- •X Reading and Comprehension
- •Text c Top 10 Painting Tips for Strong Compositions
- •Text d Guide on Choosing the Appropriate Format When You Design a Drawing or Painting
- •A painting can take on different looks with each format.
- •XI. Oral Practice
- •IV Color
- •II Reading
- •Text a Color theory
- •III. Language
- •IV. Text understanding
- •Text b What is Color Harmony?
- •Creating Color Harmony
- •Color Harmonies
- •VII Language
- •VIII Text understanding
- •IX Reading and Comprehension
- •Examples
- •Examples
- •Examples
- •X. Oral Practice
- •Appendix
- •Table 3
- •Список рекомендованої літератури
VIII Text understanding
Exercise 15. Answer the questions:
What is color harmony?
What do successful color schemes rely on?
What is the difference between monochromatic and analogous harmony?
How are tetrad, diad and triad combinations made up?
How is a double complement harmony organized?
How many colors does a split-complementary color contain?
What way do complementary colors appear on the color wheel?
IX Reading and Comprehension
Exercise 16. Skim the text C. Give the title to it. Define its main points and summarize them. Explain the essence of the work of a graphic designer.
Text D
If you’re going to use color effectively in your designs, you’ll need to know some color concepts and color theory terminology. A thorough working knowledge of concepts like chroma, value and saturation is a key to creating your own awesome color schemes.
Hue
Hue is the most basic of color terms and basically denotes an object’s color. When we say “blue,” “green” or “red,” we’re talking about hue. The hues you use in your designs convey important messages to your website’s visitors.
Examples
|
|
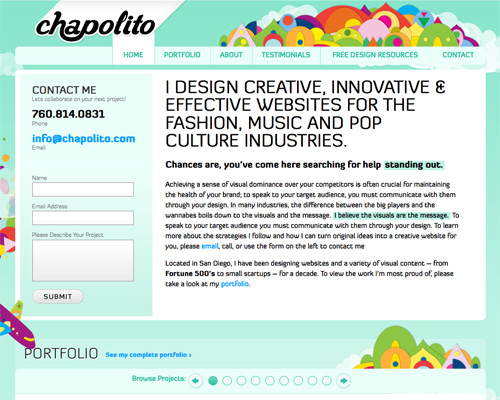
Using a lot of pure hues together can add a fun and playful look to a design, as done in the header and elsewhere on this website.
Chroma
Chroma refers to the purity of a color. A hue with high chroma has no black, white or grey in it. Adding white, black or grey reduces its chroma. It’s similar to saturation but not quite the same. Chroma can be thought of as the brightness of a color in comparison to white.
In design, avoid using hues that have a very similar chroma. Opt instead for hues with chromas that are the same or a few steps away from each other.
Examples
|
|
Saturation
Saturation refers to how a hue appears under particular lighting conditions. Think of saturation in terms of weak vs. strong or pale vs. pure hues.
In design, colors with similar saturation levels make for more cohesive-looking designs. As with chroma, colors with similar but not identical saturations can have a jarring effect on visitors.
Examples
|
|
Value
Value could also be called “lightness.” It refers to how light or dark a color is. Ligher colors have higher values. For example, orange has a higher value than navy blue or dark purple. Black has the lowest value of any hue, and white the highest.
When applying color values to your designs, favor colors with different values, especially ones with high chroma. High contrast values generally result in more aesthetically pleasing designs.