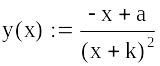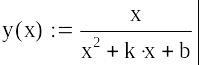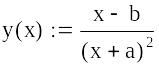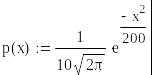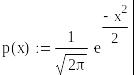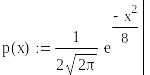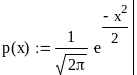- •1. Simplify the expression
- •2. Factor the expression into a product
- •IV. Разложить на простые дроби рациональную дробь:
- •5. Solve equation symbolically. If symbolical solution cannot be found solve it numerically
- •6. Solve the system of equations
- •7. Solve the system of equations graphically
- •9. Build 3d surface. Use corresponding axes scale. Use colormap, lighting and choose the best view.
- •14. Complete and solve differential equation for the next problem.
- •15.The dependence between y (Electric current) and X (Voltage) is given as a table.
- •19. Build the function that models the signal from the table. Calculate the Fourier spectrum of the signal. Build the approximation of the signal using 4 non-zero harmonics
- •The report for homework must be done as ms PowerPoint presentation
14. Complete and solve differential equation for the next problem.
There is a lake with volume V. The damaging waste flows into the lake with constant speed g (gramme per hour). The clear water flows in lake by stream with speed w (m3 per hour). Another stream flows out from the lake with the same speed (thus the volume of the lake remains constant).
Find dynamics of the pollution as a waste concentration (in g/m3) vs time
Find the time that is required to make lake clear from the waste concentration 1g/m3 if pollution stops.
Variant N |
g |
w |
V |
Variant N |
g |
w |
V |
1 |
10 |
7 |
2·106 |
11 |
12 |
9 |
8·106 |
2 |
12 |
6 |
3·106 |
12 |
13 |
8 |
2·106 |
3 |
14 |
5 |
4·106 |
13 |
14 |
7 |
3·106 |
4 |
16 |
4 |
5·106 |
14 |
14 |
6 |
4·106 |
5 |
19 |
5 |
6·106 |
15 |
15 |
5 |
2·106 |
6 |
15 |
6 |
7·106 |
16 |
16 |
4 |
5·106 |
7 |
11 |
7 |
8·106 |
17 |
17 |
5 |
6·106 |
8 |
9 |
5 |
9·106 |
18 |
18 |
4 |
7·106 |
9 |
7 |
4 |
8·106 |
19 |
19 |
6 |
106 |
10 |
10 |
6 |
7·106 |
20 |
20 |
7 |
9·106 |
15.The dependence between y (Electric current) and X (Voltage) is given as a table.
x |
0
|
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
65 |
70 |
y |
0 |
2 |
8 |
50 |
145 |
160 |
190 |
220 |
222 |
279 |
270 |
276 |
270 |
279 |
Build the mathematical model as function according to variant number. Unknown coefficients find using least squares method. Obtain the predicting value of current for the voltage 25 using built model. Plot the graph with given points (boxes) and built function (line).
1. |
|
11 |
|
2. |
y(x)=a·x2+b·x+c |
12 |
|
3. |
y(x)=k·x3+a·x2+b·x+c |
13 |
y(x)=a·x3+b·x2+c·x |
4. |
|
14 |
|
5. |
|
15 |
|
6. |
y(x)=a·x2+b·x |
16 |
y(x)=a·x4+b·x+c |
7. |
|
17 |
|
8. |
|
18 |
|
9. |
|
19 |
y(x)=a·x4+b·x3+c |
10. |
y(x)=a·x2+b·x |
20 |
y(x)=a·x·exp(–(x–b)2) |
16. Build the graph according the table of values using cubic spline (task for all variants is the same; N is number of variant).
ei
ti
Example: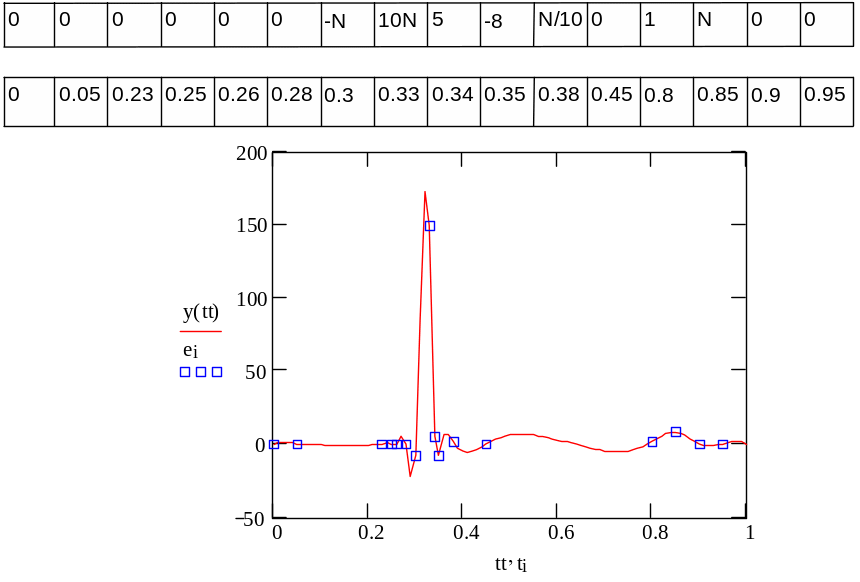
17. Find the maximum or minimum value of the function in consideration of conditions.
N |
Function |
conditions |
find |
N |
Function |
conditions |
find |
1 |
Z(x,y)=x2+y2 |
Z=2x–3y+10 |
max |
11 |
Z(x,y)=x3+5y2 |
Z=x–5y+1 |
max |
2 |
Z(x,y)=x2+2y2 |
Z=4x–3y+8 |
min |
12 |
Z(x,y)=x3–y3 |
Z=4x–5y+2 |
min |
3 |
Z(x,y)=x2–y2 |
Z=x–7y+10 |
min |
13 |
|
|
|
4 |
Z(x,y)=x3+y2 |
Z=x–5y+1 |
max |
14 |
Z(x,y)=x2+y2 |
Z=2x–3y+10 |
min |
5 |
Z(x,y)=x3–y3 |
Z=9x–5y+1 |
max |
15 |
Z(x,y)=x2+2y2 |
Z=4x–3y+8 |
max |
6 |
|
Z=x–y+2 |
max |
16 |
|
Z=0.2x+0.3y+5 |
max |
7 |
|
Z=x+0.1y+2 |
min |
17 |
|
Z=x–2y+1 |
max |
8 |
Z(x,y)=x2–y2 |
Z=2x–3y+4 |
min |
18 |
Z(x,y)=x2–2y2 |
Z=x–6y+11 |
min |
9 |
|
Z=0.1x+y+5 |
min |
19 |
Z(x,y)=x2+y2 |
Z=2x+3y+4 |
max |
10 |
Z(x,y)=x·y |
Z=5 |
min |
20 |
Z(x,y)=x·y |
Z=5–x2 –y2 |
min |
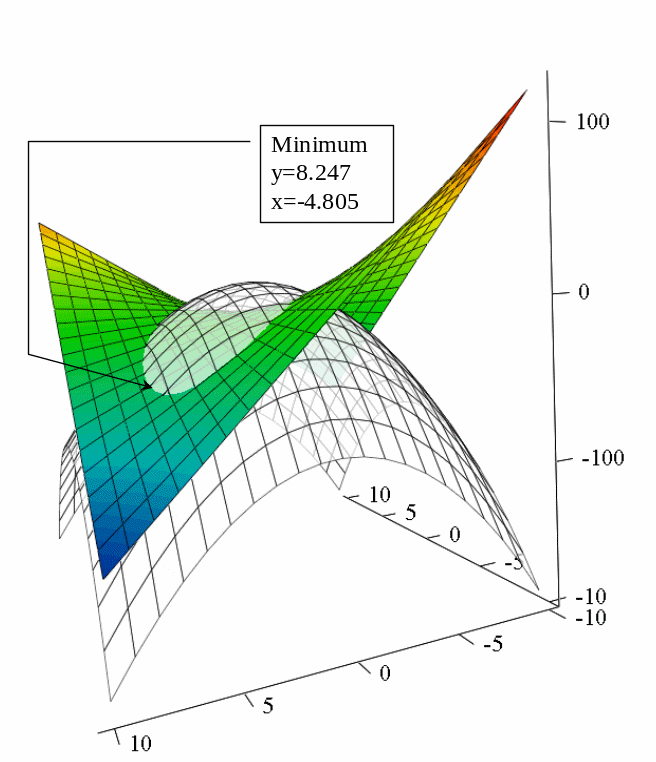
Plot 3D graph of the function and surface of conditions. Save the picture in bit-map and show the point of minimum (maximum).
Example:
The probability distribution of casual value x is given in the table. Calculate the probability of existing x within interval [a, b]. Draw the graph, copy it in the report as a vector graphics and fill by red color the square corresponding probability that has been found.
N |
P(x) |
a |
b |
N |
P(x) |
a |
b |
1 |
|
-1 |
-0.5 |
11 |
|
20 |
600 |
2 |
P(x)=e–x |
1 |
2 |
12 |
P(x)=1 |
0 |
0.1 |
3 |
|
0 |
4 |
13 |
|
2 |
25 |
4 |
|
-1 |
1 |
14 |
|
0 |
1 |
5 |
|
5 |
10 |
15 |
|
-1 |
1 |
6 |
P(x)=0.2e–x/5 |
0 |
0.2 |
16 |
P(x)=1–0.5x |
1 |
1.1 |
7 |
P(x)=2–2x |
0 |
0.3 |
17 |
P(x)=3e–3x |
0 |
1 |
8 |
|
0.5 |
2.2 |
18 |
|
-3 |
|
9 |
|
1 |
1.1 |
19 |
|
0 |
25 |
10 |
|
-3 |
3 |
20 |
|
-2 |
2 |
Example: