- •Unit 4 The Role of Environment in Rig Design Text 1. Rotary Rig Types
- •Land Rigs
- •Mobile Offshore Rigs
- •Introductory exercises
- •Match the words with their translations:
- •Give English equivalents:
- •Complete the sentences:
- •6. Make up a plan of the text and report on it in brief. Text 2. Offshore Drilling Platforms
- •Active Vocabulary
- •Introductory exercises
- •Give Russian equivalents.
- •Give English equivalents.
- •3. Answer the following questions keeping close to the text.
- •Practicing in translation
- •1. Translate the following sentences into Russian.
- •2. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •Give written translation of the text. Bottom-Supported Units
- •Sight translation. Offshore drilling
- •Text 3. Floating Units
- •Introductory exercises
- •1. Match the words with their meanings:
- •4. Express the same in Russian:
- •5. Answer the following questions:
- •Practicing in translation
Sight translation. Offshore drilling
For offshore drilling, it is crucial to construct a platform to maximize the drills' extraction, while at the same time ensuring the safety of the workers by compensating for the water's natural movement. When the drills are in operation, there is a subsea drilling template that connects the underwater well to the floating platform.
The subsea template is floated to the sea floor from the platform where it digs a small hole in the ground to "bury" itself into the seafloor. It remains connected to the platform through several elastic cables, which allow the drilling platform to sway while the subsea template remains anchored. Another component of offshore rigs is the blowout preventer, which is basically a large valve on the offshore rig that prevents oil from spilling out of the drill and mixing with water.
The blowout preventer is operated by a blowout specialist. The piece called the "marine riser" extends from above the blowout preventer onto the floating platform.
The marine riser is the center piece in a closed circuit system that acts as the transport for liquid from the sea floor onto the drilling vessel. Inside the preventer is the drillbit and drillstring. It is essential that the preventer be strong, yet flexible enough to adjust to the drill platform's movement.
Like onshore drilling, offshore drilling employs rotary drilling as its primary means to unearth crude oil. Rotary drilling is not much different that drilling that you would do around your house, it is only conducted on a larger scale. The idea is to cut into the earth using Steel Tooth Rotary Bits or diamond studded drill bits to reach the reserve. Once the reserve has been drilled, the product can be removed and sent to the refinery for processing.
Advances in drilling and production technology have increased the possibility that offshore platforms can be controlled from an onshore location. Including a function to control the automatic shutoff that will minimize pollution.
Notes:
Drilling template – опорная труба для морского бурения; временная донная направляющая платформа (служащая в качестве устья скважины в морском бурении)
Reference: ttp://www.jobmonkey.com/oilindustry/html/offshore_drilling_platforms.html
Text 3. Floating Units
Floating offshore drilling rigs include semi-submersibles and drill ships. Semi-submersibles, because of their design, are more stable than drill ships. Drill ships can carry more drilling equipment and supplies, which often make them the choice in remote waters.
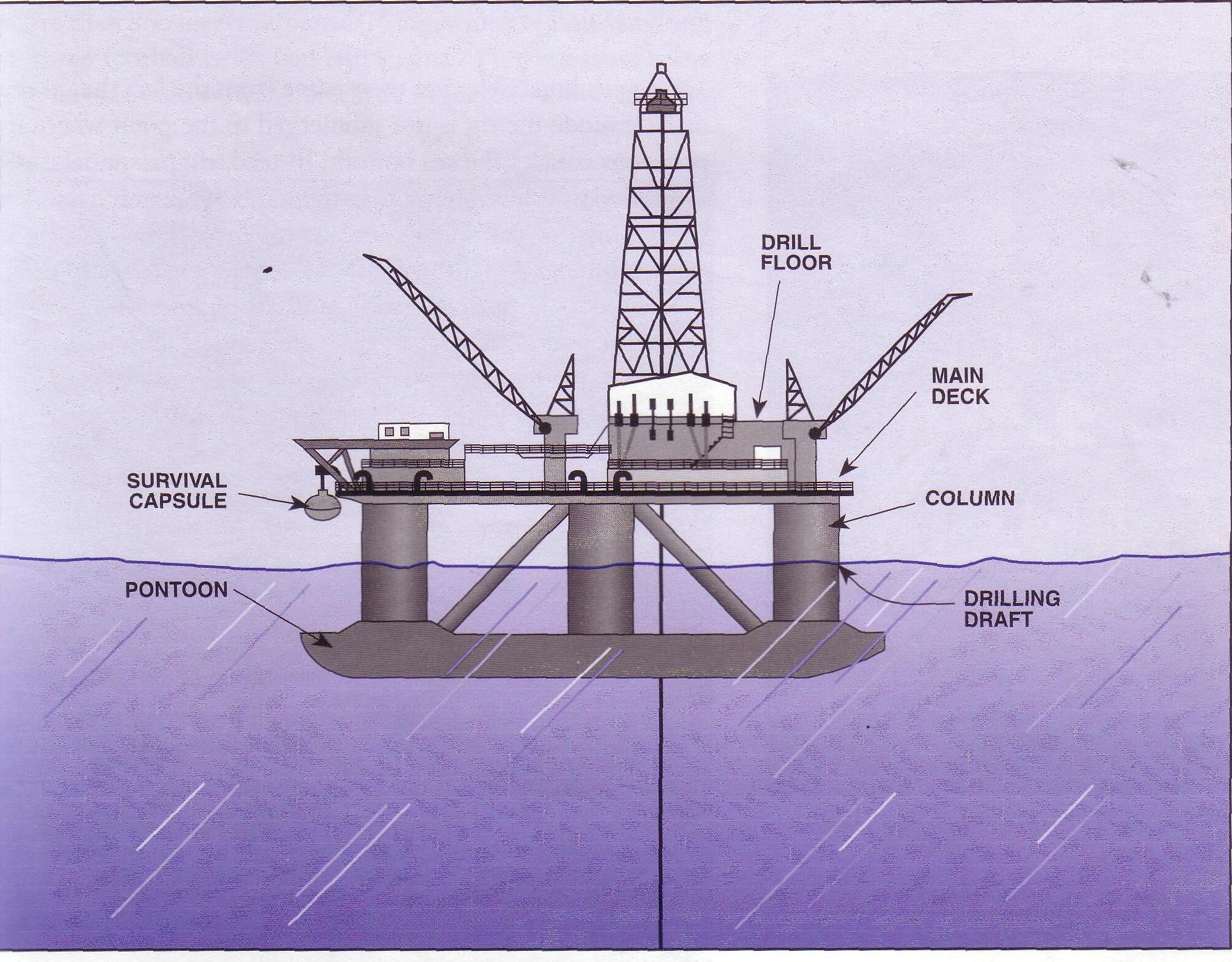
Most semi-submersible rigs have two or more pontoons on which the rig floats (fig. 6).
Figure 6. A submersible |
A pontoon is a long, relatively narrow, and hollow steel float with a rectangular or round cross section. When a semi-submersible is moved, the pontoons contain mostly air so that the rig floats on the water’s surface. In most cases, towboats then tie onto the rig and move it to the drill site. Some semi-submersible rigs are self-propelled – they have built-in power units that drive the rig from one site to another.
|
Semi-submersibles get their name from the fact that in the drilling mode the rig is not submerged to the point where its pontoons to make them submerge only a few metres below the water’s surface.
The rig is “semi-submerged”. With its pontoons submerged below the waterline, waves do not affect the rig as much as they do when it floats on the surface. A semi-submersible rig offers a more stable drilling platform than a drill ship that drills while floating on the water’s surface.
Large cylindrical or square columns extend upward from the pontoons. The main deck of a semi is big and rests on top of the columns. Semis (short for submersibles) often use anchors to keep them on the drilling station. Workers release several large anchors from the deck of the rig. An anchor-handling boat crew sets the anchors on the seafloor. Semis are capable of drilling in water thousands of metres deep.
The latest semis are capable of drilling in water depths of 2,500 metres. Semis can drill holes up to 10,000 deep. Indeed, semi-submersibles are among the largest floating structures ever made. The biggest ones soar to over 30 metres tall and their main decks can be 2,500 square metres.
A drill ship is also a floater. Drill ships are very mobile because they are self-propelled and have a streamlined hull, much like a regular ocean-going ship. A company may choose a drill ship to make hole in remote waters, far from land.
A drill ship can move at reasonable speeds under its own power. Its ship-shaped hull can carry a large amount of the equipment and material required for drilling. Frequent resupplying from a shore base is not necessary.
The latest drill ships can drill in water depths approaching 3,000 metres, or nearly 3,2 kilometres. They can drill holes over 10,000 metres deep. These big drill ships are more than 250 metres long, which is almost as long as three football fields laid end to end. They measure some 30 metres wide, or a little wider than a football field.
Anchors keep some drill ships on station while drilling, but those drilling in deep water require dynamic positioning. Dynamically positioned drill ships use computer-controlled thrusters and sophisticated electronic sensors. Thrusters are power units with propellers that the builder mounts fore and aft on the drill ship’s hull below the waterline.
Once the dynamic positioning operator tells a computer exactly where it should keep the rig positioned, the computer, using information transmitted by the sensors, automatically controls the thrusters. The thrusters offset wind, wave, and current forces that would move the rig away from the desired position.
Whether on land or offshore, and whether large, medium, or small, all rigs require personnel to operate them. The people who drill wells usually work for a company whose business involves drilling, either directly or indirectly. So, let’s look next at companies involved in drilling and the personnel who do the work.