- •Английский язык : общие вопросы электричества
- •Содержание
- •Введение
- •I. Прочитайте и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания
- •II. Прочитайте и переведите текст
- •III. Ответьте на следующие вопросы, пользуясь информацией из текста
- •IV. Составьте 5 предложений , комбинируя подходящие части, данные в колонках I и II
- •V. Найдите неправильные утверждения и исправьте их
- •Прочитайте заголовок текста. Скажите, о чем может идти речь в тексте. Прочитайте текст
- •How magnetism makes current
- •II. Прочитайте и переведите текст How magnetism makes current
- •What is a Magnetic Field?
- •II. Прочитайте и переведите текст
- •VIII. Расскажите о разнице между
- •Closed circuits and open circuits
- •Series and parallel circuits
- •Insulators, conductors and semiconductors
- •I. Прочитайте и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания
- •II. Прочитайте текст. Выделите в каждом абзаце текста ключевые слова и предложения. Используя их, определите основную мысль каждого аб-заца
- •III. Прочитайте и переведите текст
- •Insulators, conductors and semiconductors
- •IV. Ответьте на следующие вопросы, пользуясь информацией из текста
- •I. Прочитайте и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания
- •II. Прочитайте и переведите текст Electromotive Force
- •III. Ответьте на следующие вопросы, пользуясь информацией из текста
- •VIII. Определите, какой частью речи являются неличные формы в следующих предложениях. Переведите предложения на русский язык
- •IX. Прокомментируйте ту часть текста, которая показалась вам наиболее интересной
- •Unit Of Magnetic Force
- •III. Ответьте на следующие вопросы, пользуясь информацией из текста
- •What electrical force does a single cell from a flashlight create?
- •IV. Дополните следующие предложения фактами из текста
- •V. Переведите предложения, содержащие условие
- •I. Прочитайте и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания
- •II. Прочитайте и переведите текст
- •III. Ответьте на следующие вопросы, пользуясь информацией из текста
- •IV. Переведите на русский язык цепочки существительных. Обратите внимание, что последнее слово является опорным
- •V. Выразите свое согласие или несогласие, употребляя следующие слова и выражения. Подтвердите свою точку зрения фактами из текста
- •VI. Добавьте подходящие предлоги, где необходимо и составьте предложения со следующими инфинитивами
- •VII. Прокомментируйте ту часть текста, которая показалась вам наиболее интересной
- •VIII. Прочитайте текст без словаря
- •I. Прочитайте и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания
- •II. Прочитайте и переведите текст
- •III. Ответьте на следующие вопросы, пользуясь информацией из текста
- •IX. Выделите суффиксы слов с одинаковым корнем и переведите слова на русский язык
- •X. Расскажите, по-английски или по-русски , какая информация в тексте является для вас новой, а какая вам уже известна
- •I. Прочитайте и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания
- •II. Прочитайте и переведите текст
- •VII. Составьте новые слова с тем же корнем и определите, какой частью речи они являются
- •VIII. Объясните значение следующих терминов на английском языке
- •IX. Прокомментируйте ту часть текста, которая показалась вам наиболее интересной
- •Most small aircraft are equipped with a 28 volt direct current electrical system. The system is powered by an Alternator which drives the electrical devices and stores energy in the battery.
- •I. Прочитайте и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания
- •II. Прочитайте и переведите текст
- •450000, Уфа-центр, ул.К.Маркса,12
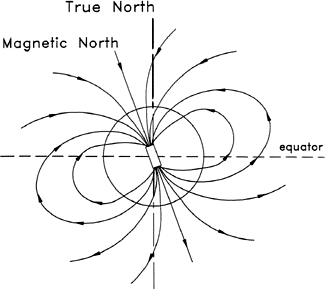
What is a Magnetic Field?
Magnetism has been known for thousands of years, though until relatively recently (ca. 1820) the only magnets were naturally occurring magnetic rocks called "lodestones" (magnetite). The word "magnetism" derives from the district of Magnesia in Asia Minor where lodestones were found. These lodestones were observed to attract bits of iron, just like a kitchen magnet which is attracted to your refrigerator door. The space around the magnet is the site of the magnetic field, where the magnetic force is felt by the bit of iron. At each point around the magnet, the magnetic field has both a strength and a direction.
We are all familiar with magnetic fields, from the magnets on your refrigerator door to the Earth itself. For example, if you have ever used a compass you are using the Earth's magnetic field to find direction. In fact, the Earth can be considered a gigantic magnet. The pattern of the Earth's magnetic field is roughly like one that would result from a short, powerful magnet near the Earth's center. |
|
|
Like the Earth, the Sun too has a magnetic field. However, on the Sun the magnetic field is far more complicated. But, before studying the Sun's magnetic field in detail, we need to understand a few basic concepts. |
Experiments using magnets and iron filings are familiar to many of us. A magnet is placed under a pane of glass or sheet of paper and iron filings are sprinkled over the top. The magnetic field pushes on the iron filings, forcing them to line up in patterns which curve around the magnet until they point in the same direction as the magnetic field. This allows you to "see" the magnetic field surrounding the magnet. There are no iron filings on the Sun, but we can still "see" the magnetic field outlined by the hot gases in the Sun's corona. |
Lesson 3
Electrical circuit
I. Прочитайте и запомните следующие слова и словосочетания
electrical circuit |
электрическая схема, электрическая цепь |
earth ground |
заземление |
appliance |
1) приспособление, прибор; 2) применение; 3) бытовое электронное или электрическое оборудование |
resistor |
1) резистор; 2) катушка сопротивления |
capacitor |
конденсатор |
flash |
1) вспышка; 2) дуговой разряд, дуговой огонь |
to complicate |
усложнять, запутывать |
to cause |
1) быть причиной, причинять, воздействовать; 2) заставить |
hazard |
1) риск, опасность; 2) шанс; 3) помеха, препятствие |
to prevent |
1) мешать, препятствовать; 2) предотвращать |
damage |
1) вред, повреждение; 2) убыток, ущерб |
II. Прочитайте и переведите текст
Electrical circuit
An electrical circuit is a path which electrons from a voltage or current source follow. Electric current flows in a closed path called an electric circuit. The point where those electrons enter an electrical circuit is called the "source" of electrons. The point where the electrons leave an electrical circuit is called the "return" or "earth ground". The exit point is called the "return" because electrons always end up at the source when they complete the path of an electrical circuit. The part of an electrical circuit that is between the electrons' starting point and the point where they return to the source is called an electrical circuit's "load".
Electrical circuits typically use alternating current sources. The load of an electrical circuit may be as simple as the wiring for a house, with outlet boxes to which electrical appliances like refrigerators, televisions, or microwave ovens can be connected as loads. But the loads for electrical circuits can also be quite complicated, such as the load upon the output of a hydroelectric power generating station.
Electronic circuits typically use low voltage direct current sources. The load of an electronic circuit may be as simple as a few resistors, capacitors, and a lamp, all connected together to create the flash in a digital camera. Or an electronic circuit can be complicated, connecting thousands of resistors, capacitors, and transistors to create the microprocessors that make computers possible.
The current flowing in an electrical or electronic circuit can be suddenly increased when a component part fails. The increase in current can cause serious damage to other components in the circuit. Or the failure can create a fire hazard. To protect the other components, or to prevent a fire hazard, a device called a "circuit breaker" can be wired into a circuit. The circuit breaker will open, or "break", the circuit in which it is installed when the current in that circuit becomes too high.
III. Ответьте на следующие вопросы, пользуясь информацией из текста
1. How does electric current flow?
2.Why is the exit point called the “return”?
3. The loads for electrical circuits are always complicated, aren’t they?
4. What can the increase in current create?
5. What is the aim of a “circuit breaker”?
IV. Найдите сказуемые в следующих предложениях и определите их видо-временную форму. Переведите предложения на русский язык.
The circuit is known to be a complete path which carries the current.
The load of electronic circuit may be simple.
To protect the components, a circuit breaker can be wired.
In the short circuit the current is allowed to return to the source of supply.
It is impossible to work with electricity without circuits.
V. Образуйте от следующих глаголов различные части речи и переведите их на русский язык
To develop - развивать, to maintain - поддерживать , to equip - обеспечивать, to install - устанавливать, монтировать , to indicate – указывать, to attach - присоединять, прикреплять, to determine - определять, устанавливать .
VI. Изложите вкратце содержание текста на английском языке. Используйте следующие ключевые слова
Electric current, the “source” of electrons, “earth ground”, electrical circuit, electronic circuit, the increase in current, the circuit breaker
VII. Прочитайте текст о типах электрических цепей без словаря
А fundamental part of circuit analysis is determining whether the matter has a return path to the power source. If the matter is blocked from returning to the power source, either wholly or partially, the entire assemblage will be prevented from accomplishing work. In an electrical circuit, an open circuit is caused intentionally when a user opens a switch or unintentionally when vibration or mechanical damage severs a wire. In a pneumatic or hydraulic circuit, this occurs when a valve is closed or there is a leak in one of the lines or components.
In electrical circuits, closing a switch creates a closed loop for the electrons to flow through. This is sometimes referred to as "completing the circuit." Other synonyms are also used.
In an electrical or electronic circuit, sometimes an unintended connection is made, such as when insulation is broken, frayed, melted or chewed by rodents, or a technician inserts a metal tool into a live device. When this happens, current bypasses some or all of the components in the circuit, taking a "shorter" path back to the power source. This can lead to excessive current drain, which in turn generates excessive heat, damaging or destroying sensitive parts of the system such as transistors and ICs.
In electronics,components of an electronic circuit can be connected in series or in parallel. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the components. Components connected in parallel are connected such that there are multiple independent paths along which the current can flow; in other words, the current is split among the different paths. A circuit composed solely of components connected in series is known as a series circuit; likewise, one connected completely in parallel is known as a parallel circuit.