
- •Module 6. Optics Unit 1. Concept of Light. Active vocabulary
- •Exercise 1. Read the definition of optics as a part of physics and discuss the questions below.
- •Reading
- •Early concepts of light
- •The Speed of Light
- •Light and transparent materials
- •Opaque materials
- •Unit 2. Reflection. Specular and Diffuse Reflection.
- •Reading
- •Interaction of light with matter. Reflection
- •The Law of Reflection
- •Specular and Diffuse Reflection
- •Application of specular and diffuse reflection
- •Unit 3. Refraction.
- •Refraction
- •Video watching ‘Rainbows’ (Video 6.2)
- •Unit 4. Dispersion.
- •Dispersion of light by prisms
- •Exercise 45. Match the word-combinations and translate them into Ukrainian.
- •Exercise 46. Insert some word-combinations from exercise 45.
- •Quiz “Dispersion of light”
- •Unit 5. Interference and Diffraction.
- •7. Diffraction [dɪ'frækʃ(ə)n] дифракція
- •Diffraction
- •Young’s Interference Experiment
- •Unit 6. Lenses and Their Application.
- •Medical application
- •Solar energy
- •10. Please help me _____ the rat.
- •Unit 7. Optical Instruments.
- •Optical instruments
- •The Camera
- •The Telescope
- •The Compound Microscope
- •Video watching ‘Amazing History of the Telescope’ (Video 6.3)
Unit 2. Reflection. Specular and Diffuse Reflection.
Active vocabulary
1. Absorption [əb'zɔːpʃ(ə)n] поглинання, абсорбція
2. Alignment [ə'laɪnmənt] вирівнювання
3. Angle of incidence ['æŋgl] ['ɪnsɪdəns] кут падіння
4. Angle of reflection [rɪ'flekʃ(ə)n] кут відбивання
5. Artificial light [ˌɑːtɪ'fɪʃ(ə)l 'laɪt] штучне світло
6. Beam [biːm] промінь, пучок
7. (To) conduct [kən'dʌkt] проводити
8. Diffuse reflection [dɪ'fjuːz rɪ'flekʃən] дифузне / розсіяне відбивання
9. Fluorescent bulb флуоресцентна лампа,
[fluə'res(ə)nt'bʌlb] лампа денного світла
10. Heat energy [hiːt 'enəʤɪ] теплова енергія
11. Incandescent bulb лампа розжарювання
[ˌɪnkæn'desənt'bʌlb]
11. Incidence ['ɪnsɪdəns] падіння
12. Incident ray ['ɪnsɪdənt'reɪ] падаючий промінь
13. Interface ['ɪntəˌfeɪs] межа поділу (двох середовищ)
14. Law of reflection [lɔː][rɪ'flekʃən] закон відбивання
15. Lens [lenz] лінза
16. Light bulb ['laɪt'bʌlb] електрична лампочка
17. Light energy ['laɪt 'enəʤɪ] світлова енергія
18. Non-luminous object предмет, що не світиться
[nɔn'luːmɪnəs 'ɔbʤekt]
19. Normal (line) ['nɔːm(ə)l'laɪn] нормаль, перпендикуляр
20. Point of incidence [pɔɪnt,'ɪnsɪdəns] точка падіння
21. Ray of light [reɪ]['laɪt] промінь світла
22. Reflected image [rɪ'flektɪd'ɪmɪʤ] відбите зображення
23. Reflected ray [rɪ'flektɪd' reɪ] відбитий промінь
24. Reflecting surface відбивальна (дзеркальна) [rɪ'flektɪŋ 'sɜːfɪs] поверхня
25. Specular reflection дзеркальне відбивання
['spekjələ rɪ'flekʃən]
26. Thermal conduction теплопровідність
['θɜːm(ə)l kən'dʌkʃ(ə)n]
27. (To) transform [træns'fɔːm] перетворювати(ся)
Reading
Exercise 15. Read and translate the text below.
Interaction of light with matter. Reflection
The reason why the sun feels warm on your skin is that the sunlight is absorbed, and the light energy is transformed into heat energy. The same happens with artificial light, so the net result of leaving a light turned on is to heat the room. It doesn’t matter whether the source of the light is hot, like the sun, a flame, or an incandescent light bulb, or cool, like a fluorescent bulb. This process of heating by absorption is different from heating by thermal conduction. Heat can only be conducted through matter, but there is vacuum between us and the sun, us and the filament of an incandescent bulb. Heat conduction can only transfer heat energy from a hotter object to a colder one, but a cool fluorescent bulb is capable of heating something warmer than the bulb itself. Not all the light energy that hits an object is transformed into heat. Some is reflected, and this leads us to the question of how we see non-luminous objects.
The Law of Reflection
L
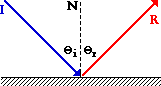
Fig. 6.2.
ight is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a law known as the law of reflection. The diagram illustrates the law of reflection.In figure 6.2, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (I). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (R). At the point of incidence where the ray strikes the mirror, a line can be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. This line is a normal line (N). The normal line divides the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray into two equal angles. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is the angle of incidence. The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is the angle of reflection. The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
