
- •Іванова с.О., Юрійчук в.М. Англійська мова: Практикум. —
- •Нізамутдінов ф.М. Дане видання — власність іфнтунг
- •Early Development
- •Modern Development
- •Components of an Automated System
- •Power to Accomplish the Process
- •Post-Text Exercises
- •Feedback Controls
- •Post-Text Exercises
- •Exercise 3.4 Read for Specific Information
- •Exercise 3.10 Focus on Translation
- •Exercise 3.11 Discussion Point
- •Machine Tools
- •Post-Text Exercises
- •Exercise 5.10 Discussion Point
- •Programmable Automation
- •Exercise 6.3 Recall Information
- •Unit 7 Robotics
- •Post-Text Exercises
- •Post-Text Exercises
- •Unit 9 Microprocessors for Fluid Properties
- •Post-Text Exercises
- •Eiffel Tower North Pillar: Automation of a Sloping Lift
- •The Lift
- •Objectives
- •Solution
- •Management of a Liquefied Petroleum Gas Storage and Distribution Centre
- •The Castelsarrasin centre
- •Objectives
- •Solution
- •Safety Interlocking Between High Voltage Supply Networks
- •The tunnel
- •The Objective
- •Technical Services Management
- •In a Multi-Media Communications Centre
- •The mmcc
- •The Objectives
- •The Solution
- •The Intelligent Building
- •Technical Services Management of a Computer Centre
- •The Installation
- •The Problem
- •The Solution
- •Automation of a Micro Hydroelectric Power Station
- •The Problem
- •The Solution
- •Bibliography
Feedback Controls
Pre-reading Task
Scan the text for answering the following questions.
1 Why are feedback controls widely used in automated systems?
2 What are five basic components of a feedback control system?
Text
Feedback controls are widely used in automated systems to ensure that the programmed commands have been properly executed. A feedback control system consists of five basic components (Figure 1.2); (1) input signal, (2) process, (3) output, (4) feedback sensing elements, and (5) controller and actuators. The input signal represents the desired value of the process output.
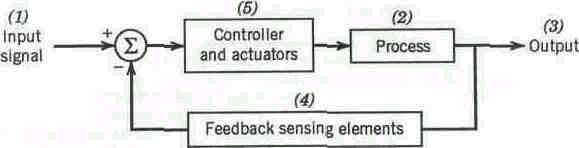
Figure 3.1 Diagram of a feedback control system.
The output is some variable that is being measured and compared with the input. The output value is a function of the process. Sensing elements close the loop between output and input. Finally, the controller and actuators compare the output with the desired input and make adjustments in the process to reduce the difference between them.
An important example of feedback control in manufacturing is a positioning system. A typical purpose of the positioning system in production operations is to move a work part to a desired location relative to a tool or work head. Examples of positioning systems include numerical control machine tools, spot welding robots, electronic component insertion machines, and coordinate measuring machines. In operation, a programmed instruction directs the positioning system to move the worktable to a certain location defined by coordinate values in an axis system (e.g., x and y values in a Cartesian coordinate system). For an x-y positioning table, two feedback control systems are required, one for each axis. A common actuator for each axis in such a system consists of a leadscrew driven by an electric motor; rotation of the leadscrew is converted into translation of the table. The controller receives the coordinate value as its input from the program and transmits a signal to the motor to drive the leadscrew. As the table moves closer to the desired location, the difference between actual position and input x -value is reduced. The actual position is sensed by a feedback sensor, commonly an optical encoder. In the ideal, the controller drives the motor until the actual table position is equal to the desired input position.
As the example of the positioning system indicates, the process input is determined by the control program in an automated system. The program consists of a sequence of steps, each step in turn being sent as an input to the controller and actuator of the system. As each step is executed, the next step is then transmitted. In this step-by-step manner, the program is executed.
Post-Text Exercises
Exercise 3.1 Read and Translate the Text into Ukrainian
Exercise 3.2 Comprehension Check.
Answer the following questions:
1 What is an important example of feedback control?
2 What are five basic components of a feedback control system?
3 Does the input signal represent the desired value of the process output?
4 How many feedback control systems are required for an x-y positioning table?
5 What does the control program in an automated system consist of?
Exercise 3.3 Recall Information.
After reading the selection, tell which of the following statements about automation are true and which are false. Correct the false statements to make them true.
A feedback control system consists of three basic components.
Feedback controls are not used in automated systems.
The controller and actuators compare the output with the desired input and make adjustments in the process to reduce the difference between them.
The process input is determined by the control program in an automated system.
The program consists of a sequence of steps.
