
- •І. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Routes of Drug Administration. Parenteral Route
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Give English equivalents of the following words and word-combinations.
- •II. Explain the meaning of the following words and word-combinations.
- •III. Form synonymous pairs from the words given below.
- •IV. Discuss pros and cons of the parenteral route of drug administration.
- •VII. Read the definition and fill in the blanks with the words given in brackets. Consult the glossary.
- •VIII. Have a bit of fun.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Open the brackets using the verbs in the proper tense and voice form.
- •II. Put down the following numerals in words.
- •III. Insert articles where necessary.
- •Lesson 2 Oral Route of Drug Administration
- •І. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Oral Route of Drug Administration
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Read the following transcriptions. Write them in words and give their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •II. Substitute the words in bold type by a word or word-combination from the text.
- •III. Render the following abstract in English.
- •IV. Solve the cross-word puzzle.
- •V. Complete the sentences by choosing appropriate prepositions from those in the brackets.
- •VI. Have a bit of fun.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Change the following from direct into indirect speech.
- •II. Choose the proper modal verb from those in brackets.
- •Lesson 3 Other Routes of Drug Administration
- •І. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Other Routes of Drug Administration
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Give English equivalents of the following words and word-combinations.
- •II. Say is the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statements to make them true.
- •III. Fill in the blanks with the words given in brackets.
- •IV. Remember the following abbreviations of the routes of administration.
- •V. Discuss pros and cons of various routes of drug administration.
- •VI. Translate into English.
- •VII. Have a bit of fun.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •II. Use the infinitives in brackets in the proper form.
- •III. Translate into English.
- •І. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Preparations for Oral Route
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Explain the meaning of the following words and word-combinations.
- •II. Substitute the words in bold type by a word or word-combination from the text.
- •III. Say what form of medication it is spoken about.
- •IV. Discuss with your fellow-students the advantages of tablets. Name any disadvantages of tablets you can think of. You may use words in brackets while speaking.
- •V. Complete the sentences by choosing appropriate prepositions from those in the brackets.
- •VI. Translate into English.
- •VII. Have a bit of fun.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •Lesson 2 Suppositories
- •І. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Suppositories
- •IV. Read the following definitions of the mentioned in the text drugs.
- •V. Translate into English.
- •VI. Have a bit of fun.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •Lesson 3 Topical Medications
- •І. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Topical Medications
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Give English equivalents of the following words and word-combinations.
- •II. Read the following transcriptions. Write them in words and give their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •III. Explain the meaning of the following words and word-combinations.
- •IV. Complete the sentences by choosing appropriate prepositions from those in the brackets. Choice of Base Formulation
- •V. Solve the cross-word puzzle.
- •VIII. Read the definition and fill in the blanks with the words given in brackets. Consult the glossary.
- •IX. Have a bit of fun.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •І. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text.
- •Vitamins
- •IV. Discuss the following information with your fellow-students.
- •V. Fill in the blanks with the words given below. Discuss the text with your fellow-students.
- •VI. Render the following text in English.
- •VII. Have a bit of fun.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Paraphrase the following sentences as in the model.
- •II. Open the brackets using the verb in a required form.
- •III. Translate the following sentences into English.
- •Lesson 2 Minerals
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Minerals
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Read the following transcriptions. Write them in words and give their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •II. Match the mineral in brackets with its definition.
- •III. Discuss the following information with your fellow-students.
- •IV. Memorize the meaning of the following term-elements.
- •V. Read the definition and fill in the blanks with the words given in brackets. Consult the glossary.
- •VI. Translate into English.
- •VII. Have a bit of fun.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Paraphrase the sentences as in the model.
- •What Is a Biologically Active Additive To Food?
- •Biologically active supplements - for or against?
- •IV. Open the brackets using the verbs in the proper tense and voice form.
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Antivirals
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Read the following transcriptions. Write them in words and give their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •II. Give English equivalents of the following words and word combinations.
- •III. Substitute the words in bold type by a word or a combination of words from the text.
- •IV. Discuss with your fellow-students the clinical application, side effects and dosage forms of some antivirals.
- •Inosine Pranobex
- •V. Translate into English
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Define the forms of the participles in bold type.
- •II. Transform the sentences according to the model.
- •III. Replace one of the homogeneous predicates by Participle I.
- •Lesson 2 Antibiotics
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Antibiotics
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Read the following transcriptions. Write them in words and give their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •IV. Fill in the gaps with suitable words or word combinations given in brackets below. Discuss the text with your fellow-students.
- •V. Complete the following dialogue.
- •VI. Translate into English.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Transform the following sentences using Participle II instead of the subordinate clauses.
- •II. Open the brackets using the appropriate form of the Participle.
- •III. Translate into English using the required form of the Participle.
- •Lesson 3 Analgesics
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Analgesics
- •V. Complete the sentences by choosing appropriate prepositions from those in brackets. Entitle the complete text and translate it into Ukrainian.
- •VI. Using the table discuss with your group-mates the main differences between opioid and non-opioid analgesics.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Translate into Ukrainian paying attention to the Objective Participle Complex.
- •II. Translate into Ukrainian. Pay attention to the Subjective Participle Complex.
- •III. Translate into English using the Objective or Subjective Participle Complexes.
- •Lesson 4 Antihistamines
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Antihistamines
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Read the following transcriptions. Write them in words and give their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •II. Give English equivalents of the following words and word combinations.
- •IV. Using the information given below discuss with your group-mates characteristics of the first and second generation antihistamines.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Transform the following complex sentences into simple ones using the Absolute Participle Complex.
- •II. Translate into English using the Absolute Participle Complex.
- •Lesson 5 Antipyretics
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Antipyretics
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Give English equivalents of the following words and word combinations.
- •III. What words from the active vocabulary may convey the following meanings.
- •V. Translate into English.
- •V. Read the following information on brief history of antipyretic therapy.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Translate the following paying attention to the way the Gerund should be translated and state its functions.
- •II. Translate into English using the Gerund.
- •Lesson 5 Cardiovascular Medications
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Cardiovascular Medications
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Give English equivalents of the following from the text.
- •III. Complete the sentences by choosing appropriate prepositions from those in brackets.
- •IV. Comment on the cardiovascular drugs described in the table.
- •V. Translate into English.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Translate into Ukrainian paying attention to the Gerundial Complexes.
- •II. Combine the sentences using Gerundial Complexes.
- •Lesson 6 Gastrointestinal Drugs
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Gastrointestinal Drugs
- •IV. Translate into English.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Insert the Infinitive, Participle I or II, or the Gerund. Translate into Ukrainian.
- •II. Translate into English.
- •Lesson 7 Drugs for Cough
- •I. Active Vocabulary
- •II. Read the following text. Drugs for Cough
- •III. Vocabulary and Speech Exercises
- •I. Explain the following words and word-combinations.
- •II. Form antonymous pairs from the words given below.
- •IV. Fill in the gaps with suitable words or word combinations given in brackets below. Discuss the text with your fellow-students.
- •V. Translate into English.
- •IV. Grammar Exercises
- •I. Translate into Ukrainian. Pay attention to the Conditional Mood.
- •II. Answer the following questions as in the model.
- •Suppose you were very busy last night reviewing for a test. Would you have watched a film on tv?
- •III. Translate into English.
Lesson 4 Antihistamines
Text: Antihistamines
Grammar: The Absolute Participle Complex
I. Active Vocabulary
allergy antihistamine to counteract itching runny nose
pollen ragweed mast cell to swell stuffy nose rash hives hay fever
decongestant drowsiness restlessness moodiness blurred vision confusion difficulty urinating glaucoma |
['xlqGI] ["xntI'hIstqmJn] ["kaVntq'xkt] ['ICIN] ['rAnI"nqVz]
['pPlqn] ['rxgwJd] ['mRst"sel] [swel] ['stAfI"nqVz] [rxS] [haIvz] ['heI"fJvq]
["dJkqn'Gestqnt] ['draVzInIs] ['restlqsnIs] ['mHdInIs] ['blE:d 'vIZn] [kqn'fjHZn] ['jVrIneItIN] [glL'kqVmq] |
алергія антигістамін протидіяти, нейтралізувати що свербить ринорея (виділення водянистого слизу з носа) пилок амброзія мастоцит набрякати закладений ніс висип кропив’янка поліноз, сінна гарячка, сезонний алергічни риніт протизастійний, протинабряковий засіб сонливість невгамовність, занепокоєність різка зміна настрою розфокусований зір втрата орієнтації утруднене сечовипускання глаукома |
II. Read the following text. Antihistamines
A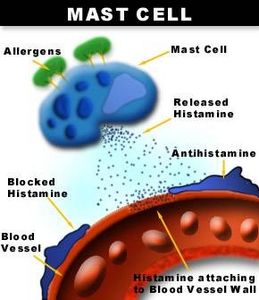 n
antihistamine is a type of drug used to fight allergic reactions. It
encompasses a broad class of drugs that can treat conditions ranging
from minor to life threatening. Different antihistamines are used for
different types of reactions. However, at their root, all
antihistamines do the same thing – they counteract a type of
chemical released by the body immune system, known as histamine.
n
antihistamine is a type of drug used to fight allergic reactions. It
encompasses a broad class of drugs that can treat conditions ranging
from minor to life threatening. Different antihistamines are used for
different types of reactions. However, at their root, all
antihistamines do the same thing – they counteract a type of
chemical released by the body immune system, known as histamine.
Antihistamines work by targeting the immune system response that leads to allergy symptoms such as itching and a runny nose. When a body comes into contact with whatever an allergic trigger may be (whether it is pollen, ragweed, or another substance), mast cells of the immune system produce substances called histamines, which act on receptors in the nose and throat. That’s what causes the tissue in the nose to swell (producing a stuffy nose), the nose and eyes to run, and the eyes to itch. Sometimes this allergic reaction also triggers an itchy rash on the skin, called hives. Antihistamines reduce or block the action of histamines by preventing them from attaching to their receptors.
Antihistamines are effective at reducing symptoms of different types of allergies, including seasonal allergies (hay fever) and food allergies, but they can’t relieve every symptom. To help treat nasal congestion, a doctor may recommend adding a decongestant (some drugs combine an antihistamine and decongestant).
Antihistamines come in different forms, including tablets, capsules, liquids, nasal sprays, and eyedrops. Some antihistamines are only available by prescription; others you can buy over the counter (OTC) at your local pharmacy or supermarket.
Examples of prescription antihistamines include: desloratadine (Clarinex), levocetirizine (Xyzal), carbinoxamine (Palgic), cyproheptadine (generic only), hydroxyzine (Atarax, Vistaril), azelastine (Astelin, Astepro nasal sprays), emadastine (Emadine eyedrops), azelastine (Optivar eyedrops), levocabastine (Livostin eyedrops). Examples of OTC antihistamines include: diphenhydramine (Benadryl), fexofenadine (Allegra), loratadine (Claritin, Alavert), chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton), brompheniramine (Dimetane), cetirizine (Zyrtec), clemastine (Tavist). Allergy eyedrops such as Emadine and Livostin can help specifically with symptoms of eye allergies, including itchy, watery eyes. Some medications contain a combination of an antihistamine and a decongestant to relieve congestion. An example is Claritin-D, which combines the antihistamine Claritin with the decongestant pseudoephedrine.
Like just about all drugs, antihistamines can cause side effects, and some antihistamines cause more side effects than others. Drugs such as Chlor-Trimeton, Tavist, and Benadryl belong to an older group of antihistamines known as “first-generation” antihistamines. They tend to cause more side effects, particularly drowsiness. Newer-generation prescription antihistamines such as Clarinex, Zyrtec, and Allegra have fewer side effects, so they may be a better choice for some people.
Some of the main side effects of antihistamines include: dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, restlessness or moodiness (in some children), difficulty urinating or inability to urinate, blurred vision confusion
When using antihistamines, follow these precautions:
If you’re taking an antihistamine that causes drowsiness, try to take it before bedtime. Avoid using during the day when driving or operating heavy machinery.
Before taking antihistamines, go over all of your medications with your doctor or pharmacist. Antihistamines may interact with other medications you are taking.
Talk to your doctor before using antihistamines if you have an enlarged prostate, heart disease, high blood pressure, thyroid problems, kidney or liver disease, a bladder obstruction, or glaucoma or other conditions that cause a rise in eye pressure. Also check with your doctor if you are pregnant or nursing.
Answer the following questions on the text.
What type of drug is an antihistamine?
How do histamines work?
What causes the tissues in the nose to swell?
Can you name any allergens? What are they?
What forms of histamines are there?
Why do some medications contain a combination of an antihistamine and a decongestant?
What antihistamines produce more severe side effects?
It is necessary to take it before bedtime, isn’t it?
Why is it required to go over all of your medications with your doctor or pharmacist before taking antihistamines?
Is it safe to take antihistamines by pregnant women or nursing mothers?
