
- •2012 Т.В. Шумило English for biologists
- •Предисловие
- •Unit 1. The science of biology.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 2. Cells as biological units.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 3. Cell structure.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 4. Cell division.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Fig. 2 Diagram of mitosis of a living cell Unit 5. Tissues and organ systems.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 6. Botany.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 7. Plant Kingdom.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 8. Plant structure.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 9. Photosynthesis.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 10. Zoology.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 11. Protozoa.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 12. Insects.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 13. Amphibians.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 14. Reptiles.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 15. Mammals.
- •Nourish ['nʌrɪʃ]
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 16. Anatomy.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 17. Skeleton and muscles.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 18. The circulatory system. Respiration.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 19. The nervous system. The brain.
- •Post-reading tasks:
- •Unit 20. The digestive system. Foods.
- •Post-reading tasks:
Post-reading tasks:
Task 1. Answer the following questions.
What is the role of the protoplasm in the life of all living organisms?
Is the chemical composition of protoplasm the same in animal and plant cells?
How much water can it contain?
What are other protoplasmic substances?
What processes are directed and controlled by protoplasm?
What do we call a cell?
What are the main parts of the cell?
What is the role of the nucleus in the physiological activities of the cell?
What are the chemical characteristics of the nucleus?
What distinguishes the cells of plants from those of animals?
Task 2. Fill in the blanks with the words and word-combinations from the text.
Nearly every organism contains lifeless as well as living … .
All the processes which go on in the body of the plant are ultimately directed and controlled by … .
A typical cell contains the …, the cytoplasm and the cell wall.
The nucleus is approximately … denser than the rest of the protoplasm and bounded by a definite membrane.
On the outside of the … a delicate membrane is developed.
The change from … to the ripe condition in many plants is due to the conversion chloroplasts into chromoplasts.
Animal cells are bounded by a thin … which consists of two or three … and is permeated by openings.
… is the main feature distinguishing plant cells from animal cells.
Task 3. Complete the text with the words from the box.
protoplasm |
elasticity |
liquid |
matter |
conditions |
metabolism |
Physically, ordinary protoplasm is a rather thick 1_________ somewhat like and egg white. It is often gelatinous. It varies widely in different parts of the plant and under different 2_________. With even the highest powers of the microscope 3____________ appears as a clear liquid in which minute granules and globules of various sizes, types and abundance are suspended. Protoplasm has a considerable contractility, 4__________ and tensile strength.
In protoplasm a wide variety of chemical and physical changes take place which we call 5___________. Extremely keen sensitivity of living material to outer changes is based on the unusual irritability of protoplasm. Furthermore all growth among organism consists in the increase in amount of living material which has the ability to convert lifeless organic 6_________ into new protoplasm exactly like itself.
TRANSLATION: Translate the following into English.
Клетка - это самая маленькая живая единица, основная структурная и функциональная единица всего живого, будь то растение, или животное, или гриб. Некоторые организмы, такие как: амеба, бактерия, некоторые водоросли и грибы состоят из одной клетки - весь организм заключен в эту одну клетку. Человеческий организм сильно отличается от этих простейших и состоит из примерно 3 000 000 000 000 клеток.
Клетки могут быть различной формы в зависимости от исполняемой функции. Клетки объединяются в ткани, органы, целые структуры (мозг, печень, кости, кожу, листья, фрукты).
В организме клетки связаны друг с другом для выполнения различных функций и задач: одни синтезируют ферменты, другие накапливают сахар или жир, составляют скелет или отвечают за связь (например, нервные клетки), на каких-то клетках лежит ответственность за защиту организма (белые кровяные тельца или стрекательные клетки медузы и растений).
Чтобы быть полноценной частичкой целого организма, большинство клеток обладают одинаковой наследственной информацией, сходными ресурсами и сходным внутриклеточным аппаратом.
Клетка высших организмов (растений или животных) состоит из следующих частей:
Клеточная мембрана, которая охватывает всю клетку. (Для прочности у растительных клеток есть еще дополнительная стенка из целлюлозы, придающая устойчивость.)
Цитоплазма - внутренняя среда клетки (за пределами ядра). Большое количество органелл. Это функциональные компоненты, напоминающие необходимые для пищеварения, накопления и выделения органы.
Ядро - командный центр клетки. Ядро содержит всю жизненно важную информацию, которая необходима клетке или целому организму, чтобы нормально функционировать, развиваться и воспроизводиться. Эта информация хранится в форме набора генов в хромосомах, которые находятся внутри ядра.
SPEAKING: Using fig.1 describe the structure of a) an animal cell (the model is given in the text below) and b) a plant cell. Tell you partner what is the difference between them. Add other facts or details besides those mentioned in the text below.
This is a drawing of a typical animal cell. The cell is filled with cytoplasm and bounded by a cell membrane. There are many different bodies in the cytoplasm, as you know. Among them are plastids, vacuoles and mitochondria. Then comes the nucleus. It is in the center of the cell. Here you can see nucleoluses and karyoplasm. The nucleus plays a very important role in the life of the cell.
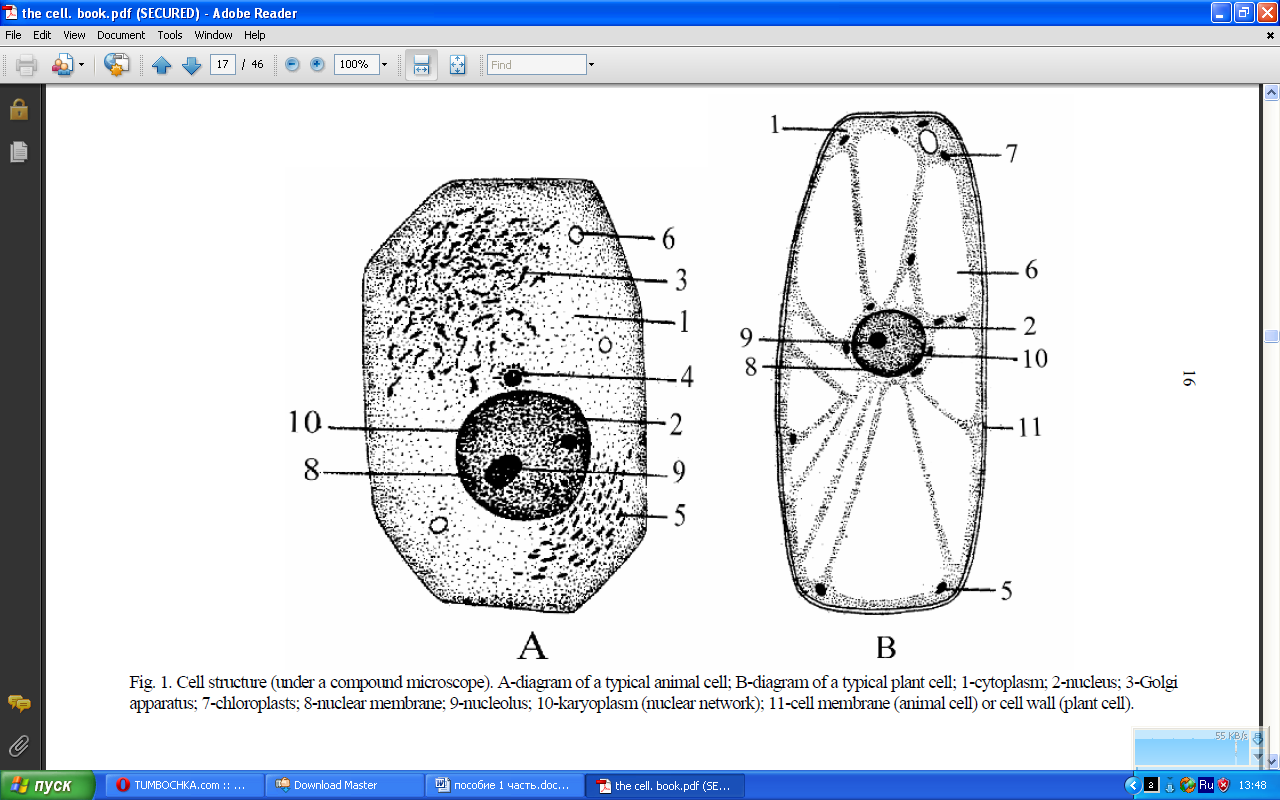
Fig. 1. Cell structure (under a compound microscope). A – diagram of a typical animal cell; B – diagram of a typical plant cell; 1 – cytoplasm; 2- nucleus; 3 – Golgi apparatus; 4 - ; 5 - ; 6 - ; 7 – chloroplasts; 8 – nuclear membrane; 9 – nucleolus; 10 – karyoplasm (nuclear network); 11 – cell membrane (animal cell) or cell wall (plant cell).
WRITING: Choose an organelle from the cell. Pretend you are this organelle for the remaining questions.
What's your job?
How others of you are there in your cell?
Do have any co-workers whose job and appearance is different from you?
When food gets taken into the cell, what do you do?
