- •Державна податкова адміністрація україни національна академія державної податкової служби україни
- •Для студентів-юристів з курсу
- •Передмова
- •Part I. Texts and Exercises unit 1
- •Transcribe and memorise the following words:
- •Read and translate the following text:
- •I am a student of law department
- •Word list
- •Answer the questions
- •Let me introduce my friend Oleg: About my friend
- •Word list
- •Find the Ukrainian equivalents in the right-hand column for the following
- •Transcribe and translate the following words:
- •Read and translate the following text: National state tax service academy of Ukraine
- •Word list
- •Find the English in the right-hand column for the following:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •Fill in the blanks with prepositions or adverbs if necessary:
- •Translate the following sentences into English:
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Speak on the topic “Our Academy”.
- •Learn the dialogue by heart.
- •Transcribe and memorise the following words:
- •Read and translate the following text: The political system of Ukraine
- •Match the following English terms with their Ukrainian equivalents:
- •Decide which is the odd word in each group and explain why. Bear in mind that more that one answer may be possible.
- •Sort out the political terms given in the box into the corresponding columns of the table according to the words with which they can go with:
- •Complete the gaps with one of the words given in the box in Activity 4. The first sentence is done for you:
- •Supply the missing members of these words families. Check your answers with the dictionary. The first word is done for you:
- •Read the texts below. Use the words given next to each line in the appropriate form related to its root to fit the space. The first is done for you:
- •Transcribe and memorise the following words:
- •Read, translate and retell the text. The Constitution of Ukraine
- •Word list
- •Match the following English words and expressions with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •Read the text and mark these statements t (true) or f (false) according to the text.
- •Choose the right preposition in brackets according to the contents of the sentences (by, under, into, of, from, to, for, with, after).
- •Translate into English the following extracts from the Constitution of Ukraine.
- •Read and retell the text. The Higher Bodies of State Authority of Ukraine
- •The political system of Great Britain
- •Word list
- •Read the text and mark these statements t (true) or f(false) according to the text
- •Fill in the blanks with the given words
- •Information for you
- •Translate the following words and word-combmnations into Ukrainian:
- •Write down as many nouns as possible with the following adjectives:
- •Match the EnglisѨ and the Ukrainian equivaleѮts:ѝ
- •Complete the sentences:
- •Translate into English:
- •Speak about Great Britain using the following information:
- •Read and translate the text The system of government
- •Word list
- •Fill in the blanks:
- •Read the following sentences and decide if they are true or false:
- •Find words and expressions in the text which mean:
- •Read and translate the text The crown
- •The political system of the usa
- •Mark these statements t (true) or f (false) according to the text. Find the part of the text that gives the correct information:
- •Substitute the active vocabulary of the lesson for the italicized parts.
- •The verbs below can all be used to form nouns. Find in the text the nouns which have related meanings and make up jour own sentences with them:
- •Who's the Chief? Match a line a with a line b
- •Rewrite the following sentences as in the example:
- •Translate the following sentences into Ukrainian.
- •Translate the following word combinations into English:
- •Translate the following sentences into English:
- •Read the text about the usa to understand what information is of primary importance or new for you.
- •What is law?
- •Word list
- •Classification of law
- •Comments
- •Word List
- •Give the English equivalents for:
- •Fill in the blanks
- •Read the following sentences and decide if they are true or false.
- •Ask questions to get the following answers.
- •Match the following.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Unit 8 Courts in Great Britain
- •Judiciary in Great Britain
- •Word list
- •Read and translate.
- •Fill in the blanks.
- •Read the following sentences and decide if they are true or false.
- •Find words and expressions in the text which mean:
- •Ask questions to get the following answers.
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Complete the following sentences by translating the words and expressions in brackets.
- •Work in pairs. Discuss the following.
- •Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian. The court system of England and Wales
- •The court system of the usa
- •Word list
- •Read and translate.
- •Find the Ukrainian in the right-hand column for the following:
- •Complete the following sentences.
- •Complete the following sentences by translating the words and expressions in brackets.
- •Match the following:
- •Read the following sentences and decide if they are true or false.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Examine the chart and read the text.
- •The organization of the federal courts today
- •Find in the text the English equivalents for the words below.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Fill in the blanks. The federal and state court systems
- •Unit 10 Legal professions
- •Legal professions in Great Britain and the usa
- •Word list
- •Read and translate.
- •Fill in the blanks.
- •Read the following sentences and decide if they are true or false.
- •Find words and expressions in the text which mean:
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Complete the following text by translating the words and expressions in brackets.
- •Choose the correct definition for each legal profession. Translate into Ukrainian.
- •Read the text and fill in the gaps with the appropriate words from the box. Sentences judge crimes behaviour murder prisoners magistrate imprisonment jury Crown
- •Match the sentences with the crimes.
- •Work in pairs and find arguments for and against the death penalty. Discuss the following questions.
- •Read, translate and discuss the text. Solicitors and barristers
- •Answer the questions.
- •Read the following text and answer the questions.
- •Match each word or expression on the left with the correct definition.
- •Read, translate and discuss the text. Attorneys in the usa
- •Speak on the profession of a lawyer in different countries. Part II. Additional reading
- •I. Political system of Great Britain
- •Read and translate the text Lawmaking process in Great Britain
- •Read and translate the text Lawmaking Process in usa
- •Making New Laws: Bills and Acts
- •Find in the text the English equivalents for the following expressions.
- •Explain the meanings of the following expressions from the text.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Read and translate the text The Executive
- •Read and translate the text Members of Parliament in Great Britain
- •Find in the text the English equivalents for the following phrases.
- •Complete the following text with the words and expressions from the box, using them in the appropriate form.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Work in pairs and discuss the following questions.
- •Read and translate the text The Election Timetable
- •Find the English equivalents for the phrases below in the text.
- •Read and translate the text Political Parties
- •II. Political system of the usa
- •The American System of Government
- •Find in the texts the English equivalents for the following words and expressions.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Read and translate the text The Constitution and the Bill of Rights
- •Complete the following text with suitable words or phrases from the text above.
- •Find the English equivalents for the expressions below in the text.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Read and translate the text Congress
- •Complete the following text by translating the words or expressions in brackets.
- •Read and translate the text The President and Federal Departments
- •Explain the meanings of the following words and expressions from the text. Make sentences with each of them.
- •Read and translate the text Federal Departments
- •Read and translate the text Checks and Balances
- •Federalism: State and Local Governments
- •Find the English equivalents for the following expressions below in the text.
- •Answer the questions
- •Read and translate the text Political Parties
- •Explain the meanings of the following expressions and give Russian equivalents for them.
- •Read and translate the text Elections
- •Find the English equivalents for the words and expressions below in the text.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Read and translate the text Political Attitudes
- •III. Courts in Great Britain and the usa
- •Read the text "Courts in England and Wales" and make comments on it. Courts in England and Wales (Part I)
- •Vocabulary Notes to text
- •Translate the micro texts “Criminal Courts”, “Magistrates’ Courts” in written form. Criminal Courts
- •Magistrates' Courts
- •Commentary and Notes
- •Read and translate the text "Courts in England and Wales" and discuss it. Courts in England and Wales (part II)
- •Read the text "Courts in Scotland" and make comments on it. Courts in Scotland
- •Vocabulary Notes to text
- •Read the text "Courts in Northern Ireland" and make comments on it. Courts in Northern Ireland
- •Commentary and Notes to the text
- •Read the text "Coroner's Courts" and make its synopsis in Ukrainian. Coroner's Courts
- •Vocabulary Notes to the text
- •Read the text "Appeals" and think over its contents. Give its annotation in Ukrainian. Appeals
- •Vocabulary Notes
- •Read and translate the text Growth of the Profession
- •Find the English equivalents for the words below in the text:
- •Answer the questions
- •Read and translate the text us Attorneys
- •Paraphrase the following expressions.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Read and translate the text The Federal Judiciary
- •Explain the meanings of the following expressions from the text and make sentences with each of them.
- •Answer the questions.
- •VI. Branches of Law
- •Read the text to understand what information is of primary importance or new for you: Law: what is it?
- •Match the following English words and expressions with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •Read and translate Civil law
- •Match the following English words and expressions with their Ukrainian equivalents:
- •Read and translate Civil law (family, contract, intellectual property)
- •Match the following English words and expressions with their Ukrainian equivalents:
- •Divide the text into logical parts and supply a title for each of them.
- •VI. Find in the text and decide from the context what the word could mean, then choose the appropriate definition.
- •Read the text to understand what information is of primary importance or new for you. Criminal law
- •Match the following English words and expressions with their Ukrainian equivalents:
- •Give the definitions for the following legal terms:
- •Answer the questions:
- •Read the text, make a plan of annotation and annotate the text. Labour Law
- •Read the text to understand what information is of primary importance or new for you. Administrative law
- •Mark these statements t (true) or f (false) according to the text.
- •Read the text to understand what information is of primary importance or new for you. Employment law
- •Part III. Grammar Exercises Дієслово to be
- •Fill in the blanks with the proper form of the verb to be:
- •Translate into English:
- •Fill in the blanks with the verb to be in the Past Indefinite Tense:
- •Write positive or negative sentences. Use am/am not, is/isn't, are/aren't.
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into English using the verb to be in the Present Indefinite or the Past Indefinite Tense.
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •A. Transform the sentences into the Past Indefinite Tense.
- •B. Transform the sentences into the Future Indefinite Tense:
- •Make the sentences interrogative
- •Ask questions according to the model.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Make the sentences negative.
- •Read and translate the sentences with the verb to be.
- •Write full sentences. Use am/is/are each time
- •Зворот there is (are, was, were, will be)
- •Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •Translate into English.
- •Make the sentences interrogative.
- •Make the sentences negative.
- •Make the sentences interrogative and negative
- •Choose the right form of the verb to be from the brackets
- •Answer the questions:
- •Put the questions to the words given in bold type:
- •Translate the sentences:
- •Read the sentences. Point out the cases when the structure to be going to indicates future time reference. Translate them.
- •Paraphrase the following sentences as in the model.
- •Дієслово to have
- •Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •Transform the sentences into the Past.
- •Transform the sentences into the Future.
- •Make the sentences negative.
- •Make the sentences interrogative.
- •Зворот have / has got
- •Answer the questions:
- •Translate into English
- •Use "many" and "much" instead of expressions such as lots of..., a lot of..., a great deal of..., plenty of...
- •Form the degrees of comparison of the following adjectives.
- •Put the adjectives in brackets into the required degrees of comparison.
- •Compare the objects according to the given example.
- •Часи групи Continuous
- •The Present Continuous Tense
- •Make the following interrogative and negative.
- •Do as you are told and say what you are doing.
- •Do as you are told and answer the questions: What are you doing at the moment? or What is he (she) doing now?
- •Ask questions as you are told.
- •Put questions to the italicized words.
- •Translate into English.
- •Read the story. Then, write questions about the story Break time
- •The Future Continuous Tense
- •Make up five sentences from each table.
- •Make the following interrogative and negative.
- •Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •Answer the questions as in the model.
- •Make the sentences interrogative.
- •Make the sentences negative.
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Put the, verb in brackets into the Present, Past or Future Continuous Tense.
- •Form questions with the question words given.
- •Translate into English.
- •Часи Групи Indefinite
- •The Present Indefinite Tense
- •Put the following into the plural
- •Put the following into the singular.
- •Make up five sentences from each table.
- •Make the following sentences interrogative and negative.
- •Ask questions as in the models.
- •Make up five sentences from each table.
- •Ask questions as in the models.
- •Ask questions about the time of the action.
- •Ask questions about the place of the action.
- •Put questions to the italicized words.
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Translate into English
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets
- •Answer the following questions
- •Translate into English
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Simple or Present Continuous
- •The Past Indefinite Tense
- •Form the Past Indefinite of the following regular verbs.
- •Make up five sentences from each table
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets
- •Make the following interrogative and negative.
- •Change the following into the Past Indefinite.
- •Ask questions as in the model
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets
- •Make the following interrogative and negative
- •Change the following into the Past Indefinite
- •Ask questions as in the model
- •Make up five sentences from each table
- •Ask questions as in the models.
- •Put questions to the italicized words.
- •Answer the following questions
- •Change the verb to be into the Past Indefinite.
- •Make up five sentences from each table.
- •Make the following interrogative and negative
- •Make up five sentences from the table.
- •Ask questions as in the models.
- •Answer the following questions
- •Make up dialogues by using the substitution table
- •Read the sentences. Analyse them and explain the use of the Past Indefinite Tense form with the did-auxiliary in the affirmative sentences. Translate them into Ukrainian.
- •Translate into English.
- •Write down the following text in the Past indefinite Tense
- •Write down the following text in the Past indefinite Tense
- •Compare using of Present Indefinite and Past Indefinite.
- •Open the brackets Use Present or Past Indefinite
- •Open the brackets Use Present or Past Indefinite
- •Open the brackets Use Present or Past Indefinite
- •Write down the following text in the Past indefinite Tense
- •Write down the following text in the Past indefinite Tense
- •Open the brackets Use Present or Past Indefinite
- •Translate into English
- •Open the brackets Use Present or Past Indefinite
- •In this exercise you have to read a sentence about the present and then write a sentence about the past.
- •This time you have to put one of these verbs in each sentence:
- •In this exercise you have to write questions. A friend has just come back from holiday and you are asking him about it.
- •This time you have to put the verb into the correct form. All the sentences are past
- •The Past Continuous Tense
- •Make up five sentences from each table
- •Make the following interrogative and negative.
- •Change the following into the Past Continuous.
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets. Explain your choice.
- •Ask questions as you are told.
- •Put questions to the italicized words.
- •Paraphrase the following sentences as in the model.
- •A group of people were staying in a hotel. One evening the fire alarm rang. Use the words in brackets to make sentences saying what each person was doing at the time.
- •Make sentences from the words in brackets. Put the verbs into the correct form, past simple (I did) or past continuous (I was doing).
- •Put the verb into the correct form, past continuous or past simple
- •Make the sentences interrogative and negative
- •Write down the sentences in the Future Continuous Tense
- •Answer the questions
- •Put questions to the words given in bold type
- •Open the brackets Use Present Continuous or Past Continuous
- •Open the brackets Use Past Indefinite or Past Continuous.
- •Open the brackets Use Past Indefinite or Past Continuous
- •Open the brackets Use Past Indefinite or Past Continuous
- •Open the brackets Use Past Indefinite or Past Continuous
- •Open the brackets Use Past Indefinite or Past Continuous
- •Open the brackets Use Past Indefinite or Past Continuous
- •Open the brackets Use Past Indefinite or Past Continuous
- •Open the brackets Use Present, Past, Future Indefinite; Present, Past Continuous.
- •Translate into English.
- •Часи групи Perfect
- •The Present Perfect Tense
- •Make up five sentences from each table
- •Make the following interrogative and negative
- •Choose the proper place of the adverb
- •Transform the following sentences into the sentences with Present Perfect
- •Replace the infinitives in brackets by the required tenses
- •Complete these sentences using the verbs in brackets. You went back to your home town after many years and you found that many things were different.
- •Complete these sentences as in the example. Use the verb in brackets.
- •Now you have to make sentences using the words in brackets.
- •Put the verb into the correct form, past perfect (I had done) or past simple (I did)
- •Translate the following sentences into English
- •Do as you are told and say what you have done.
- •Use the affirmative form of the Present Perfect instead of the negative form of the Present Continuous.
- •Extend the following sentences as in the model.
- •Ask questions as you are told.
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets. Explain your choice.
- •Replace the infinitives in brackets by the Present Perfect or the Past Indefinite.
- •Translate into English.
- •You are writing a letter to a friend and giving news about people you both know Use the words given to make sentences and put the verb into the correct form.
- •In this exercise you have to read the situation and then write a suitable sentence. Use the verb given
- •This time you have to use just. Answer the questions using the words given.
- •In this exercise you have to write sentences with already.
- •This time you have to put in been or gone.
- •You are asking someone about things be has done in his life. Use the words in brackets to make your questions.
- •Complete the answers to these questions. Use the verb in brackets
- •Now you have to write questions and answers as shown in the example
- •Answer these questions using the words in brackets
- •In this exercise you have to make questions with the words given
- •This time answer the questions in the way shown. Use yet.
- •This time you have to complete the sentence. Use so far
- •In this exercise you have to read the situation and then finish a sentence.
- •Open the brackets. Use the Present Perfect Tense.
- •Write down the sentences in Present Perfect.
- •Translate into English. Use Present Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect or Present Continuous Tense.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect or Past Simple.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect or Past Simple.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect or Past Simple.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect or Past Simple.
- •Translate into English. Use Present Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect. Pay attention on using for and since.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect, Present Continuous, Present Simple and Past Simple.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect, Present Simple, Past Simple, Present Continuous or Past Continuous.
- •The Past Perfect Tense
- •Make the following interrogative and negative.
- •Choose the right form of the verb from the brackets. Explain your choice.
- •Replace the infinitives in brackets by the Past Indefinite or the Past Perfect
- •Translate into English
- •Open the brackets. Use Past Indefinite or Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Past Indefinite, Past Continuous or Past Perfect
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect, Past Indefinite, Past Continuous or Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect, Past Indefinite, Past Continuous or Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present Perfect, Past Indefinite, Past Continuous or Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present, Past, Future Indefinite; Present, Past Continuous; Present, Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present, Past, Future Indefinite; Present, Past Continuous; Present, Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present, Past, Future Indefinite; Present, Past Continuous; Present, Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present, Past, Future Indefinite; Present, Past Continuous; Present, Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use: Present, Past, Future Indefinite; Present, Past Continuous; Present, Past Perfect.
- •Open the brackets. Use Present, Past Continuous; Present, Past Perfect
- •Open the brackets. Use Present, Past, Future Indefinite; Present, Past Continuous; Present, Past Perfect.
- •The Future Perfect Tense
- •Make up the five sentence from the table
- •Refer to the future as in the pattern:
- •Translate these sentences into English
- •Replace the infinitive in the brackets by the required tense
- •Translate the following sentences into English
- •Read the sentences, analyze them and translate into Ukrainian
- •Turn the following into the Future Perfect.
- •Replace the infinitives in brackets by the Future Indefinite or the Future Perfect
- •Translate the sentences into Ukrainian
- •Make the sentences interrogative and negative
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Put the verb in brackets into the Present, Past or Future Perfect Tense
- •Form general or special questions with the question word given
- •Translate into English
- •Reference List
Read and retell the text. The Higher Bodies of State Authority of Ukraine
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 brought Ukraine independence. Ukraine's first direct presidential election was held in 1991. In June 1996 Ukraine adopted a new constitution. Under it, the President is the head of the state and acts in its name. The President is elected by direct, majority vote for a term of five years (by secret ballot) and may serve no more than two consecutive terms. The president is also the Commander-in-Chief of the Ukrainian Armed Forces. The Prime Minister of Ukraine is appointed by the President of Ukraine with the consent of more than one-half of the constitutional composition of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine. Under the advice of the Prime Minister, the President appoints the Cabinet of Ministers (executive body). These appointments are subject to confirmation by the legislative body — the Verkhovna Rada. The Prime Minister is the head of the government and is responsible for carrying out its policies. The legislature (the Verkhovna Rada) consists of a single chamber of 450 deputies elected for four-year terms. The highest court is the Constitutional Court, which is charged with protecting and interpreting the constitution. The President, the legislature, and a conference of judges each appoint six of the court's 18 members. The Supreme Court is the highest appeals court for non-constitutional issues. The Supreme Court of Ukraine is the highest judicial body in the system of courts of general jurisdiction.
Discuss the following questions.
1. Who was the first President of Ukraine?
2. What kind of political system has Ukraine?
3. Is there a written constitution?
4. Who is the Prime Minister of Ukraine now?
5. When was the Constitution of Ukraine adopted?
Revise the information from the text and speak on the higher bodies of State Authority of Ukraine.
UNIT 5
Transcribe and memorise the following words:
Monarch, to interpret, constituency, a majority, peer, hereditary, legislation
Read, translate and retell the following text:
The political system of Great Britain
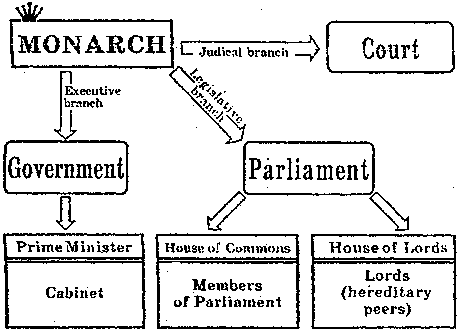
Great Britain is a parliamentary democracy with a constitutional monarch — Queen Elizabeth II — as head of the state.
The political system of Great Britain has three branches: Parliament, which makes laws, the government, which „executes” laws i.e. puts them into effect, and the law courts, which interpret laws. Although the Queen is officially head of all three branches, she has little direct power.
There is no written constitution in Great Britain. The main principles of British legislation are expressed in other documents, like "Magna Charta", "Habeas Corpus Act", "Bill of Rights", the Parliamentary Act which decided the position of the House of Lords, the Judicature Act, etc. The British legislation does not provide written guarantees or individual political rights.
Parliament in Great Britain exists since 1265 and is the eldest in the world. It has two parts: the House of Lords and the House of Commons. Members of the House of Commons are elected by the voters of 650 constituencies. They are known as MPs or Members of Parliament. The Prime Minister, or leader of the Government, is also an MP and usually the leader of the political party with a majority in the House of Commons.
The Prime Minister is advised by the cabinet of about twenty other ministers. The Cabinet includes the ministers in charge of major government departments or ministries. Members of the House of Lords (peers) are not elected. About 70 percent of them are “hereditary peers” because their fathers were peers before them. The other 30 percent are “life peers” whose titles are not passed on to their children. They are officially appointed by the Queen, on the advice of the Government, for various services to the nation.