
- •Introduction
- •Project Finance Risks in ppPs
- •Economic Benefits of ppPs as “Mixed Goods”
- •Collaborative Advantages
- •A Framework to Measure Economic Benefits of ppPs
- •How Collaboration Enhanced the Delivery of Economic Benefits
- •How Collaboration Enhanced the Delivery of Economic Benefits
- •Ppp in Kazakhstan
- •Ppp Forms
- •Functions of the existing institutions of the rk on issues of the concession contracts
- •Further improving of ppp benefits in kazakhstan
- •Main factors for the development of ppp
- •Conclusion
- •References:
How Collaboration Enhanced the Delivery of Economic Benefits
The extent of collaborative advantages that was practiced in the partnership showed that the level of collaboration is not high. The high business consideration fee provided to the Government to achieve its “no-cost” objective sparked public outrage because the public believed this inflated the toll set by the operator. Part of the public dissatisfaction was targeted not at the level of concession given but rather the lack of it. On the other hand, local road closures on the public streets around the tunnel resulted in traffic congestion and caused confusion. The low level of acceptance was evidence that the concession provided did not match the economic benefits promised to the community.
Based on these four factors, the overall level of public acceptance was below average because the total economic benefits to the community did not meet the expectation of the public. This shows that an average level of collaboration from not fully practicing collaborative advantages was responsible for the average level of public acceptance.
How Collaboration Enhanced the Delivery of Economic Benefits
Based on the practice of collaborative advantages, the model shows that there was a high level of collaboration . This high level of collaboration aided in enhancing a high level of public acceptance because greater economic benefits to the community were felt by the public. To avert public outcry, CM decided to offer a one month toll-free concession to all motorists using the tunnel. Greater management of traffic flow around the entrances to the tunnel gave the public the perception that the concessions granted by the government were socially acceptable. Some critics observed that if the government had partially funded the project, the toll charges would have been lower. Nevertheless, there was a generally higher acceptance of the toll charges, reflected in the greater number of motorists using the tunnel.
Generally, lifestyles improved as a result of a reduction in traveling time. It was accepted that the tunnel was essential to improve traffic flow. Today, the project continues to enjoy an overall high level of public acceptance. However, there remain lingering concerns that not all environmental issues have been adequately addressed. Despite this reservation, the high level of public acceptance indicates that the public believed economic benefits had been conferred upon them.
Ppp in Kazakhstan
Public Private Partnership in Kazakhstan moves to a new stage o fits development. The legal framework has been established, the medium-term PPP Development Programme to 2015 is being implemented, and current PPP projects are running, making it possible to study and learn from both positive and negative experiences at this rather early development stage. However, the really valuable experience is, first of all, the lessons allowing us to challenge the current institutional base and develop new initiatives for the development of public private partnerships in Kazakhstan.
Kazakhstan’s experience with PPP projects is relatively recent and has yet to be fully developed. As of today, the following concession projects have been signed:
1) Construction and maintenance of a new railway line “Shar – UstKamenogorsk”
2) Construction and maintenance of the interregional line of electro transmission “North Kazakhstan – Aktobe oblast”;
3) Construction and maintenance of passenger terminal of the Aqtau international airport;
4) Construction and maintenance of the gas turbine power station in Kandyagash City, Aktobe oblast;
5) Construction and maintenance of the railway line “Eraliyevo-Kurik”;
6) Construction and maintenance of kindergartens in Karaganda oblast;
PPP in Kazakhstan has received legislative, institutional and organizational support. The current legal framework of the Republic of Kazakhstan allows for the cooperation between the State and private sector according to the following mechanisms:
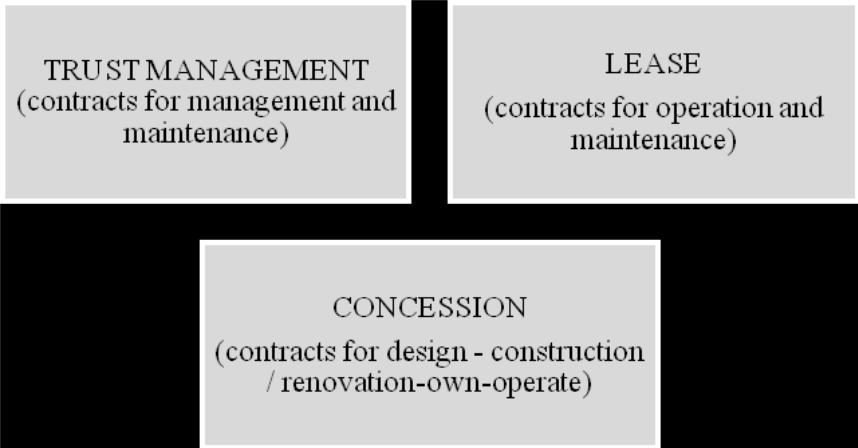
The current legal framework for PPP spells out exactly which forms of PPP are allowed (see Table “PPP Forms”). However, PPP is not defined by the Kazakh legislation and therefore the concession contracts outlined in the legislation do not legally qualify as PPP.
