
- •Тема 2.2 економіка країни, мова якої вивчається
- •Inland & outland waters
- •The report about industry of the uk is … .
- •Most of the British rivers flow into the __________ Sea.
- •23. The mountains which separate England from Scotland are __________ .
- •In Great Britain _________ appoints the ministers.
- •The head of Great Britain is __________ .
- •The name of the author of world famous bestseller “Harry Porter” is __________ .
- •Sir Isaac Newton was a(n) __________ physicist and mathematician who discovered gravity.
- •The territory of the uk is divided into _________ .
- •London was built as the __________.
- •The Scottish national costume for men is called _________ .
- •Britain got its name from the invaders who were the __________ .
- •The largest city of Scotland is __________ .
Т ЕМА
2.1 ГЕОГРАФІЧНЕ ПОЛОЖЕННЯ КРАЇНИ, МОВА
ЯКОЇ ВИВЧАЄТЬСЯ
ЕМА
2.1 ГЕОГРАФІЧНЕ ПОЛОЖЕННЯ КРАЇНИ, МОВА
ЯКОЇ ВИВЧАЄТЬСЯ
TOPIC 2.1 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION OF THE COUNTRY
THE LANGUAGE OF WHICH IS STUDIED
Тема 2.2 економіка країни, мова якої вивчається
TOPIC 2.2 ECONOMY OF THE UNITED KINGDOM of GREAT BRITAIN AND NOTHERN IRELAND
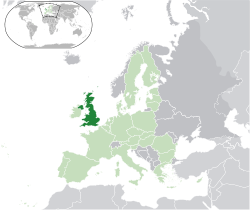


The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (commonly known as the United Kingdom, the UK, or Britain) is a sovereign state located to the northwest of Europe. It is an insular (=island) country. The UK is situated on the British Isles. Their total area is over 314 000 sq. km.
The British Isles consist of two large islands – Great Britain and Ireland – and a great number of small ones. The northern part of the island of Ireland belongs to the UK. The rest of the island is the Irish republic, or in other words, the Republic of Ireland. It is quite the other state.
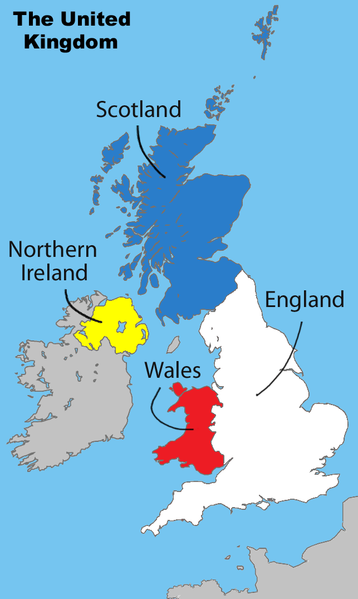
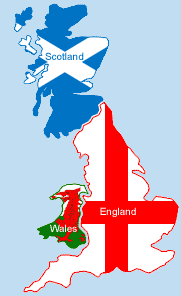
The UK consists of four countries: England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
The capital of the UK and England is London.
The capital of Scotland is Edinburgh.
The capital of Wales is Cardiff.
The capital of Northern Ireland is Belfast.
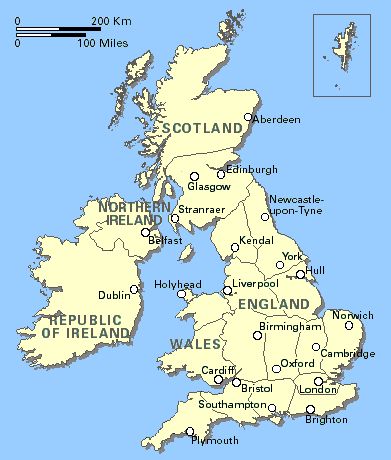
The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately 243,610 square kilometres (94,060 sq mi).
Inland & outland waters
The UK is washed by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel and the Irish Sea. Great Britain is linked to France by the Channel Tunnel.
Most of the rivers flow into the North Sea. The Thames is the deepest and the Severn is the longest of the British rivers. Some of the British greatest ports are situated in the estuaries of the Thames, the Mersey, the Trent, the Clyde and the Bristol Avon.
THE SURFACE
The surface of Scotland and Wales is mostly mountainous, but the mountains are not high. There is very little flat country except in the region known as East Anglia.
The Highlands and the Grampian mountains are situated in Scotland. Robert Burns devoted a lot of verses to his native Highlands.
The Cheviot Hills separate Scotland and England and the Pennines stretch like a backbone in the north of England.
The Cambrian mountains are situated in Wales.
MINERAL RESOURCES
Great Britain is not very rich in mineral resources, it has some deposits of coal and iron ore and vast deposits of oil and gas that were discovered in the North Sea.
THE CLIMATE
The United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with plentiful rainfall all year round. The temperature varies with the seasons but seldom drops below −10 °C (14.0 °F) or rises above 35 °C (95 °F). Atlantic currents, warmed by the Gulf Stream, bring mild winters, especially in the west, where winters are wet. Summers are never hot. Snowfall can occur in winter and early spring, though it rarely snows.
THE POPULATION

According to the census of 2001, the total population of the United Kingdom was 58,789,194, the third largest in the European Union and the twenty-first largest in the world. By mid-2009, this was estimated to have grown to 61,792,000. The main nationalities are: English, Welsh, Scottish and Irish. In Great Britain there are a lot of immigrants from former British Asian and African colonies.
The UK is a Member State of the European Union, a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, G8, G20, NATO, OECD and the World Trade Organization.
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy. The United Kingdom is governed by the Parliament but the official head of the state is the monarch, although his or her power is limited. The queen reigns but not rules. Nowadays the Queen is Elisabeth II.

HM Queen Elizabeth II,
Queen of the United Kingdom
and the other Commonwealth realms.

The Palace of Westminster, seat of the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom—the House of Lords and the House of Commons
THE LANGUAGES
The UK does not de jure have an official language but the predominant spoken language is English, a West Germanic language descended from Old English which features a large number of borrowings from Old Norse, Norman French and Latin. Largely because of the British Empire, the English language has spread across the world, and become the international language of business as well as the most widely taught second language.
Scots, a language descended from early northern Middle English, is recognised at European level. There are also four Celtic languages in use in the UK: Welsh, Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Cornish.
Across the United Kingdom, it is generally for pupils to study a second language: up to the age of 14 in England, and up to age 16 in Scotland. French and German are the two most commonly taught second languages in England and Scotland. In Wales, all pupils up to age 16 are either taught in Welsh or taught Welsh as a second language.
Religions in the United Kingdom
The Treaty of Union that led to the formation of the United Kingdom ensured that there would be a Protestant succession as well as a link between church and state that still remains. Christianity is the largest religion, followed by Islam, Hinduism, Sikhism and then Judaism in terms of number of adherents.
Religion/Denomination |
Current religion |
Percent % |
Christian |
42,079,000 |
71.6 |
No religion |
9,104,000 |
15.5 |
Muslim |
1,591,000 |
2.7 |
Hindu |
559,000 |
1.0 |
Sikh |
336,000 |
0.6 |
Jewish |
267,000 |
0.5 |
Buddhist |
152,000 |
0.3 |
Other Religion |
179,000 |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
W estminster
Abbey is
used for the coronation of British
monarchs
estminster
Abbey is
used for the coronation of British
monarchs
T he East
London Mosque is
one of the country's largest Islamic places of worship.
he East
London Mosque is
one of the country's largest Islamic places of worship.
S t.
Patrick's Cathedral, Armagh.
t.
Patrick's Cathedral, Armagh.
(*Armagh [a:'ma:] is a town in Northern Ireland, in Armagh district: seat of Roman Catholic and Protestant archbishops. Population: 14 590 (2001))

The ninth century St Martin's Cross stands outside the entrance to Iona Abbey in Iona, Scotland
(*Iona [ai'əυnə] an island off the W coast of Scotland, in the Inner Hebrides ['hebrədi:z]: site of St Columba's monastery (founded in 563) and an important early centre of Christianity. Area: 854 ha (2112 acres)
Economy of the United Kingdom
The British Empire was the largest empire in history. At its height in 1922 it encompassed almost a quarter of the world's land surface. British influence can still be observed in the language, culture and legal systems of many of its former colonies.
The UK is a developed country, with the world's sixth largest economy by nominal GDP and the sixth largest by purchasing power parity. It was the world's first industrialized country and the world's foremost power during the 19th and early 20th centuries, but the economic and social cost of two world wars and the decline of its empire in the latter half of the 20th century diminished its leading role in global affairs. The UK nevertheless remains a great power with strong economic, cultural, military, scientific and political influence. It is a recognised nuclear weapons state.
The United Kingdom's economy is made up (in descending order of size) of the economies of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK has a partially regulated free market economy. The UK is today the sixth largest economy in the world and the third largest in Europe after Germany and France.
The Industrial Revolution started in the UK with an initial concentration on heavy industries such as shipbuilding, coal mining, steel production, and textiles. The empire created an overseas market for British products, allowing the UK to dominate international trade in the 19th century. The United Kingdom began to lose its competitive advantage and heavy industry declined throughout the 20th century. Manufacturing remains a significant part of the economy, but accounted for only one-sixth of national output.
The British motor industry is a significant part of this sector. Civil and defence aircraft production is a developed industry, as well. Rolls-Royce holds a major share of the global aerospace engines market.
The chemical and pharmaceutical industry is strong in the UK, with the world's second and sixth largest pharmaceutical firms (GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca, respectively) being based in the UK.
The UK service sector, however, has grown substantially, and now makes up about 73% of GDP. The service sector is dominated by financial services, especially in banking and insurance. London is the world's largest financial centre with the London Stock Exchange, the London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange, and the Lloyd's of London insurance market all based in the City of London. London is a major centre for international business and commerce and is the leader of the three "command centres" for the global economy (along with New York City and Tokyo).
Tourism is very important to the British economy. Over 27 million tourists arrive in the United Kingdom. The UK is ranked as the sixth major tourist destination in the world. London is the most visited city in the world with 15.6 million visitors, ahead of 2nd placed Bangkok (10.4 million visitors) and 3rd placed Paris (9.7 million).
The creative industries is developing at a high speed.
The UK has a small coal reserve along with significant, yet continuously declining natural gas and oil reserves. The UK is self sufficient in coal, although at present extraction rates the reserves are decreasing.
The main industrial centres are London, Birmingham, Manchester, Leeds, Liverpool, Glasgow and Bristol.
N orth
Sea oil and gas
orth
Sea oil and gas
have supplied much of
the UK's energy needs
in recent decades,
but the country now increasingly depends on imported fossil fuels.
MONEY
T he
currency of the UK is the pound
sterling,
represented by the symbol £.
The Bank
of England is
the central
bank,
responsible for issuing currency. Banks in Scotland and Northern
Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes. The UK choose not
to join the euro at the currency's launch.
he
currency of the UK is the pound
sterling,
represented by the symbol £.
The Bank
of England is
the central
bank,
responsible for issuing currency. Banks in Scotland and Northern
Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes. The UK choose not
to join the euro at the currency's launch.

Symbols
The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack). It was created by the superimposition of the Flag of England, the Flag of Scotland and Saint Patrick's Flag in 1801. Wales is not represented in the Union Flag as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom.

The national anthem of the United Kingdom is "God Save the King", with "King" replaced with "Queen" in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.


Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain. Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag. Sometimes she is depicted as riding the back of a lion.
T he
Statue of Britannia in
Plymouth.
he
Statue of Britannia in
Plymouth.
Britannia is a national personification of the UK.
Task 1. Answer the questions:
1 .
Where is the United Kingdom situated?
2. What islands do the
British Isles consist of?
3. What ocean and seas are the British
Isles washed by?
4. What parts does the Island of Great Britain
consist of?
5. What country does Northern Ireland border on?
6.
Are there any high mountains in Great Britain?
7. What seas do
most of the rivers of the UK flow into?
8. What mineral
resources is Great Britain rich in?
9. What is the climate like
in Great Britain?
10.What is the population of Great
Britain?
11.What city is the capital of the U. K.?
12. What
kind of state is Great Britain?
.
Where is the United Kingdom situated?
2. What islands do the
British Isles consist of?
3. What ocean and seas are the British
Isles washed by?
4. What parts does the Island of Great Britain
consist of?
5. What country does Northern Ireland border on?
6.
Are there any high mountains in Great Britain?
7. What seas do
most of the rivers of the UK flow into?
8. What mineral
resources is Great Britain rich in?
9. What is the climate like
in Great Britain?
10.What is the population of Great
Britain?
11.What city is the capital of the U. K.?
12. What
kind of state is Great Britain?
Task 2. Have a look at the table and comment on it. If you can, continue the table.
TRADITIONAL INDUSTRIES |
|
THERE IS \ ARE ….. |
….. IS \ ARE DEVELPED |
Coal → |
Coal-mining & manufacturing industry |
Tin, copper, ores of other non-ferrous metals → |
Chemical industry |
Gas → |
Power-engineering |
Seas, rivers → → → |
Ship-building Fishery Foreign trade |
Hills & pastures →
cattle-breeding → sheep breeding → |
Animal husbandry including cattle-breeding, sheep breeding, Food industry Light industry & textile industry
|
|
|
|
|
N |
|
Electronics |
|
Automobile industry |
|
Aircraft engineering |
|
Space engineering |
|
|
|
|
|



















Task 3. Arrange the words into two groups.
border d) statue g) gallery j) location
territory e) distance h) square k) museum
monument f) cost i) climate l) sight
Geographical Position |
Places of Interest |
|
|

Task 4. Arrange the words into two groups.
manufacture d) factory g) construct j) produce
rye e) oats h) plough k) machinery
equipment f) barley i) weed l) cultivate
Agricaulture |
Industry |
|
|
Task 5. Write the name for each of the following groups.
sheep-breeding, dairy, cattle-breeding, plant-growing __________________
sheep, cows, goats, pigs, donkeys __________________________________
coal, gas, oil, tin, copper, iron ore __________________________________
Bently, RollsRoyce, Aston Martin, Triumph _________________________
London, Cardiff, Edinburg, Belfast _________________________________
London, Liverpool, Leeds, Manchester _____________________________
Britannia, Union Jack, "God Save the Queen" ________________________
Great Britain, Ireland, Man _______________________________________
Task 6. Encircle the letter or letter combinations which are silent.
sovereign 6. large 11. though 16. nowadays
islands 7. known 12. monarchy 17. palace
The Highlands 8. high 13. to reign 18. taught
Edinburgh 9. climate 14. monarch 19. Christianity
Birmingham 10.isle 15. hight 20. right
Task 7. Odd one out.
1. a) trade b) agriculture c) industry d) sheep-breeding
2. a) Brighton b) Belfast c) Cardiff d) London
3. a) automobile b) iron ore c) tin d) coal
4. a) the Conservative b) the Labour c) the Liberal d) Parliament
5. a) ship b) car c) sheep d) plane
6. a) sheep b) bull c) duck d) pig
7. a) coat-of-arms b) flag c) anthem d) trident
8. a) Scots b) English c) Irish d) Ukrainians
9. a) Westminster Abbey b) Buckingham c) the Tower d) Stonehenge
10.a) Aston Martin b) BMW c) Rolls-Royce d) Bently
Task 8. Choose the correct variant.
The student wants to tell about great Britain and ….. tradition.
-
a. its
b. it
c. it’s
… report is this?
-
a. Who
b. Who’s
c. Whose
She is very interested in the United Kingdom and … history.
-
a. it
b. it’s
c. its
He decided to change the title of … report.
-
a. its
b. his
c. he’s
She invited … parents to come to England.
-
a. she’s
b. her
c. her’s
The students discussed … practice in Great Britain.
-
a. there
b. they’s
c. their


 EW
INDUSTRIES
EW
INDUSTRIES