
Topic: belarus

National emblem

Flag
Motto: none
Anthem: Belarusian: Мы, беларусы (Translation: "We Belarusians")
Location of Belarus
(1) General Information. Officially, the country is known as the Republic of Belarus, while the short name is Belarus or Byelarus. (An earlier version of the name was Belorussia. Besides, Belarus is sometimes called White Russia.)
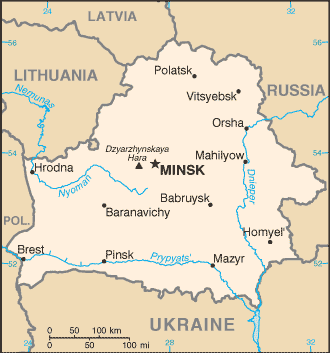
Belarus is a landlocked country in east-central Europe (2005 pop. 9,799,000; 207,600 sq km). Belarus borders on Poland in the west, on Lithuania and Latvia in the north, on Russia in the east, and on Ukraine in the south. The capital and largest city is Minsk with population about 1.9 ml people. It is a railroad junction with machine-tool, tractor, automobile, textile and food plants. In addition to the capital, other important cities are Gomel, Vitebsk, Mogilev, Grodno, and Brest. The Republic of Belarus includes 110 towns, of which 15 towns have population over 100,000, and 103 urbanised populated localities.
(2) Government. Belarus is governed under the constitution of 1994 as amended in 1996. It has a popularly elected president who serves a five-year term. The bicameral parliament consists of the 64-seat Council of the Republic and the 110-seat Chamber of Representatives. The president appoints the prime minister, who is the head of government. Administratively, the country is divided into six districts or oblasts and one municipality.
Since 1994, Alexander Lukashenko has been the state's president. Belarus is currently in negotiations with neighboring Russia to integrate both of their economies, among other things, in a plan called the Union of Russia and Belarus.j
(3) Land. Belarus is landlocked, relatively flat, and contains large tracts of marshy land (more than one third of the land). The largest marsh territory is Polesia, which is also amongst the largest marshes in Europe. There are over 20 thousand rivers and streams , and 11,000 lakes in Belarus, but the majority of the lakes are very small. Three major rivers run through the country, the Neman River, the Pripyat River, and the Dnepr River. The largest water reservoir is the Naroch Lake (80 sq. km). The available natural water resources are quite sufficient to meet both current and future needs for water.
The climate is moderate humid continental, with warm summers and cold winters.
(4) People. About 80% of the population are Belarusians; Russians, Poles, Ukrainians, Lithuanians, and Jews are the republic's largest minorities. Since the breakup the USSR, Belarus has experienced a slow decline in population.
Most demographic indicators for Belarus resemble other European countries. The population growth is currently at −0.06%. The population is also growing older, and by the year 2050, the majority of the population will be over the age of 50.
The official languages are both Belarusian and Russian, but Russian is more widely used. Eastern Orthodoxy and Roman Catholicism are the main religions.
(5) Economy
M
 acroeconomic
indicators.
Belarus is one of economically developed CIS member-states, just as
it was within the Soviet Union. Since winning independence in 1991,
Belarus has moved slowly on privatization and other market reforms.
The country has arguably handled the difficult transition better than
most of its peers. Economic output, which declined for several years
with the introduction of free market structures, revived n the late
1990s. In 2001 Belarus was first of CIS coutries to reach 1990 levels
of industrial production and agricultural production.
acroeconomic
indicators.
Belarus is one of economically developed CIS member-states, just as
it was within the Soviet Union. Since winning independence in 1991,
Belarus has moved slowly on privatization and other market reforms.
The country has arguably handled the difficult transition better than
most of its peers. Economic output, which declined for several years
with the introduction of free market structures, revived n the late
1990s. In 2001 Belarus was first of CIS coutries to reach 1990 levels
of industrial production and agricultural production.
At present, the Belarusian economy remains about 80% state-controlled, as it has been since Soviet times. Because of this fact Belarus has had trouble attracting foreign investment, which remains low. Still, the country is relatively stable, economically, but depends to a large extent on raw material supplies from its close ally Russia.
Gross domestic product (GDP) for 2005 was $79.13 billion (estimate), which equates to an annual income of approximately $7,700 dollar per head. In 2005 GDP increased by about 8-9%, with the inflation rate averaging about 8%. Belarus therefore has the highest standard of living of all the CIS states. According to the UN, average monthly income grew from 20 United States dollars to 225 USD during the last 10 years. The unemployment rate, according to Belarusian government statistics, was about 2% in 2005. A wide range of redistributive policies has helped those at the bottom of the ladder; the Gini coefficient* is among the lowest in the world.
------------------------
* The Gini coefficient is a measure of inequality of a distribution, and it is often used to measure income inequality. With the Gini coefficient , 0 corresponds to perfect income equality (i.e. everyone has the same income) and 1 corresponds to perfect income inequality (i.e. one person has all the income, while everyone else has zero income).
Natural resources. Peat, the country's most valuable mineral resource, is used for fuel and fertilizer and in the chemical industry. The total geological reserves are estimated at 4.4 billion tons. Another important natural resource is sapropel whose reserves are estimated at 3 billion cu. m. Forest covers about a third of the land, making it one of the most dominant natural resources in Belarus. Belarus also has deposits of clay, sand, chalk, dolomite, phosphorite, and rock and potassium salt. Oil reserves are not big; its production covers only 12-13 percent of the country needs. So, Belarus has to import most of its oil and gas from Russia.
Industry. About one third of the national product is created by industry. The main branches of industry produce tractors and trucks, earth movers for use in construction and mining, metal-cutting machine tools, agricultural equipment, motorcycles, chemicals, fertilizer, textiles, and consumer goods. The chief trading partners of Belarus are Russia, Ukraine, Poland, and Germany.
Agriculture is dominated by collective farming. Potatoes, flax, hemp, sugar beets, rye, oats, and wheat are the chief agricultural products. Dairy and beef cattle, pigs, and chickens are raised.
Labour resources. The number of employees at enterprises and organisations is 4.34 million people; of them, 1.14 million persons are employed in industries, and 0.51 million people in agriculture. The country has a modern system of professional training, which guarantees a high educational level of population and high skills of employees., including such sectors as automotive, tractor and agricultural machinery building, optical sector, radio and electronics, precision instruments, etc.
Chernobyl. A nuclear accident, the worst nuclear reactor disaster in history (Apr. 26, 1986), at the Chernobyl atomic power plant, across the border in Ukraine, had a devastating effect on Belarus economy; as a result of the radiation release, agriculture in a large part of the country was destroyed, and many villages were abandoned. Resettlement and medical costs were huge and long-term. The country continues to suffer from the effects of nuclear fallout from the 1986 Chernobyl accident. While the amount of radiation has decreased (by one percent) since the disaster, most of the area is considered uninhabitable.(2005-Zhdanov)
