
- •Version 1.0g
- •The tag Introduction to prince2
- •Course Objectives – Classroom Preparation Course
- •Course Contents
- •Organization
- •Project Organization Introduction
- •What is a Programme?
- •Organization Roles
- •The Executive Role
- •The Senior Supplier Role
- •The Project Manager Role
- •The Team Manager Role
- •The prince2 Process Model Diagram
- •Process Model Diagram Introduction
- •Direction
- •Initiating a
- •Delivery
- •Process Model Using Color
- •Four Management Levels
- •Process Model – Processes
- •Initiating a Project (ip)
- •Exercise Diagram
- •Work Package mp Outputs
- •The prince2 Process Model
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Project Mandate Contents
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Su: Starting Up a Project
- •Starting Up a Project: Three main deliverables
- •Starting Up a Project Activities
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Su: Project Approach
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Карпова ______________________
- •Su: Assemble Project Brief
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Su: Plan the Initiation Stage
- •Plan the Initiation Stage Tasks
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Request to Initiate a Project
- •Dp: Authorize initiation
- •Direction
- •Ip: Initiation Stage
- •Initiating a Project Process introduction
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Initiating a Project Process – 8 Activities
- •Ip: Project Initiation Documentation (pid)
- •Project Initiation Documentation
- •Project Initiation Documentation Contents
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Sb: Managing a Stage Boundary after the Initiation Stage
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Inputs:
- •Dp: Authorize the project
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Cs: Controlling a Stage
- •Direction
- •Initiating a
- •Delivery
- •Cs: Controlling a Stage / Managing Product Delivery
- •Assign Work to Teams using Work Packages
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Initiation Stages - Execution
- •Managing Product Delivery Objectives
- •Mp: Managing Product Delivery: Outputs
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Initiation Stages - Execution
- •Cs: Controlling a Stage – Give ad hoc direction
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Initiation Stages - Execution
- •Cs: Project Manager Day to day activities
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Work Package
- •Initiation Stages - Execution
- •Sb: Managing a Stage Boundary
- •Managing a Stage Boundary and Objectives
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Initiation Stages - Execution
- •Managing a Stage Boundary Outputs
- •Dp: Authorize a Stage or Exception Plan
- •Authorize a Stage or Exception plan
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Initiation Stages - Execution
- •Exception Plans - Authorize a Stage or Exception Plan Activity
- •Last Controlling a Stage Process
- •Cp: Closing a Project: Introduction and Objectives
- •Closing a Project and Premature Close
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Closing a Project Objectives
- •Cp: Closing a Project Outputs
- •Closing a Project Outputs
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •Last actions for Project Manager in Closing a Project
- •Dp: Authorize project closure
- •Project Board activities in “Authorize project closure”
- •Direction
- •Delivery
- •“Authorize project closure” activity outputs
- •Summary
- •Course Summary
- •Direction
- •Initiating a
- •Delivery
- •Learn Thru Questions
- •Introduction
- •About Learn Thru Questions
- •Introduction to prince2
- •Acknowledgements
- •Distribution Copyright
- •Customize this book
- •About the Author
- •The prince2 Training Manual: Book
- •About tag
- •The Process Model Learn Thru Questions
- •Appendix a
- •Appendix b Simple Glossary
- •Issue Register
Work Package
Delivery
Team Manager
Work Package Completed WP
Managing Product Delivery (MP)
Is s u e activities
Work Package
Capture and examines issues & risksEscalate issues and risks
Take corrective action
Products get created & quality checked
Based on OGC PRINCE2® material. Reproduced under license from OGC
Initiation Stages - Execution
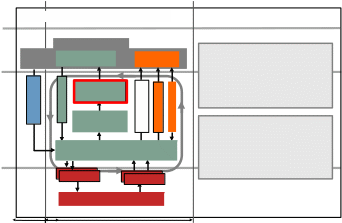
Fig 3.17 CS: Project Manager day-to-day activities
The Issue activities are:
Capture and examine issues and risks: Any person can raise an issue and the Project Manager must gather and review them. Reviewing also includes categorizing and assessing the impact of each issue.
Escalate issues and risks: If there are issues to report or if the stage is expected to go out of tolerance, then create an Exception Report and send it to the Project Board.
Take corrective action: Normally, Taking Corrective Action is used when extra work has to be done to solve an issue and the stage can stay within tolerance.
As you can see, we have already covered four of these in the previous slides. One final comment: These activities can be done numerous times by the Project Manager and there is no set order.
Sb: Managing a Stage Boundary
Managing a Stage Boundary and Objectives
The Managing a Stage Boundary process provides information to the Project Board about the current status of the project at the end of each stage. This process happens after all the work in the current stage plan has been completed and before the next stage can begin.
The Stage Boundary Objectives
The objectives of the “Managing a Stage Boundary” process are:
To confirm to the Project Board which products have been produced in the current stage as documented in the stage plan, and also update the Project Plan to show what has been done so far and forecast the planning for the next stage.
So you see, the Project Plan is a living document (kept up to date)
To provide the Project Board with information so they can:
Assess the viability of the project – meaning checking that it still worth doing
Approve Stage Completion – which is to approve the stage (that was just done) and
 Authorize
the
start
of the Next
Stage
Authorize
the
start
of the Next
Stage
Corp..
Corporate or Programme Managementwww.Mgm tPlaza.com
