
- •Basic Concepts of Geology
- •Vocabulary section
- •Be sure you know the following words and their translation
- •Match the words in column a with their definitions in column b
- •Skim the text and define classification of geological structure of the Earth
- •Scan the text and answer the following questions
- •Petroleum geology
- •Basic concepts of geology
- •Plate Tectonics
- •Crustal Plates
- •Petroleum Geology
- •Geologic Structures
- •Warps and Folds
- •Life on Earth
- •Geologic time scale
- •Categorizing Rocks
- •Types of Rock
- •The Rock Cycle
- •Say whether the following statements are true or false
- •5 Fill in the gaps
- •Grammar section noun
- •Noun Gender
- •Noun Plurals
- •Write the following nouns and word-combinations in plural
- •Give the plural forms of the following nouns
- •Translation section
- •Translate the following sentences from English into Ukrainian
- •Translate the following sentences from Ukrainian into English
Types of Rock
Deep in the earth's crust, temperatures are high enough to melt rock into magma. Magma sometimes erupts to the surface as lava, or it may force its way into other solid rock underground. In either case, when magma cools, it solidifies, forming igneous rocks, such as granite and basalt.
Sedimentary rocks are rocks formed in horizontal layers, or strata, from sediments. A sediment can consist of eroded particles of older rock (igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic) that wash downhill to lakes or to the oceans. Sediment may also consist of minerals that precipitate out of water. In any case, water is a crucial ingredient in forming sedimentary rocks. Over tens of thousands of years, the layers become thick, and the weight of the overlying sediments compacts the earlier deposits (fig. 1.10). Minerals in the water cement these deposits together into sedimentary rocks. Limestone, sandstone, and clay are typical sedimentary rocks.
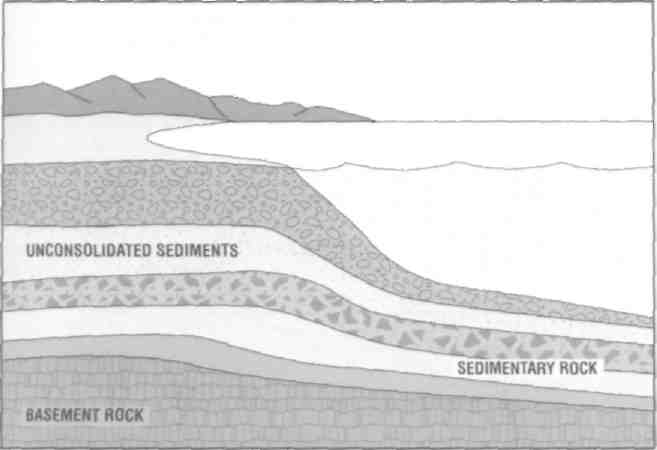
Figure 1.10 The weight of overlying sediments, combined with minerals in water, compacts sediments into rock.
Metamorphic rocks are rocks – either igneous, sedimentary, or other metamorphic rocks – that have been buried deep in the earth where they were subjected to high temperatures and pressures. The term comes from the Greek meta, to change, and morphe, form or shape. During the metamorphic process, the original rock undergoes physical and chemical changes that may greatly alter its composition and appearance. So, for example, limestone can be metamorphosed into marble, and sandstone into quartzite. A belt of one type of rock is known as a formation. Formations are stacked on top of one another and then deformed by folding, warping, and faulting.
The Rock Cycle
As you can see, over time, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks are all changed into one another. Wind, water, and moving ice erode all types of rock, carry the particles to the ocean or lakes, and create new sedimentary rock. The movement of magma into rock not only creates new igneous rock when it cools, but also metamorphoses the existing rock with its heat. Tectonic movement raises buried rock to the surface, where it erodes, or pushes it deeper into the earth, where it may metamorphose or become magma. Erosion, movement of crustal plates, and movement of molten rock continuously create new types of rock from the old.
Sedimentary rocks are the most interesting to petroleum geologists because most oil and gas accumulations occur in them; igneous and metamorphic rocks rarely contain oil or gas. Furthermore, most of the world's oil lies in sedimentary rock formed from marine sediments deposited on the edges of continents. This is why many of the largest deposits lie along seacoasts, such as along the Gulf of Mexico and the Persian Gulf, for example.
Say whether the following statements are true or false
Geology is the science that deals with the origin, history, and physical structure of the earth and its life, as recorded in rocks.
Geologists try to answer such questions as how old the earth is, where it came from, and what it is made of.
Astronomers and physicists think today that the earth was formed at least 14 billion years ago out of a cloud of cosmic dust.
It is considered that the core has two parts: an inner solid core and an outer liquid core.
Mantle around the inner core is formed by heavy minerals.
Geologists distinguish between oceanic crust, which lies under the oceans, and continental crust, of which the continents are made.
They believe that the tallest mountains in the world, the Himalayas, formed when Japan smashed into Asia.
Fossils of marine organisms found in some of the highest mountains and in the deepest oilwells prove that the rocks there were formed in ancient seas and then rose or fell to their present positions.
Rock strata that have crumpled and buckled into wavelike structures are called faults.
Sedimentary rocks are rocks formed in vertical layers.
