
S p2 Hybridization
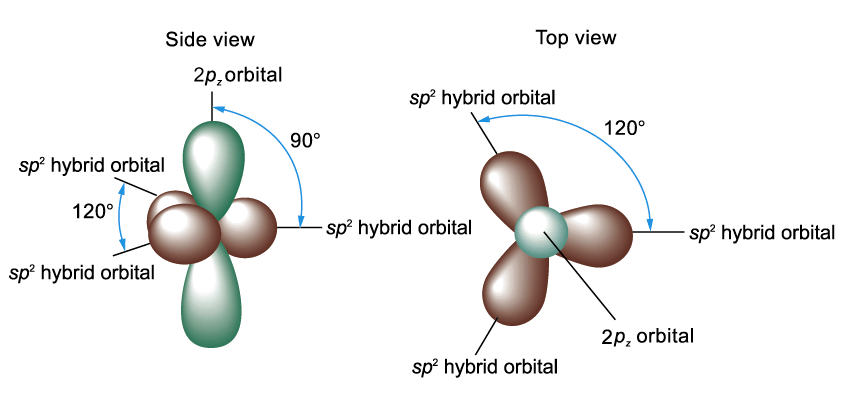

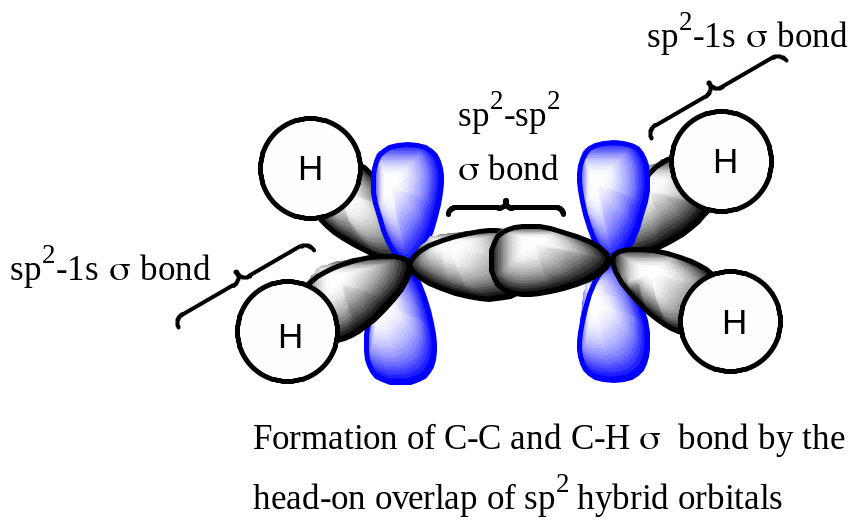
Ethene (C2H4)

π-bonding – bonding created by the side overlap of not hybrid p-orbitals in the plane, that goes through atoms’ nuclei. This plane makes it impossible for atoms to rotate free around the axis of bonding.


Cyklohexane (С6H10)
Differences between the σ bond and the p bond in the carbon-carbon double bond:
σ bond |
p bond |
Head-on overlap of the sp2 hydridized orbitals of two carbon atoms |
Side-way overlap of the vacant p orbitals of two carbon atoms |
The bonding electrons in are localized symmetrically along the internuclear axis of two bonded carbon atoms. |
The electrons in the p bond appear as two lobes, one above and one below the internuclear axis of the two bonded atoms |
Stronger |
Weaker |
Free to rotate |
Restricted to rotation |
sp Hybridization
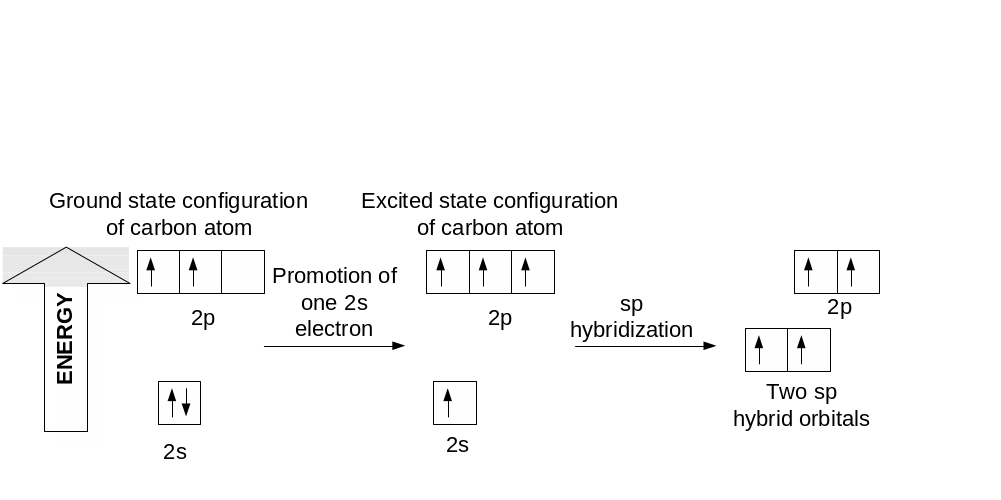
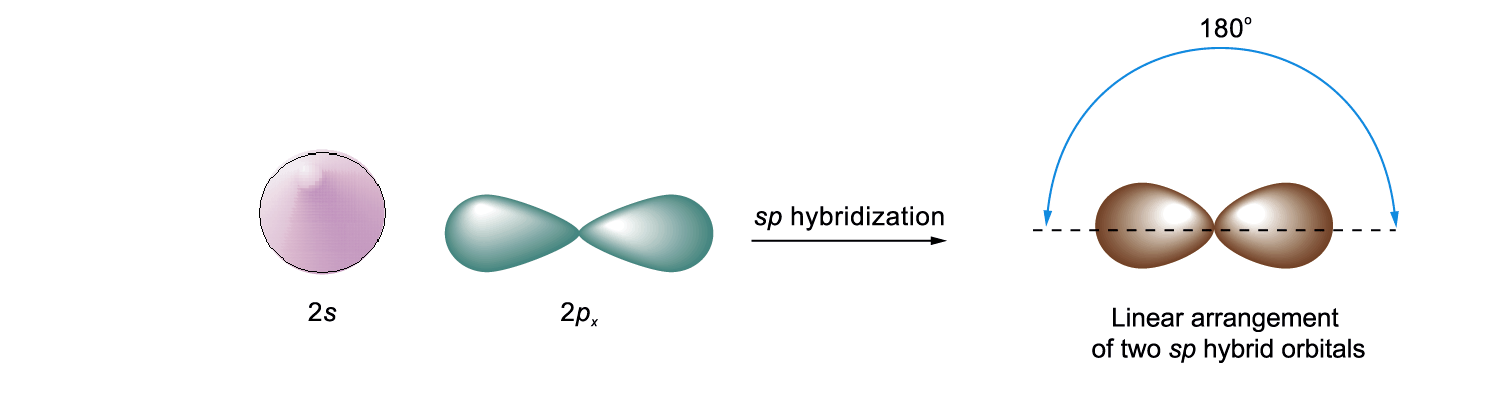

E thyne
(С2H2)
thyne
(С2H2)

Ability to Catenate
Carbon atoms can link themselves together to form chains of varying length, branched chains and rings of different sizes.
Catenation: The ability of atoms in forming stable bonds with itself and joining up in chains or rings.
e.g.
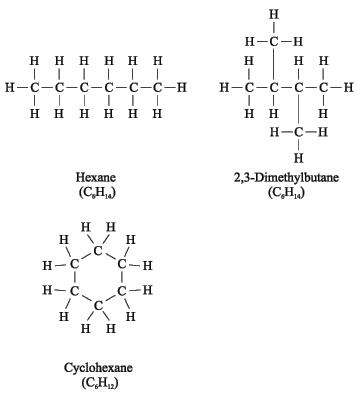

Methods of representation of organic molecules
Molecular (empirical) formula shows qualitative and quantitative composition of molecule. It doesn’t show the structure.
Structural (graphical) formula shows qualitative and quantitative composition , and the order and the type of bonding of atoms in molecule.
Carbon has the valency 4 in all the organic compounds.
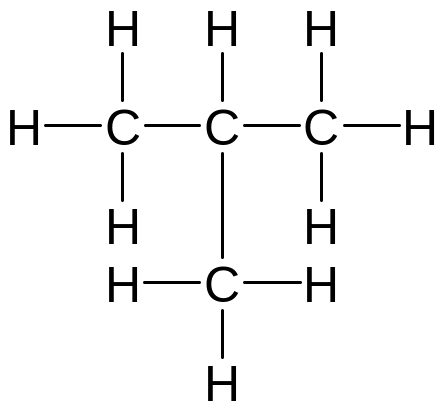

Kekulé structure – all bonds are shown as dashes, all atoms as symbols
isobutane acetone
Condensed structure – some bonds are not shown, it shows only those bonds, which are necessary
 or
(СН3)2СНСН3
or
(СН3)2СНСН3
![]() or
СН3СОСН3
or
СН3СОСН3
Skeletal structure – carbon skeleton is shown only by valence bonds, the atoms of carbon are not shown. Skeletal structure are used mostly in cyclocompounds:

![]()
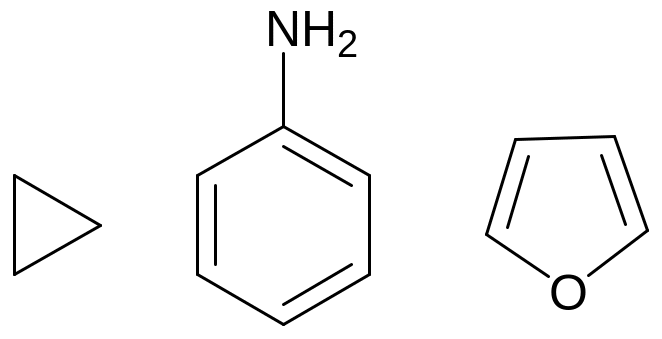
cyclopropane aniline furane
A cross-coupling of atoms in a molecule
The commutual influence of atoms in molecule is defined by the kind of dividing of electron density in molecule and by the ability of covalent bonds to polarization.
Electron displacements are divided into two kinds: inductive and resonance (mesomeric) effects.
Inductive Effect
Due to the difference in electronegativity between two atoms linked up by s bonds, the bonding electrons will displace towards the more electronegative atom. The atom exhibits a partial negative charge.
The electronic effect of a group that is transmitted by the polarization of electrons in s bonds is called an inductive effect.
![]()
![]()
Inductive effect is represented by an arrow head in the middle of the covalent bond pointing in the direction of the displacement of electrons.

Electron-withdrawing group exerts a negative inductive effect.
Electron-donating group exerts a positive inductive effect.
Groups which exert negative inductive effects
(i.e. electron-withdrawing groups):
e.g.
–NO2 > –F > –COOH > –Cl > –Br > –I
2. Groups which exert positive inductive effects (i.e. electron-releasing groups):
e.g.
alkyl groups like –CH3, –C2H5, –C3H7
The main characteristics of inductive effect
Always present when there are atoms with different electronegativity.
Spreads only through σ-bonds and in only one direction.
Dies out after 3-4 σ-bonds through the chain.
Conjugation
Conjugation (mesomerism) is the process of traffic of substituent electron influence through the conjugated system of π-bonds.
Conjugate system is the system that consists of simple and multiple bonds that alternates, or when there is an atom with a lone р-electron pair, or an atom that has an empty р-orbital, near the carbon atom that creates multiple bond. Conjugate systems can have open or closed chain.

Depended on the kind of overlapped orbitals, there can be different kinds of conjugation

Conjugation is energetically advantageous process that goes with energy emission. Conjugate systems has high thermodynamic stability.
Resonance effect is displacement of electron density in conjugate system
The displacement of electron density present in conjugate system only if there are electron-withdrawing groups or electron-releasing substituents.
Resonance (mesomeric) effect is marked as letter М.
Positive resonance effect is defined by substituents that gives electrons to the conjugate system.
Among them there are the atoms with negative charge (anions) or atoms that have a lone electron pair.
![]()
Negative resonance effect is defined by substituents that takes electrons from the conjugated system.
Among them there are atoms with empty orbital (carbocations) and atomic groups –СН=Х, or -С≡Х, where Х – more electronegative atom, than atom C.

The main examples of resonance effect:

The main characteristics of resonance effect
It is present only if there is a conjugate system.
It is present only if the conjugated system consists electron-withdrawing groups or electron-releasing substituents.
It makes more displacement of electron density than inductive effect and particularly doesn’t die out through the chain
The action of both inductive and resonance effects
Inductive and resonance effects of the same substituent can have not the same direction.

The stronger influence on the polarization of molecules makes the resonance effect, because π-bonds can be polarized easier than σ-bonds. Halogens are the only exception.
Hyperconjugation is a stabilization effect resulting from interaction between C=C π-bond orbital and a C-H σ bond orbital on a neighboring substituent (σ,π-conjugation), or the empty orbital and a C-H σ bond orbital on a neighboring substituent (σ,р- conjugation).

T he
more
atoms of hydrogen
are near the atom of carbon that is bonded with unsaturated system or
with empty orbital, the bigger
hyperconjugation effect
is.
he
more
atoms of hydrogen
are near the atom of carbon that is bonded with unsaturated system or
with empty orbital, the bigger
hyperconjugation effect
is.
Further increasing the degree of substitution leads to still further stability of double bond

Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases: The BrØnsted Definition
Accoding to the BrØnsted definition, an acid is any species that donates a proton, and base is a substance that accepts a proton.
In a
general sense

where Ka acidity constant, (in the dilute aqueous solution)
A stronger acid (larger Ka) has a smaller pKa, and weaker acid (smaller Ka) has a larger pKa
Relative Strengths of Same Common Acid and Their Conjugate Bases
|
Acid |
Name |
pKa |
Conjugate base |
Name |
|
Weaker acid
Stronger acid |
CH3CH2OH
H2O
HCN
CH3COOH
HF |
Ethanol
Water
Hydrocyanic acid Acetic acid Hydrofluoric acid |
16.00
15.74
9.31
4.76
3.45 |
CH3CH2O-
HO-
CN-
CH3COO-
F- |
E Hydroxide ion Cyanid ion
Acetat ion
Fluorid ion |
Stronger base
Weaker base |
Acids and Bases: The Lewis Definition
Of even more use is the Lewis definition of acid and base, which is not limited to compounds that gain or lose proton.
Lewis acid is a substance that accepts an electron pair and a
Lewis base is a substance that donates an electron pair

Questions and problems
On which orbital is situated electron that has the following quantum numbers n=3, l=0?
а)2s; b) 3d; c) 3s; d) 2p;
Which of the following formulas are the short structural formulas? а)
 ;
b) СН3СН2ОН;
c)
;
b) СН3СН2ОН;
c)
 ;
d) С2Н6О;
e)
;
d) С2Н6О;
e)
 .
.
Which of the following compounds has no atoms that have lone electron pairs on the outside energetic level?
а) СзОСН3; b) СН3NHСН3; c) С6Н14; d) С2Н6.
The result of hybridization of one s- and three р-orbitals. а) σ-bond; b) sp-hybridization; c) sp2- hybridization; d) π-bond; e) sp3- hybridization.
What kind of hybridization has the atoms of carbon in the following compound

а) 1- sp3-, 2- sp2-, 3- sp2-, 4- sp2-, 5- sp2-,6- sp2-,7- sp2-;
b) 1- sp3-, 2- sp-, 3- sp-, 4- sp3-, 5- sp3-,6- sp3-,7- sp3-;
c) 1- sp3-, 2- sp3-, 3- sp3-, 4- sp3-, 5- sp3-,6- sp2-,7- sp2-;
d) 1- s p3-, 2- sp-, 3- sp-, 4- sp3-, 5- sp2-,6- sp2-,7- sp3-;
e) 1- s p-, 2- sp-, 3- sp3-, 4- sp3-, 5- sp3-,6- sp2-,7- sp2-.
What kind of conjugation is there in the following compound? Using the arrows of inductive and resonance effects show the situation of electron density in molecula
 а)
π-π- conjugation;
b) р-π- conjugation;
c) σ-π- conjugation;
d) σ-р- conjugation;
e) р-р- conjugation;
f) no
conjugation
а)
π-π- conjugation;
b) р-π- conjugation;
c) σ-π- conjugation;
d) σ-р- conjugation;
e) р-р- conjugation;
f) no
conjugation

 thoxide
ion
thoxide
ion