
20)Fixed Assets– type and definition
Fixed assets are held and used by a business for a number of years, but they wear out or lose their usefulness over time. Every tangible fixed asset has a limited life. The only exception is land held freehold or on a very long leasehold.
The accounts of a business recognize that the cost of a fixed asset is consumed as the asset wears out, by writing off the asset’s cost in the profit and loss account over several accounting periods. For example, a machine costs £1,000 and is expected to wear out after ten years. We can reduce the balance sheet value by £100 each year. This process is known as ‘depreciation’.
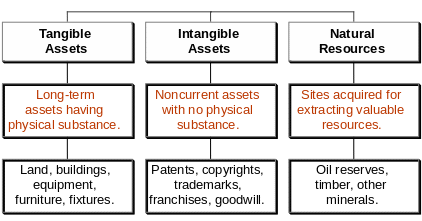
Intangible Assets
Amortize over shorter of economic life or legal life, subject to a maximum of 40 years.
Use straight-line method. Research and development costs are normally expensed as incurred.
Characteristics:
Noncurrent assets without physical substance;Often provide exclusive rights or privileges;Useful life is often difficult to determine;Usually acquired for operational use.
Intangible Assets - Record at current cash equivalent cost, including purchase price, legal fees, and filing fees. It could be:
Patents(Exclusive right granted by federal government to sell or manufacture an invention.)
Copyrights(Occurs when one company buys another company, only purchased goodwill is an intangible asset)
Leaseholds
Leasehold Improvements
Goodwill
Trademarks and Trade Names (A symbol, design, or logo associated with a business.)
Natural Resources
Total cost, including exploration and development, is charged to depletion expense over periods benefited.Extracted from the natural environment and reported at cost less accumulated depletion.
Examples: oil, coal, gold
21)Intangible Assets - Noncurrent assets without physical substance. Often provide exclusive rights or privileges. Useful life is often difficult to determine. Usually acquired for operational use.
Record at current cash equivalent cost, including purchase price, legal fees, and filing fees. ( Patents Copyrights, Leaseholds, Leasehold Improvements, Goodwill, Trademarks and Trade Names ).
Intangible Assets : Amortize over shorter of economic life or legal life, subject to a maximum of 40 years; Use straight-line method; Research and development costs are normally expensed as incurred.
Goodwill. Occurs when one company buys another company. Only purchased goodwill is an intangible asset. The amount by which the purchase price exceeds the fair market value of net assets acquired
Patents. Exclusive right granted by federal government to sell or manufacture an invention. Cost is purchase price plus legal cost to defend. Amortize cost over the shorter of useful life or 17 years.
Trademarks and Trade Names. A symbol, design, or logo associated with a business. Internally developed trademarks have no recorded asset cost. Purchased trademarks are recorded at cost, and amortized over shorter of legal or economic life, or 40 years.
Franchises. Legally protected right to sell products or provide services purchased by franchisee from franchisor. Purchase price is intangible asset which is amortized over the shorter of the protected right or 40 years.
Copyrights. Exclusive right granted by the federal government to protect artistic or intellectual properties. Legal life is life of creator plus 50 years. Amortize cost over a period not to exceed 40 years.
22.Fixed assets are held and used by a business for a number of years, but they wear out or lose their usefulness over time. Every tangible fixed asset has a limited life. The only exception is land held freehold or on a very long leasehold.
The accounts of a business recognize that the cost of a fixed asset is consumed as the asset wears out, by writing off the asset’s cost in the profit and loss account over several accounting periods.
Long-lived assets acquired for use in business operations.
Similar to long-term prepaid expenses: The cost of plant assets is the advance purchase of services, than as years pass, and the services are used, the cost is transferred to depreciation expense.
Acquisition of Fixed Assets. Cost = asset price + Reasonable and necessary costs for getting the asset to the desired location or for getting the asset ready for use.
Depreciation. The allocation of the cost of a plant asset to expense in the periods in which services are received from the asset.
Learning objectives: 1. Definition of depreciation 2. Causes of depreciation 3.Factors that affect the calculation of depreciation 4,Methods of depreciation (Straight-line method; Equation; Fixed percentage of cost of asset; Reducing balance method (Fixed percentage)) 5. Double entry records for depreciation and the disposal of fixed assets
Causes of Depreciation. Economic factors -= Obsolescence –(This is the process of becoming out of date. For instance, replacing a computer with old operating system with a new computer with XP system) and Inadequacy (This arises when an asset is no longer used because of the growth and changes in the size of the firm. For instance, a small ferryboat that is operated by a firm at a coastal resort will become entirely inadequate when the resort becomes more popular, to be more efficient and economical, the firm may replace it with a large ferryboat). The time factor (the effluxion of time) Some assets might have a legal life fixed in terms of years. For example, the patents, and leasehold. You may agree to rent some buildings for 10 years. This is normally called a lease. When the years are finished, the lease is worth nothing to you, as it has finished. Whatever you paid for the lease is now of no value. Depletion (Other assets are of wasting character, perhaps due to the extraction of raw materials from them. These materials are then either used by the firm to make something else, or are sold in their raw state to other firms. Natural resources such as mines, quarries and oil wells come under this heading. )
Straight-Line Depreciation. Depreciation Expense per Year = Cost - Residual Value / Years of Useful Life
Depreciation for Fractional Periods. When an asset is acquired during the year, depreciation in the year of acquisition must be prorated. Half-Year Convention / In the year of acquisition, record six months of depreciation.
Declining-Balance Method. Depreciation in the early years of an asset’s estimated useful life is higher than in later years. Depr.Expense = remaining book value * accelerated depr. Rate
23. Bankruptcy is a legal status of an insolvent person or an organization, that is, one that cannot repay the debts owed to creditors. In most jurisdictions bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor.
If the financial condition unsatisfactory, it is insolvent and can be declared bankrupt.
The question of recognition of the company bankrupt solved the economic court at the location of the debtor. The grounds for initiating bankruptcy of the enterprise is a written statement to the commercial court of any creditor or debtor.
The debtor turns to the economic court in the event of financial failure or its threat.
If the property sufficient to cover costs, the borrower submits an application to the commercial court, together with a plan of reorganization of the enterprise.
The creditor can apply for violation of bankruptcy legal entity, if the debtor is unable to meet within three months found him pretentious claims to the debtor in an amount not less than 300 minimum wages. Thus creditors may be recognized as legal and natural persons. To do this they must provide the debtor property requirements, the appropriate documents. Persons, property claims are fully secured by collateral, not creditors.
Submitted to the economic court the application and relevant documents considered by the judge that based on the correctness and completeness of the executed documents shall decide on approval of the application for consideration.
If the application for initiating bankruptcy judge no later than the fifth day after its receipt shall render a ruling to institute proceedings in the bankruptcy case and sends it to the parties and the public authority on bankruptcy.
Grounds for liquidation may be:
• completion of the period for which it was created, or the goal, set at its creation;
• the decision owner (s), the authority competent to create an enterprise;
• court or economic court invalidation of statutory documents and the decision to establish the enterprise;
• Commercial Court decision on the recognition of the enterprise bankrupt;
• a court decision banning activity of the enterprise;
• court or commercial court to cancel the state registration of enterprises for various reasons;
• other grounds provided by legislation of Ukraine.
24. Sanation - a system of financial-economic, technological, organizational, legal and social measures to achieve or restore solvency, liquidity, profitability and competitiveness of the debtor in the long run.
The purpose of financial sanation - cover current losses and eliminate the cause, recovery of liquidity and solvency of the enterprise, reducing all types of debt, improving the structure of capital and the formation of financial resources required for sanation measures of technological nature.
Sanation can occur merging companies, which is on the brink of bankruptcy with a strong company, issuance of new shares or bonds to raise cash capital increase of bank loans and the provision of government subsidies, converting short-term debt to long-term, full or partial purchase of state shares, which is in verge of bankruptcy.
According to sources the mobilization of financial resources, distinguish two kinds of sanation.
First kind provides funding Recovery Company by its own resources and funds provided by owners and other persons (without engaging in the process sanation outsiders).
Second kind is characterized by participation of outsiders, such as banks and other creditors, customers and the state.
Sanation program consists of 4 steps.
1. Shows the initial situation at the enterprise: evaluation of external conditions, analysis of financial and economic situation, analysis of the causes of the financial crisis and weak points, available potential.
2. Formulated strategic goals and developed a strategy of reorganization of the enterprise.
3. Major part of the plan. It helps to restore profitability and competitiveness in the long run: marketing Plan and assessment of markets for products, plan of production and investment, institutional Plan.
4. Contains a calculation of the efficiency and a list of institutional arrangements to implement the plan and monitor the implementation. In this section, detailing the expected effects from the project and forecast the possible risks and losses.
The main criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of rehabilitation are:
• liquidity and solvency;
• profitability;
• additional value created as a result of reorganization;
• competitive advantage.
