
Practical_class_1
.docxQuestions:
-
Linguistics is the study of all languages of the world that existed before, which exist now or may exist. This is the science of human language in general. Linguistics describes the characteristics and properties of the language. Linguistics tells about the language elements, describes and studies the changes in the language.
-
General linguistics studies the similarities and tendencies in language. Applied linguistics studies the practical tasks associated with language, using the language in real life, for example: translation, orthography, how to learn language.
-
I think that the most interesting field of general linguistics is the nature and essence of language. It seems to me quite interesting to know what language, what is its nature, what is its function. It is interesting to know how society influence on the language and how the language influence on the society. Any language that exists today is already quite developed, so it is very interesting to find out who, when and how create a language.
-


 Charles
Babbage-
the
first
person, who suggested the idea of machine translation
suggested the idea of machine translation.
Charles
Babbage-
the
first
person, who suggested the idea of machine translation
suggested the idea of machine translation.
 the
birth of machine translation
the
birth of machine translation
Classification of machine translation systems by Larry Child

- Fully automatic translation;
- Automated machine translation with human intervention;
- Translation carried out person using the computer.
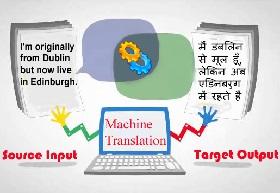
The place of machine translation in the translation process

classical scheme
machine translation scheme

a source
a source

interpreter
machine translation

recipient
interpreter

recipient
Features
of work with robot-translator
advantages
disadvantages
1. The ability to customize
2. predictability
3. The absence of errors due to human factors
-
Need the skills to work
-
understanding of the algorithm
-
difficult correctable errors of developers
Practical assignments
History
(How has a languages changed, history helps us to know why languages changed, how and where appeared new languages. Languages can tell us about people’ life)
Anthropology
( with the evolution of human- occurred language evolution)
-
LINGUISTICS


Sociology
(The variation of language use between different socioeconomic groups. For example: how speak men and women, teachers vs. students, Old people vs. young people, etc)
-
In our research the inductive method is used to do logical conclusion how subjective mood expressed now in English, how subjective mood expressed in the past, why and when subjective mood stopped using the past. The use of the deductive method allows us to gradually approach to logical conclusions. Slowly analyze and tell he reasons for rejection of using subjective mood. The method of linguistic description helps us to describe and analyze the components and parts of subjective mood.
-
The Traditional Methods in Linguistics
|
The name of the method |
The definition |
The method was developed in and by |
|
Inductive and deductive methods |
set of methods to conclusions,moving from particular facts to general provisions |
Aristotle |
|
descriptive method |
assembly, initial analysis and presentation their characteristics, giving a detailed and thorough description of language units |
|
|
comparative historical method |
set of methods and procedures to determine historical patterns of language development. |
Franz Bopp in 1816, Rasmus Rask in 1818, Jacob Grimm in 1819, Vostokov in 1820 |
|
contrastive method |
study and description of the language through its systematic compared to other languages |
The idea was theoretically substantiated by Baudouin de Courtenay, but as a linguistic method with certain principles, he began to take shape in the 30-40, 20th in USSR- Polivanov, Szczerba, Bernstein |
|
structural method |
understanding of language as a sign system with the structural elements |
Ferdinand de Saussure |
|
distributive analysis |
study of individual units in the text and not use the information on the full lexical or grammatical meaning of these units. |
L. Bloomfield in the 20 of the 20th century |
|
immediate constituents analysis or IC Analysis |
representation of word-formation structure of the word and the syntactic structure of phrases or sentences into a hierarchy |
L. Bloomfield in the 20 of the 20th century |
|
transformational analysis aims |
substitution of the facts of its variants having a different form, at close to substitute values. |
H. Harrison and N. Chomsky |
