
- •Molecular Biology of the Cell Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter Fourth Edition.
- •15. Cell Communication
- •General Principles of Cell Communication
- •Intracellular Signaling Complexes Enhance the Speed, Efficiency, and Specificity of the Response
- •Signaling through g-Protein-Linked Cell-Surface Receptors
- •Figure 15-44. Cyclic gmp.
- •Table 15-1. Some Hormone-induced Cell Responses Mediated by Cyclic amp
- •Signaling through Enzyme-Linked Cell-Surface Receptors
- •Table 15-4. Some Signaling Proteins That Act Via Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
- •Table 15-5. Some Signaling Proteins That Act Through Cytokine Receptors and the Jak-stat Signaling Pathway
- •Signaling Pathways That Depend on Regulated Proteolysis
Figure 15-44. Cyclic gmp.
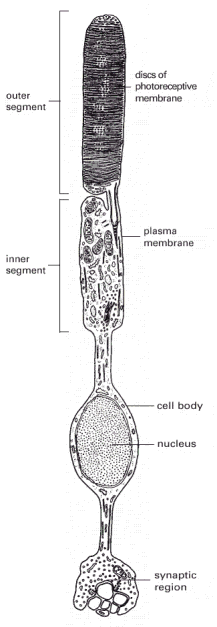 Figure
15-45. A rod photoreceptor cell.
There are about 1000 discs in the outer segment. The disc membranes
are not connected to the plasma membrane.
Figure
15-45. A rod photoreceptor cell.
There are about 1000 discs in the outer segment. The disc membranes
are not connected to the plasma membrane.
 Figure
15-46. The response of a rod
photoreceptor cell to light. Rhodopsin molecules in the
outer-segment discs absorb photons. Photon absorption leads to the
closure of Na+ channels in the plasma membrane, which
hyperpolarizes the membrane and reduces the rate of neurotransmitter
release from the synaptic region. Because the neurotransmitter acts
to inhibit many of the postsynaptic retinal neurons, illumination
serves to free the neurons from inhibition and thus, in effect,
excites them.
Figure
15-46. The response of a rod
photoreceptor cell to light. Rhodopsin molecules in the
outer-segment discs absorb photons. Photon absorption leads to the
closure of Na+ channels in the plasma membrane, which
hyperpolarizes the membrane and reduces the rate of neurotransmitter
release from the synaptic region. Because the neurotransmitter acts
to inhibit many of the postsynaptic retinal neurons, illumination
serves to free the neurons from inhibition and thus, in effect,
excites them.
 Figure
15-47. Amplification in the
light-induced catalytic cascade in vertebrate rods. The
divergent arrows indicate the steps where amplification occurs.
Figure
15-47. Amplification in the
light-induced catalytic cascade in vertebrate rods. The
divergent arrows indicate the steps where amplification occurs.
 Figure
15-48. The roles of
G-protein-linked receptor kinases (GRKs) and arrestins in receptor
desensitization. The binding of an arrestin to the
phosphorylated receptor prevents the receptor from binding to its G
protein and can direct its endocytosis. Mice that are deficient in
one form of arrestin fail to desensitize in response to morphine, for
example, attesting to the importance of arrestins for
desensitization.
Figure
15-48. The roles of
G-protein-linked receptor kinases (GRKs) and arrestins in receptor
desensitization. The binding of an arrestin to the
phosphorylated receptor prevents the receptor from binding to its G
protein and can direct its endocytosis. Mice that are deficient in
one form of arrestin fail to desensitize in response to morphine, for
example, attesting to the importance of arrestins for
desensitization.
Table 15-1. Some Hormone-induced Cell Responses Mediated by Cyclic amp
|
TARGET TISSUE |
HORMONE |
MAJOR RESPONSE |
|
Thyroid gland |
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) |
thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion |
|
Adrenal cortex |
adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) |
cortisol secretion |
|
Ovary |
luteinizing hormone (LH) |
progesterone secretion |
|
Muscle |
adrenaline |
glycogen breakdown |
|
Bone |
parathormone |
bone resorption |
|
Heart |
adrenaline |
increase in heart rate and force of contraction |
|
Liver |
glucagon |
glycogen breakdown |
|
Kidney |
vasopressin |
water resorption |
|
Fat |
adrenaline, ACTH, glucagon, TSH |
triglyceride breakdown |
Table 15-2. Some Cell Responses in Which G-Protein-linked Receptors Activate the Inositol-Phospholipid Signaling Pathway
|
TARGET TISSUE |
SIGNALING MOLECULE |
MAJOR RESPONSE |
|
Liver |
vasopressin |
glycogen breakdown |
|
Pancreas |
acetylcholine |
amylase secretion |
|
Smooth muscle |
acetylcholine |
contraction |
|
Blood platelets |
thrombin |
aggregation |
Table 15-3. Three Major Families of Trimeric G Proteins*
|
FAMILY |
SOME FAMILY MEMBERS |
ACTION MEDIATED BY |
FUNCTIONS |
|
I |
Gs |
|
activates adenylyl cyclase; activates Ca2+ channels |
|
|
Golf |
|
activates adenylyl cyclase in olfactory sensory neurons |
|
II |
Gi |
|
inhibits adenylyl cyclase |
|
|
|
|
activates K+ channels |
|
|
Go |
|
activates K+ channels; inactivates Ca2+ channels |
|
|
|
and |
activates phospholipase C- |
|
|
Gt (transducin) |
|
activates cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase in vertebrate rod photoreceptors |
|
III |
Gq |
|
activates phospholipase C- |
|
* Families are determined by amino acid sequence relatedness of the subunits. Only selected examples are shown. About 20 subunits and at least 4 subunits and 7 subunits have been described in mammals. |
|||
