
Physics and chemistry of bioluminescence - Rajeev Ranjan, PhD
.pdf
Biological engineering Program
Physics and chemistry of bioluminescence
Rajeev Ranjan, PhD

Biological engineering Program
Compulsory course
Physics and chemistry of bioluminescence
(3 ECTS)
•Diversity among luciferase class of enzyme, reaction mechanisms
•Enzyme commission (EC) number
•Different Luciferin structures, their role in luminescence emission
•Introduction to Photoprotein(s)

Overview of bioluminescence: bioluminescence in nature
k
h
a b
c |
e |
g |
i |
l |
|
||||
|
|
|
d
m
f
j n

Introduction to luciferase: the enzyme that triggers the oxidation of the luciferin
•Luciferase is a generic term
•Belong to the class oxidoreductase and catalyse oxidation of respective substrates
•Form product molecules in their electronically excited state which subsequently decay in form of light
•Range of wavelength emission (visible) but generally in the range of 470-560 nm but is not limited in this range

Basic Bioluminescent systems
S. |
Enzyme |
Bioluminescent |
Luciferase/MW(kDa)/ |
Substrate |
|
No. |
Commission |
protein |
Subunit |
(Luciferin) |
|
|
No. |
|
|
|
|
1. |
1.14.14.3 |
Bacterial luciferase |
Bluc ≈ 79, dimer |
Aliphatic |
|
|
|
|
|
aldehyde |
|
2. |
1.13.12.7 |
Firefly luciferase |
Fluc≈ 62, monomer |
D-Luciferin |
|
3. |
1.13.12.5 |
Renilla luciferase |
Rluc≈ 36, monomer |
a |
Coelenterazine |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
1.13.12.18 |
Gonyaulax |
LCF≈ 130, monomer |
Open |
|
|
|
luciferase |
|
tetrapyrrole |
|
5. |
? |
Fungi |
? |
b |
ND |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
1.13.12.6 |
Gaussia luciferase |
Gluc≈ 20 monomer |
a |
Coelenterazine |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. |
1.13.12.6 |
Metridia luciferase |
Mluc≈ 24 monomer |
a |
Coelenterazine |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
1.13.12.6 |
Vargula luciferase |
Vhl≈ 62 monomer |
a |
Coelenterazine |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. |
1.13.12.6 |
Cypridina luciferase |
Cnl≈ 62 monomer |
a |
Coelenterazine |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cPhotoprotein |
|
|
|
1. |
1.13.12.5 |
Aequorin |
Aeq≈ 22 monomer |
a |
Coelenterazine |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
1.13.12.6 |
Obelin |
Obe≈ 22 monomer |
a |
Coelenterazine |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
aGroup of structurally related compounds, bNot determined, cLuciferase– luciferin complex
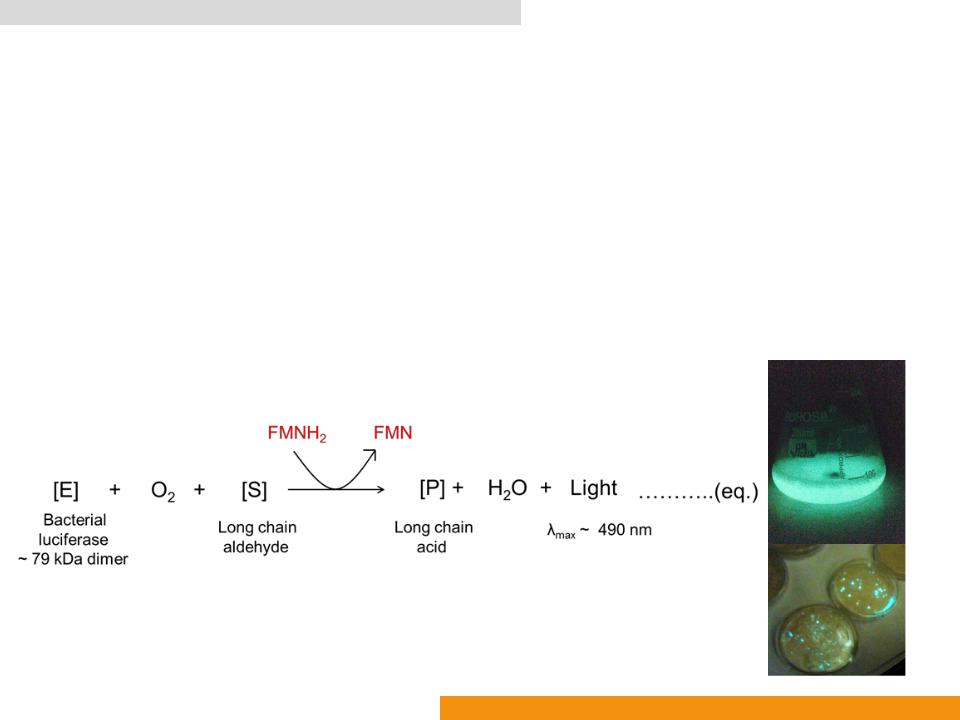
Bacterial luciferase (Bluc: EC 1.14.14.3)
•Catalyzes oxidation of reduced flavin mononucleotide (FMNH2)
•In the presence of luciferin (a long chain aldehyde) to yield the corresponding acid (a long chain acid), FMN, H2O and light (λmax: ≈ 490 nm)
•EC 1. Oxidoreductase (A– + B → A + B–)
•EC 1.14. Acting on paired donors, with O2 as oxidant and incorporation or reduction of oxygen. The oxygen incorporated need not be derived from O2
•EC 1.14.14. With reduced flavin or flavoprotein as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen into the other donor
•EC 1.14.14.3 alkanal monooxygenase (FMN)
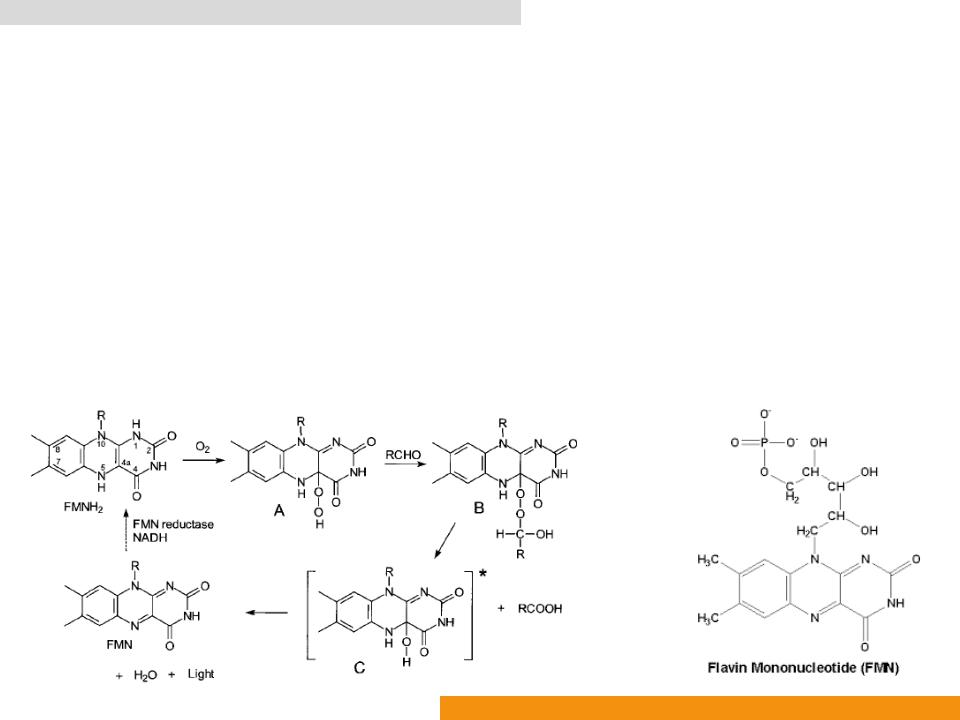
Bacterial luciferase (Bluc: EC 1.14.14.3)
•The molecule of FMNH2 is deprotonated at N1 when bound to a luciferase molecule
•Readily peroxidized at C4a to form Intermediate
•Intermediate A reacts with a fatty aldehyde (such as dodecanal and tetradecanal) to form Intermediate
•Intermediate B decomposes and yields the excited state of 4ahydroxyflavin (Intermediate C) and a fatty acid
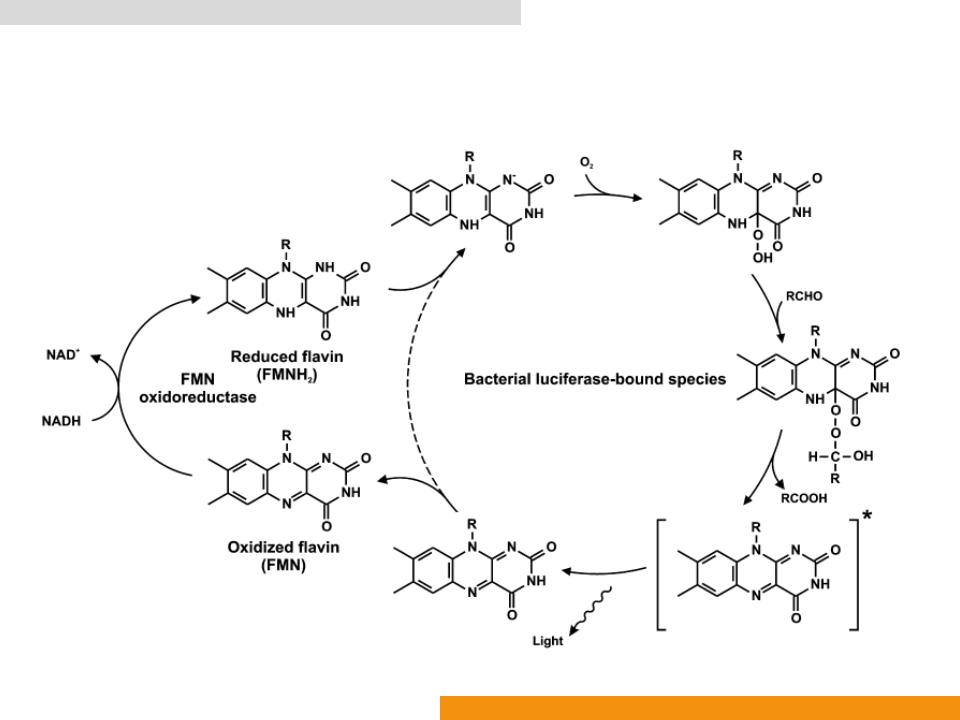
Bacterial bioluminescence system (Bluc: EC 1.14.14.3)
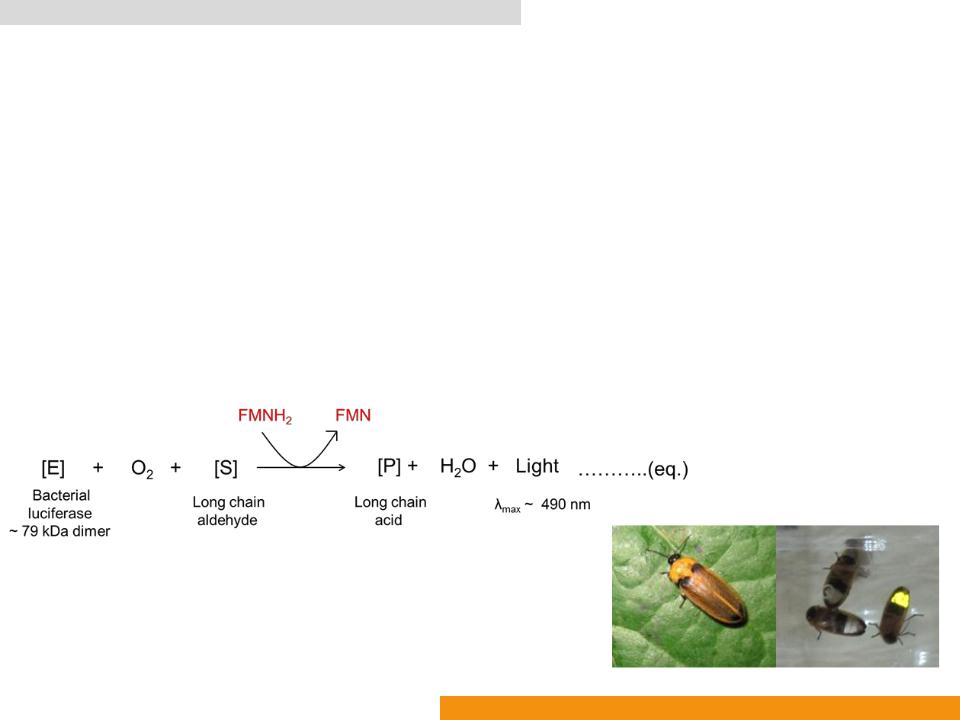
Firefly luciferase (Fluc: EC 1.13.12.7)
•Catalyzes oxidation of D-luciferin (Benzothiazole)
•In the presence of Adenosine-5ꞌ-phosphate (ATP) to yield oxyluciferin (Oxidized benzothiazole), AMP, CO2 and light (λmax: ≈ 560 nm)
•EC 1. Oxidoreductase (A– + B → A + B–)
•EC 1.13. Incorporation of oxygen into the substrate (oxygenases). The oxygen incorporated need not be derived from O2
•EC 1.13.12. Incorporation of one atom of oxygen atom into the other donor
•EC 1.13.12.7 Photinus-luciferin 4-monooxygenase (ATP-hydrolysing)
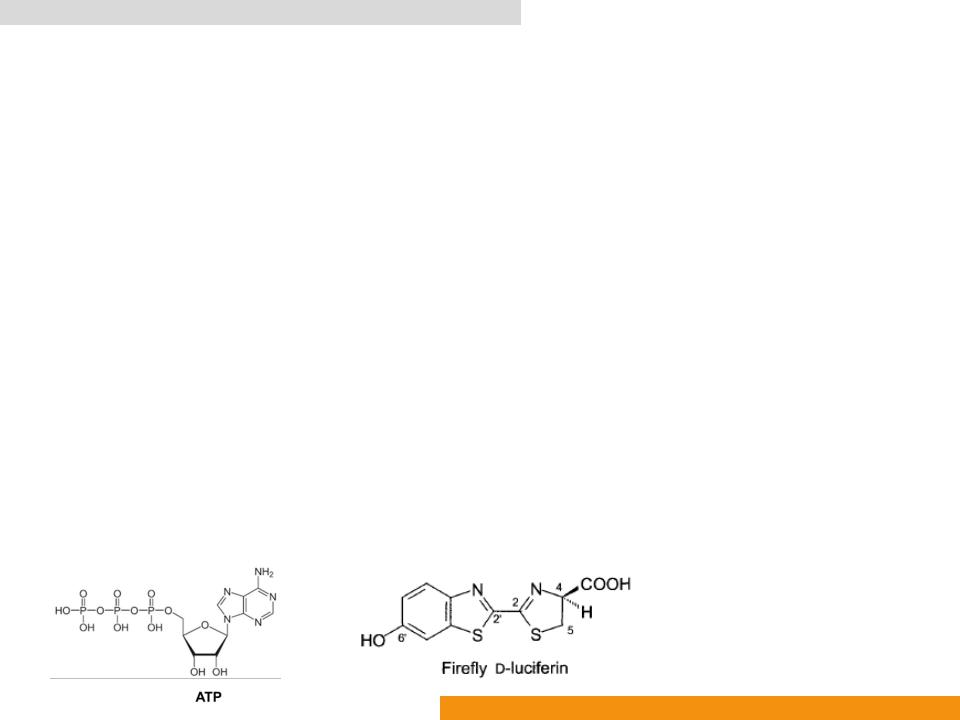
Firefly luciferase (Fluc: EC 1.13.12.7)
•firefly luciferase (FLuc), beetle luciferin (LH2), oxyluciferin (OxyLH2), Mg-ATP, emitter oxyluciferin (OxyLH2), inhibitory side product dehydroluciferyl-AMP (L-AMP)
•Two FLuc-catalyzed half reactions
•Production of luciferyl-adenylate (LH2-AMP)
•Reaction of LH2-AMP with O2 to produce OxyLH2 in an electronically excited state
•Formation of a key dioxetanone intermediate
•FLuc reaction is initiated when a presumed active site base
•abstracts the C4 proton of LH2-AMP producing a carbanion
