
posobie
.pdf6)What services do the public agriservices provide?
7)What services do the private agriservices provide?
2.Explain the following numbers: 13%; 8.5 trillion; 4%; 70; 45 billion; 12,000; 20 million; 30,000; 9%; 17,500.
3.Comment on the Figure 2.
4. Fill the blanks according to the text.
1)________is the value of goods and services that America produces in a year.
2)The agricultural industry ________17 percent of the GDP.
3)These related industries ________food and fiber from farmers.
4)Another $45 billion comes from ________sources.
5)The agribusiness ________sector needs approximately 20 million workers.
6)`The USDA ________that over 600,000 businesses are involved in marketing food products.
7)This represents about 9 percent of the consumers' disposable personal
________.
5.Provide the summary of this text in the written form.
V. Read the text. Name the text and divide it into parts.
Text III. _____________
Specifically, there are three major areas of private agriservices available to the agricultural industry: financial services, trade associations, and agricultural cooperatives.
Financial services are a vital part of the agricultural industry. Lending money to all three sectors of the agricultural industry (input, production, and output) is big business. Outstanding loans for farm real estate alone amount to nearly $80 billion, in addition to other outstanding loans and non-real estate debt, which is nearly another $65 billion. Commercial banks, the Farm Credit System, the Farm Service Agency, individual businesses and cooperatives, and insurance companies all provide funds that farmers need to buy land, equipment, livestock, machinery, seed, fertilizer, and the other products they use in their daily farming operations. Many of these same agencies are also involved with providing financial services to the agribusiness input
11
suppliers and those that buy, transport, process, and market agricultural products. These agribusinesses need credit and capital for their day-to-day operations, buildings, and equipment, just as farmers do. Trade associations, as well as dairy and livestock associations, are vital to the agricultural industry. Every agribusiness and production agriculture enterprise has a trade association, society, or institute, which are supported by members who are active in a particular enterprise. Thousands of trade associations operate in America. They serve agribusiness and promote certain agricultural products, and they have become an essential part of agribusiness relationships. Associations perform a wide variety of services for their members in areas such as public relations, promotion, legislative lobbying, communications, sales training, auditing and record keeping, publicity, transportation, research, and legislative and marketing information. These and similar services can be provided better by organized groups rather than by individuals. Members may pay dues to an association to receive its benefits, or producers may pay a check-off from sales of their products. Agricultural cooperatives serve many needs and engage in a variety of essential services to the agricultural industry. Over 4,200 cooperatives market agricultural products and furnish the agricultural industry with production supplies and services. Their annual business volume is over $83 billion. Cooperatives market over one-quarter of all agricultural products and provide one-quarter of the production supplies for farmers. They also furnish electricity to the agricultural industry. Cooperatives enable livestock producers to better market their animals and improve dairy products through dairy herd improvement associations. The United States has long played a major role in world agricultural trade and is rapidly increasing its role relative to most other countries. Currently, the United States is the major participant in international trade of agricultural products. The five major farm commodities sold in world markets were feed grains and feed grain products, soybeans and soybean products, wheat and wheat products, live animals, meat and meat products, and vegetables, for a total value of $46.7 billion. In comparison, the total value of all agricultural exports was only $6 billion several decades ago. Almost every country of the world purchases some agricultural products from the United
States. In addition to being a major world exporter of agricultural products, the
12
United States is also a major importer of agricultural products. Over a decade, annual farm imports increased from $4.45 billion to $10.50 billion, a 136 percent increase. Although the major quantity is imported from Latin America, Asia, and Europe, U.S.importscome from every continent except Antarctica. Although imports are greater than ever, the U.S. trade surplus (dollars exported minus dollars imported) was $18.9 billion. In addition to providing markets for American farmers, foreign exports provide additional advantages. Between 25,000 and 30,000 jobs are created in the United States for each billion dollars of agricultural exports. Between 1.2 and 1.4 million full-time jobs could be attributed to American agricultural exports. Exports account for approximately one-third of U.S. agricultural production. In many states, as much as one-half of farm income comes from agricultural exports.
1. Give the definitions to the terms.
Term |
Definition |
|
|
Check-off |
|
|
|
Funds |
|
|
|
Importer |
|
|
|
Lending |
|
|
|
Loan |
|
|
|
Lobby |
|
|
|
Promote |
|
|
|
Real estate |
|
|
|
Supplier |
|
|
|
Value |
|
|
|
2.Explain the numbers: 80 billion; 83 billion; 136; 25,000; 4,200; 4.45 billion;
46.7billion; 18.9 billion.
3.Provide the written description of each major area of private agriservices. VI. Compare figures 2 and 3. How could you characterize domestic and
global agricultural markets of the USA?
13

VII. Translate the text into English. List the keywords.
Text IV. Инвесторы с надеждой смотрят на российский агробизнес
Российский агробизнес становится все более привлекательным для инвестиций. Такое мнение в интервью РБК высказал глава российского подразделения компании Syngenta, являющейся одним из крупнейших мировых разработчиков и производителей средств защиты растений и семян, Кристофер Николлс.
По его словам, рынок после кризиса восстановился практически полностью и отмечается рост количества инвесторов, которые берут землю в аренду и вкладывают средства в сельское хозяйство.
Наибольший интерес у инвесторов сейчас вызывают сельскохозяйственные предприятия, действующие на территории Краснодарского и Ставропольского краев, Ростовской области и Центрального региона.
Приветствуя появление крупных инвесторов в сельском хозяйстве,
Кристофер Николлс высказал мнение, что в данных условиях наиболее
14
эффективными являются мелкие и средние формы бизнеса. Появление таких инвесторов позволит решить проблему нехватки оборотных средств сельхозпредприятий, инвестиций в основной капитал и новые технологии, а
значит, и повысить их рентабельность.
По мнению Николлса, во многом позитивные процессы, наблюдающиеся сейчас в российском агробизнесе, обусловлены ростом доступности банковских кредитов для сельхозпроизводителей.
VIII. Prepare the presentation on the state of agribusiness in Russia.
15

UNIT 2
WAYS OF DOING BUSINESS
I. Find the translation of the given words. Write them down.
articles of incorporation |
interest rate |
patronage |
share |
board of directors |
IRS |
personal assets |
shareholder |
bylaws |
issue stock |
preferred stock |
share of stock |
charge |
legal entity |
property |
sole proprietor |
common stock |
LLC |
raise capital |
stockholder |
equity capital |
limited partner |
retailer |
supply cooperative |
file |
limited partnership |
rural credit union |
tax preparation |
general partnership |
marketing co-op |
secretary of state |
tax return |
incorporate |
operating agreement |
service cooperative |
voting stock |
II.Look at the Fig. 1 and make assumption about the shares of the business structures in the economy of the USA.
Figure 1. The proportion of total business revenue
16
III.Read the text. Explain the words in bold type. Name the text.
Text I. ____________
As American society becomes increasingly complex, the process of selecting the most desirable type of agricultural business, or legal structure, for an agribusiness becomes very important. The amount of restrictions by government, the tax structure, and other legal requirements are determined, to a large degree, by the legal type of agribusiness.
The type of agribusiness, or legal classification, you choose may make the difference between success or failure. Although there are many specific legal structures available, most legal specialists agree that the three major types of business organizations are:
-the sole proprietorship;
-the partnership;
-the corporation.
The three types of corporations are regular corporations, family farms and small businesses, and cooperatives. Cooperative corporations are increasing in importance (there are 20,000 of them in USA), and many authors list the cooperative as a fourth major type of business. 68.5 thousand Small U.S. businesses operate as family corporations. Another corporation that is a special form of business organization is limited liability companies (LLCs) that make approximately 1% of agricultural business.
Some agribusinesses are relatively easy to start, such as a lawn service or landscaping business. An organization that is owned, and usually managed, by one person is called a sole proprietorship. It is the most common form of business ownership with over 2.5 million businesses.
Many people lack the money, time, or desire to run a business on their own. They prefer to have someone else or some group of people get together to help them form an agribusiness. When two or more people legally agree to become co-owners of a business, the organization is called a partnership. In the United States, there are more than 110,000 partnership businesses.
17
It is sometimes best to create a business that is separate and distinct from the owners. A legal classification with authority to act and have liability separate from its owners is called a corporation. Although there are only 182,000 corporations in the United States, comprising only 8 percent of all businesses, they do 87 percent of the sales volume.
No single type of legal structure is best for all businesses. Therefore, when developing a new agribusiness, all structures should be considered relative to their advantages and disadvantages. Although sole proprietorships are more numerous in all types of industries except manufacturing, they are especially dominant in production agriculture, including forestry and fisheries. Corporations are the least numerous for these groups, but they exceed partnerships in all other types of industries.
1.Answer the questions:
1)Why does selecting of the type of agribusiness become very important?
2)What are the major types of business organizations?
3)What are the three types of corporations?
4)What type of legal structure is more numerous in almost all types of industries? Why?
2.Explain the following word combinations: legal structure, tax structure, sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, cooperative, to run a business, coowners, liability, forestry.
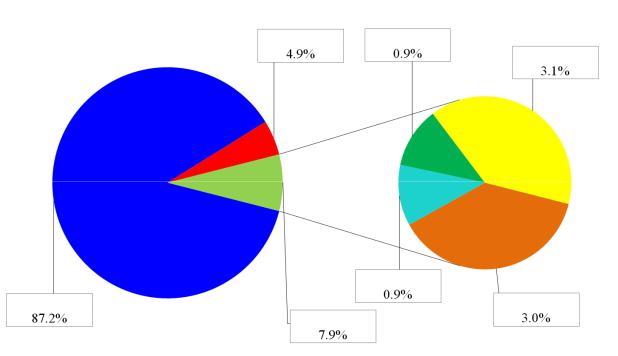
IV.Look at the Fig. 2. Define the business structures according to their share in the market.
Figure 2. The proportion of the business structures in the U.S. agribusiness
18
V. Look through the text. Name it. Explain the words in bold type.
Text II. ________
Sole proprietorships have several advantages. As mentioned, they are simple to start. There are few government regulations or restrictions. Depending on local laws, the only requirement may be a license, which is a legal permit for doing business. Management and control are solely in the owner's hands. Therefore, no voting is necessary. This allows owners to make quick decisions, without waiting to talk with others. Sole proprietors can choose their own products and set their own hours. Another advantage is that the owners receive all the profits from the business. Finally, sole proprietors pay taxes only once on the income from the company.
Even though we tend to stress the advantages of sole proprietorships, they also have certain disadvantages. The major one is the claim that creditors can make on the owner's personal assets, as well as the business assets, in the payment of business debts. This relationship is known as unlimited liability. Another major disadvantage of one-owner firms is that the accumulation of the large amounts of capital required to begin and operate many businesses today is limited. In some cases, an owner may be good in the "product" of the business (repairing tractors, for instance) but he or she may not have business skills in other areas, such as leadership, human and public relations, or tax preparation. Owners may have to seek outside help to keep the business going. Another disadvantage of the sole proprietorship is its limited life.
Partnerships are found in many other areas of the agricultural industry. A few examples include agricultural supply stores, landscaping businesses, and hunting preserves. Many times the names of the business will give you a clue about how many partners are involved: a two-person partnership might be called "Walker and Jones Feed Store," and a three-person partnership might be named something like "Rodriguez, Rochelle and Jordan Meat Processors". A general partnership is an association of two or more people who, as owners, manage a business together. General partnerships contain certain recognizable factors. An agreement should be formalized explaining the terms of the partnership and outlining who is to contribute what, how decisions are to be made, and how profits are to be split. A
19

general partnership is dissolved by death, agreement, or bankruptcy. Generally, voting and profit sharing are based on the amount each partner contributes to the partnership. Each partner is fully liable for the partnership's activities. The partnership must file tax returns, but it pays no taxes. The partnership's tax return provides information so that each partner can file an individual return. Any profit earned by the partnership is divided between the partners based on previous agreements. There is a special type of partnership in which some partners are not completely liable for their partners' debts. This type is usually called a limited partnership. To be a limited partner, one must invest in the business but may not participate in the management phase. The limited partner's name cannot even appear in the partnership name. Limited partnerships are for investment purposes only. Limited partners are liable for partnership obligations only up to the amount of their investment in the partnership and may not be held personally liable. This provides incentive for investing in a business without the fear of losing personal or other business assets.
1.Answer the following questions:
1)What is sole proprietorship?
2)What allows owners to make quick decisions without waiting to talk with others?
3)What is unlimited liability?
4)When does this type of business legally end?
5)When can the business be organized as a partnership?
6)What does it mean to be a limited partner?
7)What is the difference between a general partnership and a limited one?
2.Provide the definitions of the given terms.
Term |
Definition |
Accumulation
Bankruptcy
Claim
Contribute
20
