
- •Practical Unit Testing with JUnit and Mockito
- •Table of Contents
- •About the Author
- •Acknowledgments
- •Preface
- •Preface - JUnit
- •Part I. Developers' Tests
- •Chapter 1. On Tests and Tools
- •1.1. An Object-Oriented System
- •1.2. Types of Developers' Tests
- •1.2.1. Unit Tests
- •1.2.2. Integration Tests
- •1.2.3. End-to-End Tests
- •1.2.4. Examples
- •1.2.5. Conclusions
- •1.3. Verification and Design
- •1.5. Tools Introduction
- •Chapter 2. Unit Tests
- •2.1. What is a Unit Test?
- •2.2. Interactions in Unit Tests
- •2.2.1. State vs. Interaction Testing
- •2.2.2. Why Worry about Indirect Interactions?
- •Part II. Writing Unit Tests
- •3.2. Class To Test
- •3.3. Your First JUnit Test
- •3.3.1. Test Results
- •3.4. JUnit Assertions
- •3.5. Failing Test
- •3.6. Parameterized Tests
- •3.6.1. The Problem
- •3.6.2. The Solution
- •3.6.3. Conclusions
- •3.7. Checking Expected Exceptions
- •3.8. Test Fixture Setting
- •3.8.1. Test Fixture Examples
- •3.8.2. Test Fixture in Every Test Method
- •3.8.3. JUnit Execution Model
- •3.8.4. Annotations for Test Fixture Creation
- •3.9. Phases of a Unit Test
- •3.10. Conclusions
- •3.11. Exercises
- •3.11.1. JUnit Run
- •3.11.2. String Reverse
- •3.11.3. HashMap
- •3.11.4. Fahrenheits to Celcius with Parameterized Tests
- •3.11.5. Master Your IDE
- •Templates
- •Quick Navigation
- •Chapter 4. Test Driven Development
- •4.1. When to Write Tests?
- •4.1.1. Test Last (AKA Code First) Development
- •4.1.2. Test First Development
- •4.1.3. Always after a Bug is Found
- •4.2. TDD Rhythm
- •4.2.1. RED - Write a Test that Fails
- •How To Choose the Next Test To Write
- •Readable Assertion Message
- •4.2.2. GREEN - Write the Simplest Thing that Works
- •4.2.3. REFACTOR - Improve the Code
- •Refactoring the Tests
- •Adding Javadocs
- •4.2.4. Here We Go Again
- •4.3. Benefits
- •4.4. TDD is Not Only about Unit Tests
- •4.5. Test First Example
- •4.5.1. The Problem
- •4.5.2. RED - Write a Failing Test
- •4.5.3. GREEN - Fix the Code
- •4.5.4. REFACTOR - Even If Only a Little Bit
- •4.5.5. First Cycle Finished
- •‘The Simplest Thing that Works’ Revisited
- •4.5.6. More Test Cases
- •But is It Comparable?
- •Comparison Tests
- •4.6. Conclusions and Comments
- •4.7. How to Start Coding TDD
- •4.8. When not To Use Test-First?
- •4.9. Should I Follow It Blindly?
- •4.9.1. Write Good Assertion Messages from the Beginning
- •4.9.2. If the Test Passes "By Default"
- •4.10. Exercises
- •4.10.1. Password Validator
- •4.10.2. Regex
- •4.10.3. Booking System
- •Chapter 5. Mocks, Stubs, Test Spies
- •5.1. Introducing Mockito
- •5.1.1. Creating Test Doubles
- •5.1.2. Expectations
- •5.1.3. Verification
- •5.1.4. Conclusions
- •5.2. Types of Test Double
- •5.2.1. Code To Be Tested with Test Doubles
- •5.2.2. The Dummy Object
- •5.2.3. Test Stub
- •5.2.4. Test Spy
- •5.2.5. Mock
- •5.3. Putting it All Together
- •5.4. Example: TDD with Test Doubles
- •5.4.2. The Second Test: Send a Message to Multiple Subscribers
- •Refactoring
- •5.4.3. The Third Test: Send Messages to Subscribers Only
- •5.4.4. The Fourth Test: Subscribe More Than Once
- •Mockito: How Many Times?
- •5.4.5. The Fifth Test: Remove a Subscriber
- •5.4.6. TDD and Test Doubles - Conclusions
- •More Test Code than Production Code
- •The Interface is What Really Matters
- •Interactions Can Be Tested
- •Some Test Doubles are More Useful than Others
- •5.5. Always Use Test Doubles… or Maybe Not?
- •5.5.1. No Test Doubles
- •5.5.2. Using Test Doubles
- •No Winner So Far
- •5.5.3. A More Complicated Example
- •5.5.4. Use Test Doubles or Not? - Conclusion
- •5.6. Conclusions (with a Warning)
- •5.7. Exercises
- •5.7.1. User Service Tested
- •5.7.2. Race Results Enhanced
- •5.7.3. Booking System Revisited
- •5.7.4. Read, Read, Read!
- •Part III. Hints and Discussions
- •Chapter 6. Things You Should Know
- •6.1. What Values To Check?
- •6.1.1. Expected Values
- •6.1.2. Boundary Values
- •6.1.3. Strange Values
- •6.1.4. Should You Always Care?
- •6.1.5. Not Only Input Parameters
- •6.2. How to Fail a Test?
- •6.3. How to Ignore a Test?
- •6.4. More about Expected Exceptions
- •6.4.1. The Expected Exception Message
- •6.4.2. Catch-Exception Library
- •6.4.3. Testing Exceptions And Interactions
- •6.4.4. Conclusions
- •6.5. Stubbing Void Methods
- •6.6. Matchers
- •6.6.1. JUnit Support for Matcher Libraries
- •6.6.2. Comparing Matcher with "Standard" Assertions
- •6.6.3. Custom Matchers
- •6.6.4. Advantages of Matchers
- •6.7. Mockito Matchers
- •6.7.1. Hamcrest Matchers Integration
- •6.7.2. Matchers Warning
- •6.8. Rules
- •6.8.1. Using Rules
- •6.8.2. Writing Custom Rules
- •6.9. Unit Testing Asynchronous Code
- •6.9.1. Waiting for the Asynchronous Task to Finish
- •6.9.2. Making Asynchronous Synchronous
- •6.9.3. Conclusions
- •6.10. Testing Thread Safe
- •6.10.1. ID Generator: Requirements
- •6.10.2. ID Generator: First Implementation
- •6.10.3. ID Generator: Second Implementation
- •6.10.4. Conclusions
- •6.11. Time is not on Your Side
- •6.11.1. Test Every Date (Within Reason)
- •6.11.2. Conclusions
- •6.12. Testing Collections
- •6.12.1. The TDD Approach - Step by Step
- •6.12.2. Using External Assertions
- •Unitils
- •Testing Collections Using Matchers
- •6.12.3. Custom Solution
- •6.12.4. Conclusions
- •6.13. Reading Test Data From Files
- •6.13.1. CSV Files
- •6.13.2. Excel Files
- •6.14. Conclusions
- •6.15. Exercises
- •6.15.1. Design Test Cases: State Testing
- •6.15.2. Design Test Cases: Interactions Testing
- •6.15.3. Test Collections
- •6.15.4. Time Testing
- •6.15.5. Redesign of the TimeProvider class
- •6.15.6. Write a Custom Matcher
- •6.15.7. Preserve System Properties During Tests
- •6.15.8. Enhance the RetryTestRule
- •6.15.9. Make an ID Generator Bulletproof
- •Chapter 7. Points of Controversy
- •7.1. Access Modifiers
- •7.2. Random Values in Tests
- •7.2.1. Random Object Properties
- •7.2.2. Generating Multiple Test Cases
- •7.2.3. Conclusions
- •7.3. Is Set-up the Right Thing for You?
- •7.4. How Many Assertions per Test Method?
- •7.4.1. Code Example
- •7.4.2. Pros and Cons
- •7.4.3. Conclusions
- •7.5. Private Methods Testing
- •7.5.1. Verification vs. Design - Revisited
- •7.5.2. Options We Have
- •7.5.3. Private Methods Testing - Techniques
- •Reflection
- •Access Modifiers
- •7.5.4. Conclusions
- •7.6. New Operator
- •7.6.1. PowerMock to the Rescue
- •7.6.2. Redesign and Inject
- •7.6.3. Refactor and Subclass
- •7.6.4. Partial Mocking
- •7.6.5. Conclusions
- •7.7. Capturing Arguments to Collaborators
- •7.8. Conclusions
- •7.9. Exercises
- •7.9.1. Testing Legacy Code
- •Part IV. Listen and Organize
- •Chapter 8. Getting Feedback
- •8.1. IDE Feedback
- •8.1.1. Eclipse Test Reports
- •8.1.2. IntelliJ IDEA Test Reports
- •8.1.3. Conclusion
- •8.2. JUnit Default Reports
- •8.3. Writing Custom Listeners
- •8.4. Readable Assertion Messages
- •8.4.1. Add a Custom Assertion Message
- •8.4.2. Implement the toString() Method
- •8.4.3. Use the Right Assertion Method
- •8.5. Logging in Tests
- •8.6. Debugging Tests
- •8.7. Notifying The Team
- •8.8. Conclusions
- •8.9. Exercises
- •8.9.1. Study Test Output
- •8.9.2. Enhance the Custom Rule
- •8.9.3. Custom Test Listener
- •8.9.4. Debugging Session
- •Chapter 9. Organization Of Tests
- •9.1. Package for Test Classes
- •9.2. Name Your Tests Consistently
- •9.2.1. Test Class Names
- •Splitting Up Long Test Classes
- •Test Class Per Feature
- •9.2.2. Test Method Names
- •9.2.3. Naming of Test-Double Variables
- •9.3. Comments in Tests
- •9.4. BDD: ‘Given’, ‘When’, ‘Then’
- •9.4.1. Testing BDD-Style
- •9.4.2. Mockito BDD-Style
- •9.5. Reducing Boilerplate Code
- •9.5.1. One-Liner Stubs
- •9.5.2. Mockito Annotations
- •9.6. Creating Complex Objects
- •9.6.1. Mummy Knows Best
- •9.6.2. Test Data Builder
- •9.6.3. Conclusions
- •9.7. Conclusions
- •9.8. Exercises
- •9.8.1. Test Fixture Setting
- •9.8.2. Test Data Builder
- •Part V. Make Them Better
- •Chapter 10. Maintainable Tests
- •10.1. Test Behaviour, not Methods
- •10.2. Complexity Leads to Bugs
- •10.3. Follow the Rules or Suffer
- •10.3.1. Real Life is Object-Oriented
- •10.3.2. The Non-Object-Oriented Approach
- •Do We Need Mocks?
- •10.3.3. The Object-Oriented Approach
- •10.3.4. How To Deal with Procedural Code?
- •10.3.5. Conclusions
- •10.4. Rewriting Tests when the Code Changes
- •10.4.1. Avoid Overspecified Tests
- •10.4.2. Are You Really Coding Test-First?
- •10.4.3. Conclusions
- •10.5. Things Too Simple To Break
- •10.6. Conclusions
- •10.7. Exercises
- •10.7.1. A Car is a Sports Car if …
- •10.7.2. Stack Test
- •Chapter 11. Test Quality
- •11.1. An Overview
- •11.2. Static Analysis Tools
- •11.3. Code Coverage
- •11.3.1. Line and Branch Coverage
- •11.3.2. Code Coverage Reports
- •11.3.3. The Devil is in the Details
- •11.3.4. How Much Code Coverage is Good Enough?
- •11.3.5. Conclusion
- •11.4. Mutation Testing
- •11.4.1. How does it Work?
- •11.4.2. Working with PIT
- •11.4.3. Conclusions
- •11.5. Code Reviews
- •11.5.1. A Three-Minute Test Code Review
- •Size Heuristics
- •But do They Run?
- •Check Code Coverage
- •Conclusions
- •11.5.2. Things to Look For
- •Easy to Understand
- •Documented
- •Are All the Important Scenarios Verified?
- •Run Them
- •Date Testing
- •11.5.3. Conclusions
- •11.6. Refactor Your Tests
- •11.6.1. Use Meaningful Names - Everywhere
- •11.6.2. Make It Understandable at a Glance
- •11.6.3. Make Irrelevant Data Clearly Visible
- •11.6.4. Do not Test Many Things at Once
- •11.6.5. Change Order of Methods
- •11.7. Conclusions
- •11.8. Exercises
- •11.8.1. Clean this Mess
- •Appendix A. Automated Tests
- •A.1. Wasting Your Time by not Writing Tests
- •A.1.1. And what about Human Testers?
- •A.1.2. One More Benefit: A Documentation that is Always Up-To-Date
- •A.2. When and Where Should Tests Run?
- •Appendix B. Running Unit Tests
- •B.1. Running Tests with Eclipse
- •B.1.1. Debugging Tests with Eclipse
- •B.2. Running Tests with IntelliJ IDEA
- •B.2.1. Debugging Tests with IntelliJ IDEA
- •B.3. Running Tests with Gradle
- •B.3.1. Using JUnit Listeners with Gradle
- •B.3.2. Adding JARs to Gradle’s Tests Classpath
- •B.4. Running Tests with Maven
- •B.4.1. Using JUnit Listeners and Reporters with Maven
- •B.4.2. Adding JARs to Maven’s Tests Classpath
- •Appendix C. Test Spy vs. Mock
- •C.1. Different Flow - and Who Asserts?
- •C.2. Stop with the First Error
- •C.3. Stubbing
- •C.4. Forgiveness
- •C.5. Different Threads or Containers
- •C.6. Conclusions
- •Appendix D. Where Should I Go Now?
- •Bibliography
- •Glossary
- •Index
- •Thank You!
Appendix B. Running Unit Tests
There are many ways to run tests written with JUnit, as all the major tools support it out-of-the-box. This section describes how to run JUnit tests using the most popular IDEs and build tools: Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, Gradle and Maven.
The tools presented in this section are capable of much more than simply executing tests. Please consult their documentation to find out more.
As far as Gradle and Maven are concerned, I will assume that your project has a layout compatible with what was discussed in Section 3.1. The main requirement is that your production code resides in src/ main/java and test classes in src/test/java. Both Gradle and Maven treat this layout as the default. If you use a different directory structure then you will need to inform your build tool about it. Please refer to the appropriate documentation about how to do it.
One could ask why it is that we need to bother with build tools, if our powerful IDEs are capable of running tests. The thing is, the tests we write will be executed on the machines of other developers (who may be using different IDEs), and even on the IDE-free environment of a CI server. Having a build script capable of running tests is the first step in helping to overcome the "it works on my machine" syndrome.
This appendix concentrates on running tests on your local machine. However, bear in mind that every team should have a separate machine (a continuous integration server) dedicated to the building (compiling, testing, packaging, etc.) of the code it is developing. Continuous integration is well beyond the scope of this book, but there is plenty of information available on the Internet if you need it.
B.1. Running Tests with Eclipse
Eclipse supports JUnit out of the box. There is no need to install any plugins.
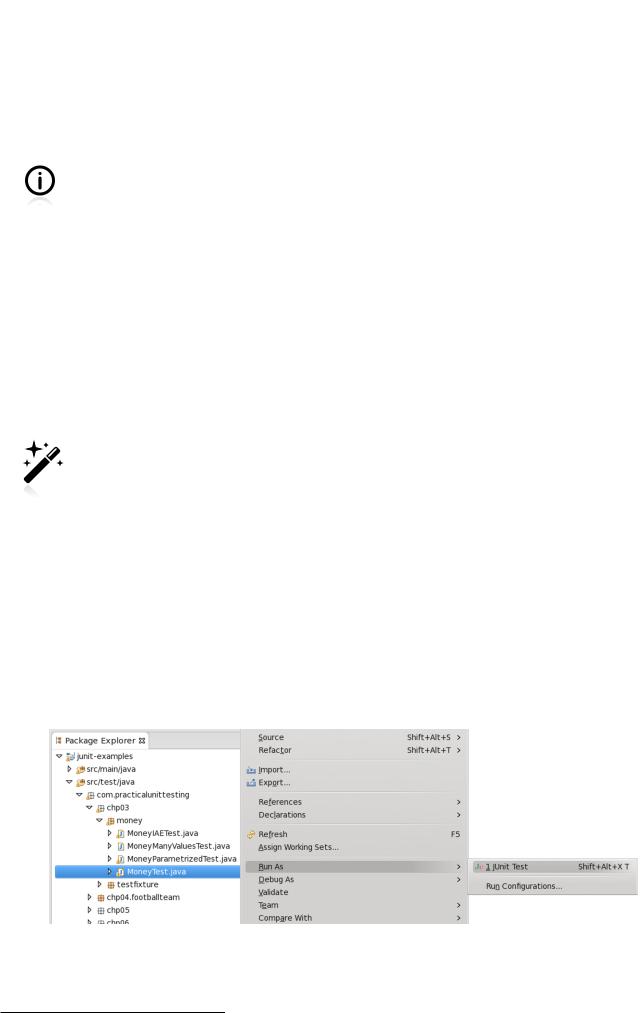
If you prefer to use a mouse, then right-click on the selected test class (e.g. MoneyTest) and choose Run As / JUnit Test. Likewise, to run a single test method, right-click it and choose Run As / JUnit Test.
Figure B.1. Running a single test with Eclipse
To run more tests right-click on, for example, src/test/java directory (or any package inside it which includes some tests), in project tree view, and choose the same option as previously: Run As / JUnit Test.
270
Appendix B. Running Unit Tests
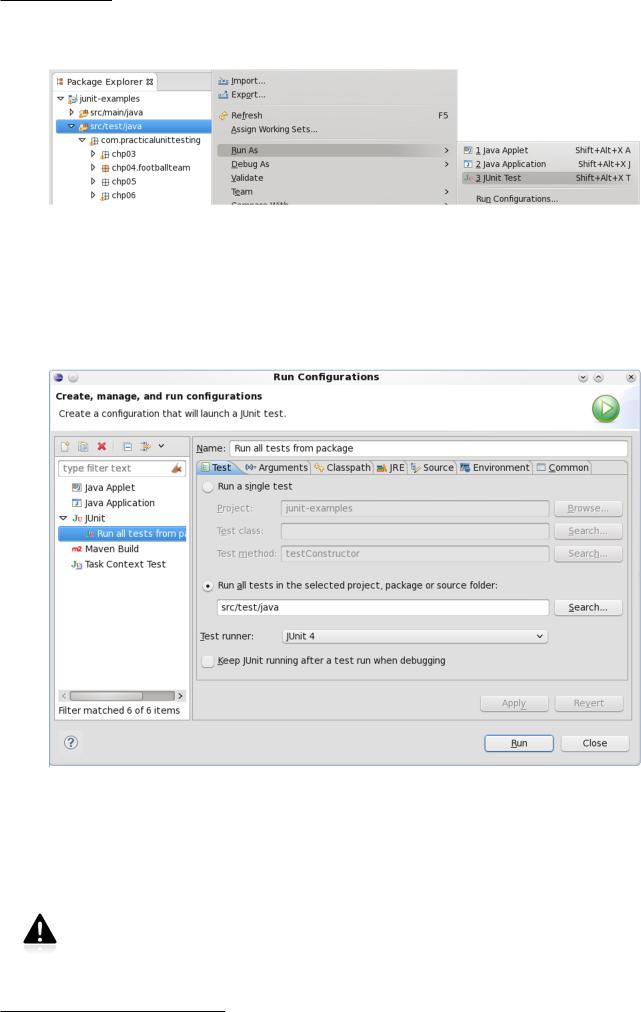
Figure B.2. Running multiple tests with Eclipse
Ufortunately, for various reasons Eclipse works inconsistently when running multiple tests. Sometimes +Run As is not available for certain packages. What will help here is creating your own configuration (Run As / Run Configurations...). All you need to do is choose a directory (e.g. src/test/java) or a package (e.g. com.practicalunittesting) to run tests from.
Figure B.3. Running multiple tests with Eclipse - custom configuration
If you prefer typing, then first make sure you have the correct test class in focus (i.e. that it is open in the editor and the cursor is there, or that it is highlighted in Package Explorer). To run all tests from this selected class, place the cursor somewhere outside any test method and press SHIFT+ALT+X followed by T. If you want to run a particular test method, place the cursor on this method, and use the same combination: SHIFT+ALT+X followed by T.
At the time of writing there is a bug in Eclipse which means that the keyboard shortcut only works if you type the T key really fast (before the pop-up windows shows up). In the event of difficulties this link should give you some insight into this problem: https://bugs.eclipse.org/ bugs/show_bug.cgi?id=369860.
271
