
- •Velocity of a body depends on time by the following form . What is the unit of the coefficient [b]?
- •If the electric field is uniform and makes an angle θ with the normal to a surface of area a, the electric flux through the surface is:
- •If two or more capacitors are connected in series, the equivalent capacitance of the series combination is given by:
- •If a wire coil has 10 turns and carries 500 mA of current, what is the magnetomotive force in ampere-turns?
- •If the cross-sectional area of a magnetic field increases, but the flux remains the same, the flux density
- •If the steel disk in a crankshaft position sensor has stopped with the tab in the magnet's air gap, the induced voltage
- •If vector b is added to vector a, which two of the following choices must be true in order for the resultant vector to be equal to zero?
- •In inelastic collision between the two bodies __________.
- •In elastic collision between the two bodies __________.
- •In rotational motion, the quantity, which plays the same role as the inertial mass in linear motion, is called ___________.
- •If a potential difference of 10 V is maintained across a 1.0-m length of the Nichrome wire with resistance 4.6 Ohm, what is the current in the wire?
- •If a loop in a basic dc generator suddenly begins rotating at a faster speed, the induced voltage
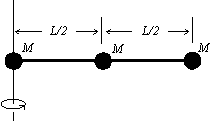
Three identical objects, each of mass M, are fastened to a massless rod of length L as shown. The rotational inertia about one end of the rod of this array is:
How defines period of physical pendulum?
Find a sample of the physical pendulum:
A sound wave can be characterized as
Sound travels faster in
A woman sits on a spinning stool with her arms folded. When she extends her arms, which of the following occurs
The pressure at the surface of the ocean is 1 atm (1 x 105 Pa). At what approximate depth in the ocean water (ρ = 1025 kg/m3) would the absolute pressure be 2 atm?
What is the direction of angular momentum for the bowling ball that rotates about z-axis?
A parallel-plate capacitor with air between the plates has an area A=2.00·10-4 m2 and a plate separation d=1.00 mm. Find its capacitance. (ε0=8.85 · 10-12 F/m).
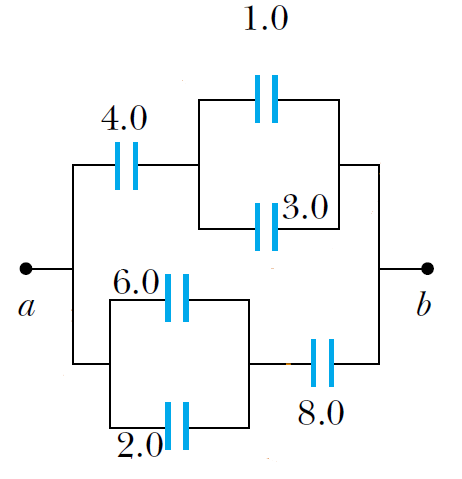
Find the equivalent capacitance between a and b for the combination of capacitors shown in Figure. All capacitances are in microfarads.
A parallel-plate capacitor has plates of dimensions 2.0 cm by 3.0 cm separated by a 1.0-mm thickness of paper. Find its capacitance (k = 3.7, ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2).
Find the electric flux though the spherical surface, covers the point-like charges q1=5 nC and q2=-2 nC. (ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2)
Find the attractive force F between nuclei of hydrogen atom and electron. Radius of hydrogen atom is r=0.5·10-10 m; modules charge of nuclei are equal and opposite to charge sign of electron (ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2).
Two point-like charges in air (ε=1) at the distance r1=20 сm from each other interact with some force. At what distance r2 one needs to place this charges in oil (ε2=5) to get the same force of interaction?
What times the gravitational force between two protons less the electrostatic force of their repulsion? The charge of proton is equal on module and opposite on sign of charge of electron.
The electron and proton of a hydrogen atom are separated (on the average) by a distance of approximately 5.3·10-11 m. Find the magnitudes of the electric force between the two particles. (ke=8.99·109 N·m2/C2)
Calculate the resistance of an aluminum cylinder that has a length of 10.0 cm and a cross-sectional area of 2.00·10-4 m2 (ρ=2.82·10-8 Ohm·m).
Calculate the resistance of an glass cylinder that has a length of 10.0 cm and a cross-sectional area of 2.00·10-4 m2 (ρ=3·1010 Ohm·m).
Calculate the resistance per unit length of a 22-gauge Nichrome wire, which has a radius of 0.321 mm (The resistivity of Nichrome is 1.5·10-6 Ohm·m).
If a potential difference of 10 V is maintained across a 1.0-m length of the Nichrome wire with resistance 4.6 Ohm, what is the current in the wire?
An electric heater is constructed by applying a potential difference of 120 V to a Nichrome wire that has a total resistance of 8.00 Ohm. Find the current carried by the wire.
An electric heater is constructed by applying a potential difference of 120 V to a Nichrome wire that has a total resistance of 8.00 Ohm. Find the power rating of the heater.
A battery has an emf of 12.0 V and an internal resistance of 0.05 Ohm. Its terminals are connected to a load resistance of 3.00 Ohm. Find the terminal voltage of the battery.
Calculate the power delivered to the load resistor, if the current in the circuit is 3.93 A, the load resistance is 3.00 Ohm.
Calculate the power delivered to the internal resistance of the battery, if the current in the circuit is 3.93 A, the internal resistance of 0.05 Ohm.
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points a and b.
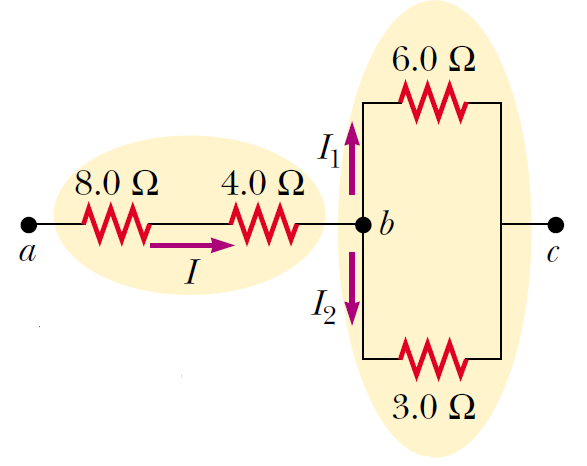
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points b and c.
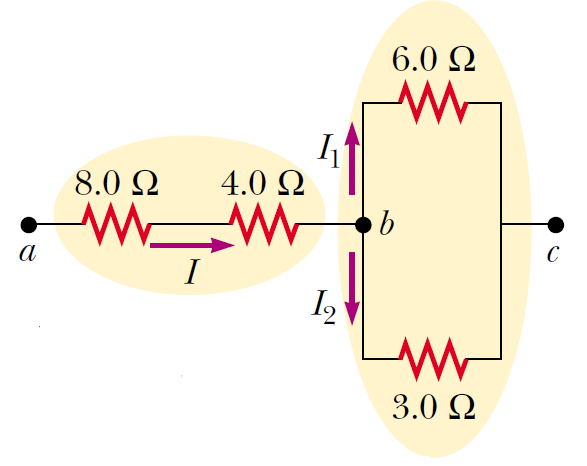
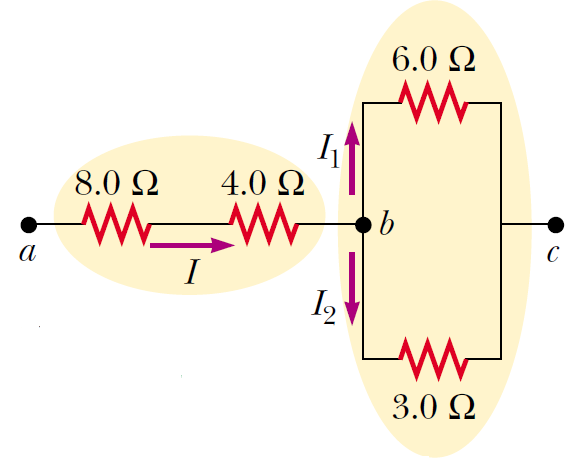
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points a and c.
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Find the current I1.

Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Find the current I2.
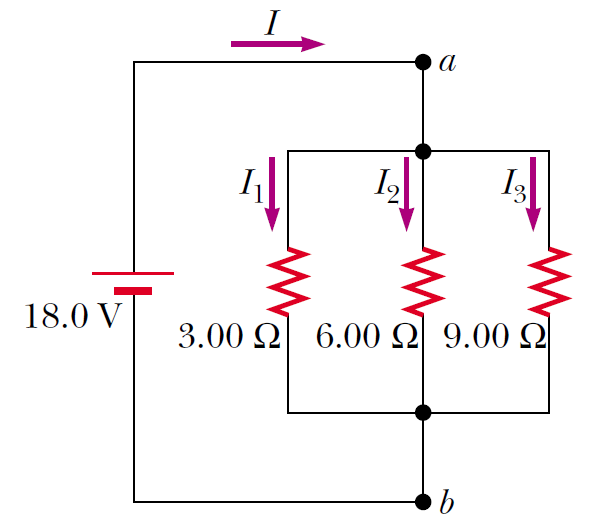
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Find the current I3.
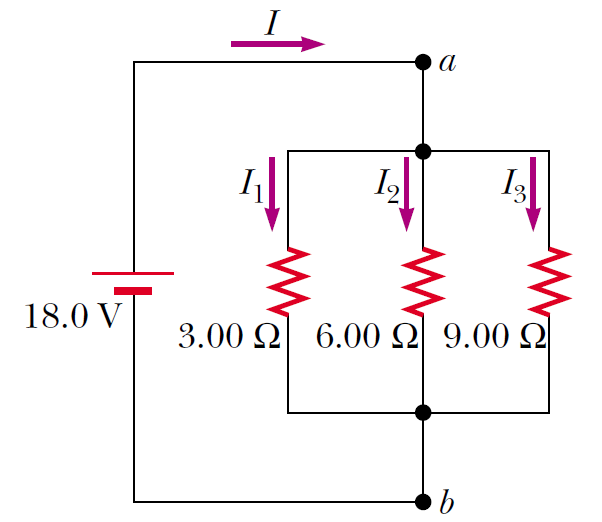
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Calculate the power delivered to resistor R1.
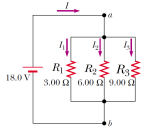
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
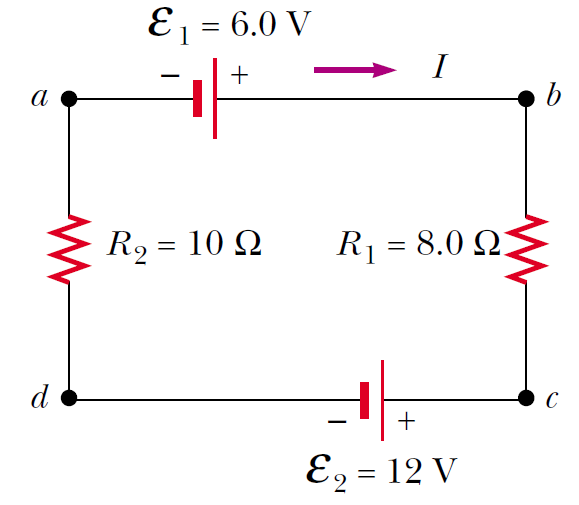
A single-loop circuit contains two resistors and two batteries, as shown in Figure. (Neglect the internal resistances of the batteries.) Find the current in the circuit.
A segment of steel railroad track has a length of 30.000 m when the temperature is 0.0°C. What is its length when the temperature is 40.0°C? (Average linear expansion coefficient for steel is α=11* 10-6 °C-1).
An ideal gas occupies a volume of 100 cm3 at 20°C and 100 Pa. Find the number of moles of gas in the container (Universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K).
The concrete sections of a certain superhighway are designed to have a length of 25.0 m. The sections are poured and cured at 10.0°C. What minimum spacing should the engineer leave between the sections to eliminate buckling if the concrete is to reach a temperature of 50.0°C? (Average linear expansion coefficient for concrete is α=12* 10-6 °C-1).
Just 9.00 g of water is placed in a 2.00-L pressure cooker and heated to 500°C. What is the pressure inside the container? (Molar mass of water M(H2O) = 18 g/mol, universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K ).
The temperature of a silver bar rises by 10.0°C when it absorbs 1.23 kJ of energy by heat. The mass of the bar is 525 g. Determine the specific heat of silver.
A 50.0-g sample of copper is at 25.0°C. If 1 200 J of energy is added to it by heat, what is the final temperature of the copper? (Specific heat of copper c= 387 J/kg . °C).
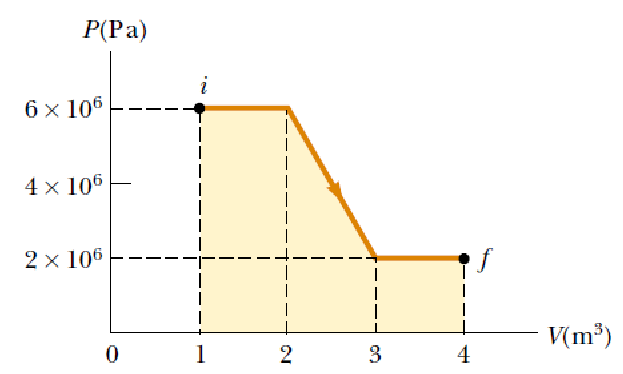
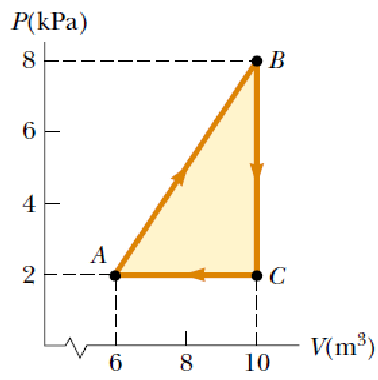
Determine the work done on a fluid that expands from i to f as indicated in Figure.
A gas is taken through the cyclic process described in Figure. Find the net energy transferred to the system by heat during one complete cycle.
An ideal gas undergoes an isobaric expansion at 2.50 kPa. If the volume increases from 1.00 m3 to 3 m3 and 12.5 kJ is transferred to the gas by heat, what is the change in its internal energy?
A glass window pane has an area of 3.00 m2and a thickness of 0.600 cm. If the temperature difference between its faces is 25.0°C, what is the rate of energy transfer by conduction through the window? (Thermal conductivity of glass is k= 0.8 W/m* °C)
A cylinder contains a mixture of helium and argon gas in equilibrium at 150°C. What is the average kinetic energy for each type of gas molecule? (Boltzmann constant kB= 1.38* 10-23 J/K).
Calculate the change in internal energy of 3.00 mol of helium gas when its temperature is increased by 2.00 K (Universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K ).
A 2.00-mol sample of a diatomic ideal gas expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. What is the final pressure of the gas?(γ=1.4)
A 2.00-mol sample of a diatomic ideal gas expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. What are the initial and final temperatures? (Universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K, 1 atm= 1.013* 105 Pa)
A 2.00-mol sample of a diatomic ideal gas expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. The initial and final temperatures equel to 365 K and 253 K. Find Q and ΔEint (Universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K, γ=1.4).
A heat engine performs 200 J of work in each cycle and has an efficiency of 30.0%. For each cycle, how much energy is (a) taken in and (b) expelled by heat?
A particular heat engine has a useful power output of 5.00 kW and an efficiency of 25.0%. The engine expels 8 000 J of exhaust energy in each cycle. Find the energy taken in during each cycle
The unit for permeability is
What is the magnetomotive force in a 75-turn coil of wire when there are 4 A of current through it?
The direction of a magnetic field within a magnet is
When the north poles of two bar magnets are brought close together, there will be
The ability of a material to remain magnetized after removal of the magnetizing force is known as
The voltage induced across a certain coil is 200 mV. A 120
 resistor
is connected to the coil terminals. The induced current is
resistor
is connected to the coil terminals. The induced current isThe induced voltage across a stationary conductor in a stationary magnetic field is
When a solenoid is activated, the force that moves the plunger is
What is the magnetomotive force (mmf) of a wire with 8 turns carrying three amperes of current?
If a loop in a basic dc generator suddenly begins rotating at a faster speed, the induced voltage
If an electron moves perpendicular to the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.35 T with the speed equal to 4.69×106, what is the radius of its circular orbit? (me = 9.11×10-31kg)
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of protons in a cyclotron of radius 0.50 m in a magnetic field of 0.35 T.
A rectangular copper strip 1.5 cm wide and 0.1 cm thick carries a current of 5 A. A 1.2 T magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the strip. Find the Hall voltage that should be produced.
A toroidal winding carrying a current of 5 A is wound with 300 turns/m of wire. The core is iron, which has a magnetic permeability of 5000µ0 under the given conditions. Find H inside the iron core.
A toroidal winding carrying a current of 5 A is wound with 300 turns/m of wire. The core is iron, which has a magnetic permeability of 5000µ0 under the given conditions. Find B inside the iron core.
Assume that a motor having coils with a resistance of 10 Ohm is supplied by a voltage of 120 V. When the motor is running at its maximum speed, the back emf is 70V. Find the current in the coils when the motor is first turned on.
Assume that a motor having coils with a resistance of 10 Ohm is supplied by a voltage of 120 V. When the motor is running at its maximum speed, the back emf is 70 V. Find the current in the coils when the motor has reached maximum speed.
Calculate the inductance of a solenoid containing 300 turns if the length of the solenoid is 25 cm and its cross-sectional area is 4 cm2.
Calculate the self-induced emf in the solenoid containing 300 turns if the length of the solenoid is 25 cm and the current through it is decreasing at the rate of 50 A/s.
Calculate the time constant of RL circuit consisting of a 30 mH inductor in series with 6 Ω resistor and 12 V battery.
For isovolumetric process:
Specific heat ratio
The amount of energy absorbed during melting and is equivalent to the amount of energy released during freezing.
Schematic diagram of a refrigerator:
Which of the reversible processes listed below are used to form a Carnot cycle?
A heat engine has a thermal efficiency of 45%. How much power does the engine produce when heat is transferred into it at a rate of 109kJ/hr?
The thermodynamic efficiency of a heat engine that rejects heat at a rate of 20 MW when heat is supplied to it at a rate of 60 MW is:
A heat engine takes in 360 J of energy from a hot reservoir and performs 25.0 J of work in each cycle. Find the efficiency of the engine.
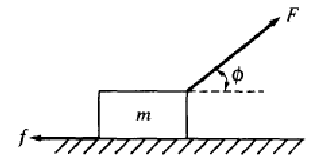 A
block of mass m is accelerated across a rough surface by a force of
magnitude F that is exerted at an angle φ with the horizontal, as
shown above. The frictional force on the block exerted by the
surface has magnitude f.
What
is the acceleration of the block?
A
block of mass m is accelerated across a rough surface by a force of
magnitude F that is exerted at an angle φ with the horizontal, as
shown above. The frictional force on the block exerted by the
surface has magnitude f.
What
is the acceleration of the block?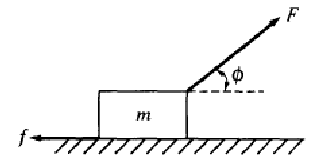 A
block of mass m is accelerated across a rough surface by a force of
magnitude F that is exerted at an angle φ with the horizontal, as
shown above. The frictional force on the block exerted by the
surface has magnitude f.
What
is coefficient of friction between the block and surface
A
block of mass m is accelerated across a rough surface by a force of
magnitude F that is exerted at an angle φ with the horizontal, as
shown above. The frictional force on the block exerted by the
surface has magnitude f.
What
is coefficient of friction between the block and surface A section of hollow pipe and a solid cylinder have the same radius, mass, and length. They both rotate about their long central axes with the same angular speed. Which object has the higher rotational kinetic energy?
Two spheres roll down an incline, starting from rest. Sphere A has the same mass and radius as sphere B, but sphere A is solid while sphere B is hollow. Which arrives at the bottom first?
Two solid spheres roll down an incline, starting from rest. Sphere A has twice the mass and twice the radius of sphere B. Which arrives at the bottom first?
When a thin uniform stick of mass M and length L is pivoted about its midpoint, its rotational inertia is ML2/12. When pivoted about a parallel axis through one end, its rotational inertia is:
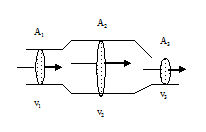
The three sections of the pipe shown above have areas A1, A2, and A3. The speeds of the fluid passing through each section of the pipe are v1, v2, and v3, respectively. The areas are related by A2 = 4A1 = 8A3. Assume the fluid flows horizontally. Which of the following is true of the speeds of the fluid in each section in the pipe?
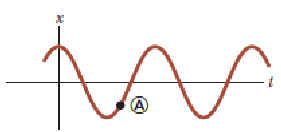
Consider a graphical representation (Fig.) of simple harmonic motion as described mathematically by equation
 .
When the particle is at point A on the graph, what can you say about
its position and velocity?
.
When the particle is at point A on the graph, what can you say about
its position and velocity?
For an object undergoing simple harmonic motion,
Which of the following statements is not true regarding a mass- spring system that moves with simple harmonic motion in absence of friction?
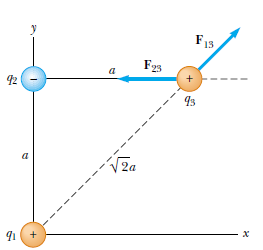
Consider three point charges located at the corners of a right triangle as shown in Figure, where q1 = q3 = 5.0 μC, q2 =-2.0 μC, and a = 0.10 m. Find the resultant force exerted on q3 ( 8.99*109 N*m2/C2).
Calculate the ratio of the electrostatic to gravitational interaction forces between two electrons, between two protons. At what value of the specific charge q/m of a particle would these forces become equal (in their absolute values) in the case of interaction of identical particles? (γ=6.67·10-11 m3/(kg·s2), me=9·10-31kg, mp=1·10-27kg, ke=8.99·109 N·m2/ C2)
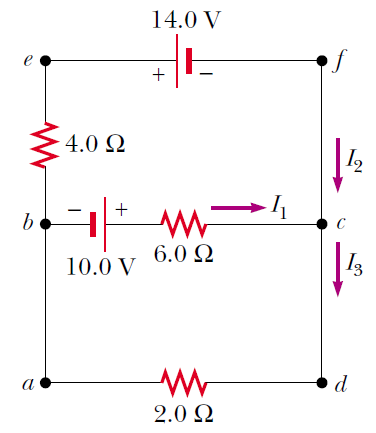
Find the currents I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit shown in Figure.
The water (H2O) molecule has an electric dipole moment of 6.3·10-30 C·m. A sample contains 1021 water molecules, with the dipole moments all oriented in the direction of an electric field of magnitude 2.5·105 N/C. How much work is required to rotate the dipoles from this orientation (θ=0°) to one in which all the moments are perpendicular to the field (θ=90°)?
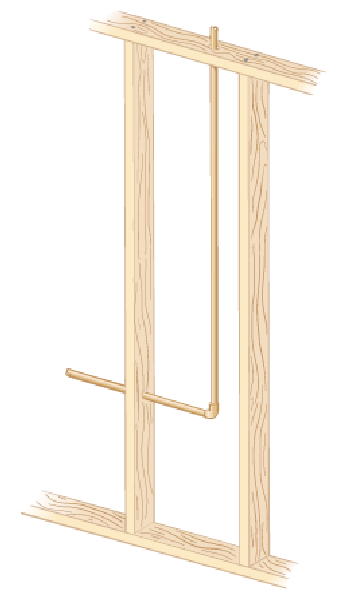
Inside the wall of a house, an L-shaped section of hot-water pipe consists of a straight horizontal piece 28.0 cm long, an elbow, and a straight vertical piece 134 cm long (Figure). A stud and a second-story floorboard hold stationary the ends of this section of copper pipe. Find the magnitude of the displacement of the pipe elbow when the water flow is turned on, raising the temperature of the pipe from 18.0°C to 46.5°C. (Linear expansion for copper α= 17*10-6 0C-1).
At 25.0 m below the surface of the sea (ρ= 1 025 kg/m3), where the temperature is 5.00°C, a diver exhales an air bubble having a volume of 1.00 cm3. If the surface temperature of the sea is 20.0°C, what is the volume of the bubble just before it breaks the surface? (P0= 1.013* 105 Pa, g=9.8 m/s2).
An aluminum cup of mass 200 g contains 800 g of water in thermal equilibrium at 80.0°C. The combination of cup and water is cooled uniformly so that the temperature decreases by 1.50°C per minute. At what rate is energy being removed by heat? Express your answer in watts. (Specific heat of aluminium and water cal =900 J/kg . °C, cw =4186 J/kg . °C).
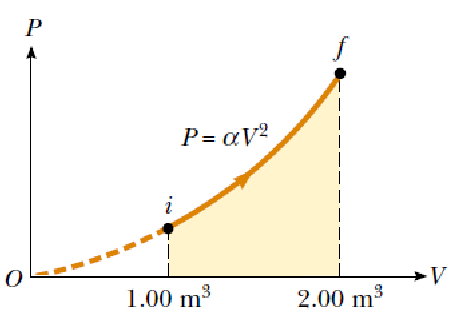
A sample of ideal gas is expanded to twice its original volume of 1.00 m3 in a quasi-static process for which P= αV2, α=5.00 atm/m6, as shown in Figure. How much work is done on the expanding gas? (1 atm= 1.013* 105 Pa).
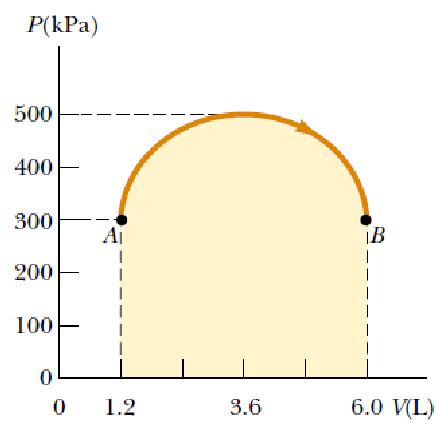
A sample of an ideal gas is in a vertical cylinder fitted with a piston. As 5.79 kJ of energy is transferred to the gas by heat to raise its temperature, the weight on the piston is adjusted so that the state of the gas changes from point A to point B along the semicircle shown in Figure. Find the change in internal energy of the gas.
A multicylinder gasoline engine in an airplane, operating at 2 500 rev/min, takes in energy 7.89 * 103 J and exhausts 4.58 *103 J for each revolution of the crankshaft. How many liters of fuel does it consume in 1.00 h of operation if the heat of combustion is 4.03 * 107 J/L?
Suppose a heat engine is connected to two energy reservoirs, one a pool of molten aluminum (660°C) and the other a block of solid mercury (-38.9°C). The engine runs by freezing 1.00 g of aluminum and melting 15.0 g of mercury during each cycle. The heat of fusion of aluminum is 3.97 * 105 J/kg; the heat of fusion of mercury is 1.18* 104 J/kg. What is the efficiency of this engine?
A plane loop of wire consisting of a single turn of cross-sectional area 100 cm2 is perpendicular to a magnetic field that increases uniformly in magnitude from 0.5 T to 2.5 T in a time of 1.5 s. What is the resulting induced current if the coil has a total resistance of 4 Ohm?
Three point charges are arranged as shown in Figure. Find the vector electric field that the 6.00-nC and -3.00 nC charges together create
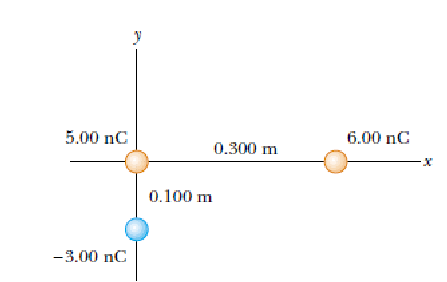 at the origin.
at the origin.
