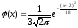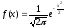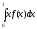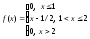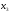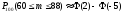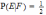- •Indicate the formula of computing variance of a random variable X with expectation µ.
- •Indicate the expectation of a Poisson random variable X with parameter .
- •Indicate the variance of a Poisson random variable X with parameter .
- •Indicate the formula for conditional expectation.
- •If a fair die is tossed twice, the probability that the first toss will be a number less than 4 and the second toss will be greater than 4 is
- •If one person is selected randomly, the probability that it did not pass given that it is female is:
- •If X and y are independent random variables with ,,and,,,. Thenis
- •If p(e) is the probability that an event will occur, which of the followings must be false?
- •If one person is selected randomly, what is the probability that it did not pass given that it is male.
- •In the first step, Joe draws a hand of 5 cards from a deck of 52 cards. What is the probability that Joe has exactly one ace?
- •If the variance of a random variable X is equal to 3, then Var(3x) is :
- •Indicate the correct statement related to Poisson random variable .
- •In each of the 20 independent trials the probability of success is 0.2. Find the variance of the number of successes in these trials.
- •Indicate the pdf for standard normal random variable.
- •Indicate the function that can be cdf of some random variable.
- •Indicate the function that can be pdf of some random variable.
- •If two random variables X and y have the joint density function, , find the conditional pdf.
- •If two random variables X and y have the joint density function, , find the conditional pdf.
In each of the 20 independent trials the probability of success is 0.2. Find the variance of the number of successes in these trials.
3.2
A coin tossed twice. What is the probability that head appears in the both tosses.
1/4
Continuous random variable X is normally distributed with mean=1 and variance=4. Find P(4≤x≤6).
0,0606
Random variable X is uniformly distributed on the interval [-2, 2]. Indicate the right values for E[X] and Var(X).
E[X]=0 and Var(X)=1.33
Expectation and standard deviation of the normally distributed random variable X are respectively equal to 15 and 5. What is the probability that in the result of an experiment X takes on the value in interval (5, 20)?
(1) + (2)-1
Normally distributed random variable X is given by density
 . Find the mean.
. Find the mean.
0
Indicate the density function of the normally distributed random variable X when mean=2 and variance=9.
Indicate the pdf for standard normal random variable.
Random variable X is uniformly distributed in interval [0, 3]. What is the variance of X?
0.75
Random variable X is uniformly distributed in interval [0, 15]. What is the expectation of X?
7.5
Random variable X is uniformly distributed in interval [-2, 1]. What is the distribution of the random variable Y=2X+2?
Y is uniformly distributed in the interval [-2, 4]
Random variable X is uniformly distributed in interval [-11, 26]. What is the probability P(X> - 4)?
30/37
Random variable X is uniformly distributed in interval [1, 3]. What is the distribution of the random variable Y=3X+1?
Y is uniformly distributed in the interval [4, 10]
Random variable X is uniformly distributed in interval [-11, 20]. What is the probability P(X ≤ 0) ?
11/31
Random variable X is given by density function f(x) in the interval (0, 1) and otherwise is 0. What is the expectation of X?
Random variable X is given by density function f(x) = x/2 in the interval (0, 2) and otherwise is 0. What is the expectation of X?
4/3
Random variable X is given by density function f(x) = 2x in the interval (0, 1) and otherwise is 0. What is the expectation of X?
2/3
Random variable X is given by density function f(x) = 2x in the interval (0, 1) and otherwise is 0. What is the probability P(0 < X < 1/2) ?
1/4
Indicate the function that can be cdf of some random variable.
Indicate the function that can be pdf of some random variable.
Continuous random variable X has the following CDF:
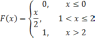 .
What is the PDF of X in the interval 1<X≤2?
.
What is the PDF of X in the interval 1<X≤2?
1/2
Continuous random variable X is given in the interval [0, 100]. What is the probability P(X=50)?
0
CDF of discrete random variable X is given by
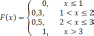 What
is the probability P{1.3<X≤2.3}?
What
is the probability P{1.3<X≤2.3}?
0.2
PMF of discrete random variable is given by
|
Х |
0 |
2 |
4 |
|
Р |
0,1 |
0,5 |
0,4 |
Find the value of CDF of X in the interval (2, 4].
0.6
PMF of discrete random variable is given by
|
Х |
0 |
2 |
4 |
|
Р |
0,3 |
0,1 |
0,6 |
Find F(2).
0.4
PMF of discrete random variable X is given by
|
Х |
-1 |
5 |
|
Р |
0,4 |
0,6 |
Find standard deviation of X.
2.9393
PMF of discrete random variable X is given by
|
Х |
-1 |
5 |
|
Р |
0,4 |
0,6 |
Find variance of X.
8.64
PMF of discrete random variable X is given by
|
Х |
0 |
5 |
|
|
Р |
0,6 |
0,1 |
0,3 |
If E[X]=3.5 then find the value of x3.
10
Probability of success in each of 100 independent trials is constant and equals to 0.8. What is the probability that the number of successes is between 60 and 88?
A man is made 10 shots on the target. Assume that the probability of hitting the target in one shot is 0,7. What is the most probable number of hits?
7
Consider two boxes, one containing 4 white and 6 black balls and the other - 8 white and 2 black balls. A box is selected at random, and a ball is drawn at random from the selected box. If the ball occurs to be white, what is the probability that the first box was selected?
1/3
Each of two boxes contains 6 white and 4 black balls. A ball is drawn from 1st box and it is replaced to the 2nd box. Then a ball is drawn from the 2nd box. What is the probability that this ball occurs to be white?
0.6
Consider two boxes, one containing 3 white and 7 black balls and the other – 1 white and 9 black balls. A box is selected at random, and a ball is drawn at random from the selected box. What is the probability that the ball selected is black?
0.8
Urn I contains 4 black and 6 white balls, whereas urn II contains 3 white and 7 black balls. An urn is selected at random and a ball is drawn at random from the selected urn. What is the probability that the ball is white?
0.45
A coin is tossed twice. Event A={ at least one Head appears}, event B={at least one Tail appears}. Find the conditional probability P(B|A).
2/3
A coin is tossed twice. Event A={ Head appears in the first tossing}, event B={at least one Tail appears}. Find the conditional probability P(B|A).
1/2
Probability that each shot hits a target is 0.9. Total number of shots produced to the target is 5. What is the probability that at least one shot hits the target?
1-0,15
An urn contains 1 white and 9 black balls. Three balls are drawn from the urn without replacement. What is the probability that at least one of the balls is white?
0.3
Four independent shots are made to the target. Probability of missing in the first shot is 0.5; in the second shot – 0.3; in the 3rd – 0.2; in the 4th – 0.1. What is the probability that the target is not hit.
0.003
Probability of successful result in the certain experiment is 3/4. Find the most probable number of successful trials, if their total number is 10.
8
Let E and F be two mutually exclusive events and P(E)=P(F)=1/3. The probability that none of them will occur is:
Let Eand Fbe two events. If
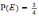 ,
,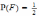 ,
,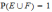 and
and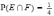 ,
then the conditional probability of Egiven
F is:
,
then the conditional probability of Egiven
F is:
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable. What is the value of Z if the area to the left of Z is 0.9382?
1.54
At a university, 14% of students take math and computer classes, and 67% take math class. What is the probability that a student takes computer class given that the student takes math class?
0.21
Let
 ,
,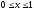 ,
,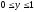 ,
be the joint p.d.f. of X and Y. Find the marginal PDF of X.
,
be the joint p.d.f. of X and Y. Find the marginal PDF of X.
x+1/2
If two random variables X and Y have the joint density function,
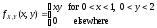 ,
find the probability P(X+Y<1).
,
find the probability P(X+Y<1).
1/24