
- •Reznichenko Valery
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
- •Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure

Reznichenko Valery
Organization of data and knowledge bases
Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
National Aviation University
Computer Science Faculty
Department of Software Engineering
1

Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
CONTENT
Relation in mathematics
Relation definition
Domains, attributes, schemas and instances of relations in RDM
Relations and tables
Keys of relations
CSF NAU |
2 |

Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
Nonformal introduction to relations

 Relation is an association between any number of entities.
Relation is an association between any number of entities.
Like subject |
|
Is more |
|
|
Supply |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Who |
What |
First |
Second |
Who |
Whom What |
Q-ty |
|
John |
DBMS |
5 |
3 |
П1 |
К7 |
table |
200 |
Peter |
С |
17 |
5 |
П3 |
К14 |
door |
150 |
Ann |
XML |
2 |
1 |
П18 |
К9 |
window |
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form of representation:
As a table
By using a condition
CSF NAU |
3 |

Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
Relation definition
Let’s given sets D1, D2,…, Dn (does not obligatory distinct). Relation R, defined on these sets, is a set of ordered n-tuples (d1, d2,…, dn), such that d1 D1, …, dn Dn
Lets given sets D1, D2,…, Dn (does not obligatory distinct). Cartesian product of these sets, denoted as D1 D2 … Dn, is a set of all
possible tuples (d1, d2,…, dn), such that di Di, i = 1,n. R is a relation on the sets D1, D2,…, Dn, if:
R D1 D2 … Dn = {(d1, d2,…, dn) di Di, i = 1,2,…,n}
CSF NAU |
4 |
Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
Additional terms
-Sets D1, D2,…, Dn are called domains of the relation R .
-n is a degree of the relation R or its arity.
-Number of tuples in a relation is called cardinality.
-Tuple is a row of the relation.
Relation |
D1 |
D2 … |
Dn |
||
name |
|||||
|
R |
|
|
|
|
a11 |
a12 … |
a1n |
|||
Tuple |
|
|
a22 |
a22 … |
a2n |
|
|||||
|
|
|
. . . |
ak2 … |
|
|
|
|
ak1 |
akn |
|
Domains
Relation
Cardinality
Degree, arity
CSF NAU |
5 |
Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
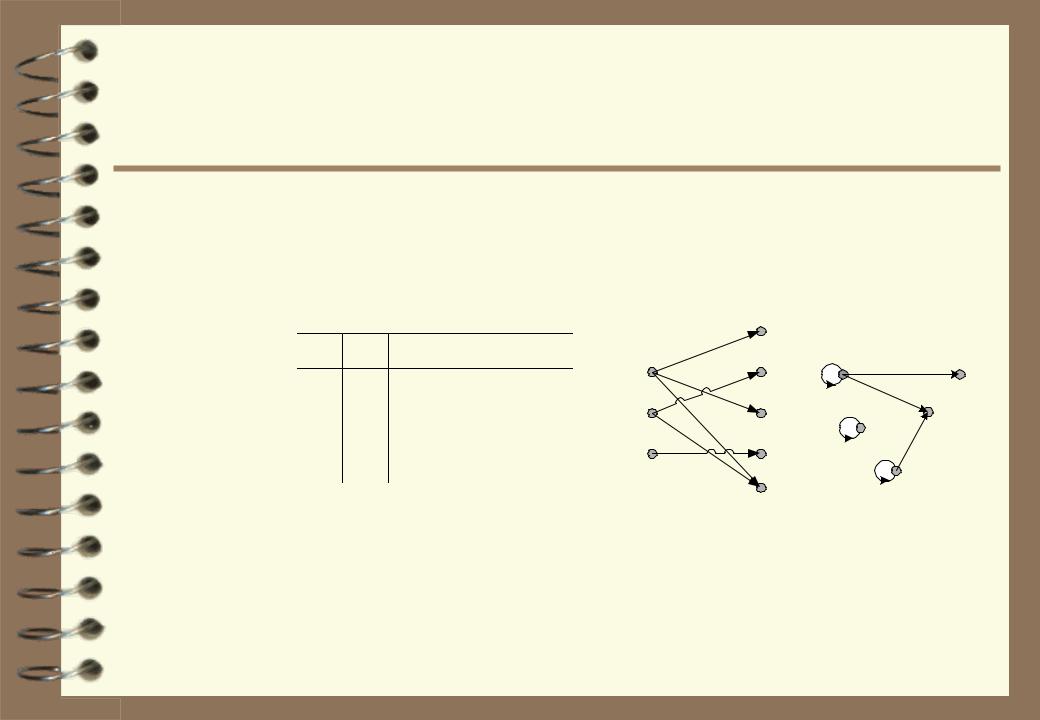
Representation of binary relations
As a matrix |
|
As a table |
|
|||
|
a |
a |
R |
a b |
c d |
e |
|
a |
c |
a |
* |
* |
* |
|
a |
e |
||||
R |
|
|
|
|
||
b b |
b |
* |
|
* |
||
|
b |
e |
d |
|
* |
|
|
d d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Graphical |
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
a |
b |
a |
|
c |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
b |
c |
|
d |
e |
|
|
|||
d |
d |
|
|
b |
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As a logical condition: R(x,y,...,z) = {(x,y,...,z) | φ(x,y,...,z)}
CSF NAU |
6 |

Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
Basic operations
Union: |
R S = {t | t R t S} |
Intersection: |
R S = {t | t R & t S} |
Negation: |
R = {t | t R} |
Cartesian product: |
R S = {(r,s) | r R & s S } |
CSF NAU |
7 |

Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
Property of binary relations
Reflexivity: Relation R is reflexive if:a R(a, a).
Symmetry: Relation R is symmetric ifa b (R(a, b) R(b, a))
Transitivity: Relation R transitive if:
a b с (R(a, b) & R(b, с) R(a, c)).
Antisymmetry: Relation R is antisymmetric if:a b (R(a, b) & R(b, a) a = b).
CSF NAU |
8 |

Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
Examples of binary relations
Relation Look-Like(x,y) is reflexive (any person looks like himself), symmetric (if b looks like d, then d looks like b), but not transitive (if have chain of pairs of similar persons it does not mean that persons at the ends of this chain are similar).
Relation Is-Higher(x,y) is transitive but not reflexive and symmetric. Relation Is-Equal (=) is reflexive, symmetric and transitive.
Relation Teach(x,y) is not reflexive, symmetric and transitive.
CSF NAU |
9 |
Lecture 5. Relational Data Structure
Schema of a relation
In mathematics order of columns is essential.
Is More |
|
|
Is More |
||
5 |
3 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
|
|
||||
17 |
5 |
|
5 |
17 |
|
In relational data structure order of “columns” is not essential. It is achieved at the expense of introducing of the concept “attribute”.
Attribute – is semantically sensible names of the relation columns.
Attribute names |
Domain names |
R(A1: Di1, A2: Di2, …, An: Din)  Schema of relation in RDM
Schema of relation in RDM
CSF NAU |
10 |
