
Angliyska_mova_Zoshit_1_kurs_002
.pdf
Give yourself a score:
More than |
20- |
you definitely won’t have problems at the airport |
|
15-20- you probably won’t have any problems at the airport, but bring |
|
|
|
your dictionary with you just in case. |
Less than |
12- |
study the words again or you won’t find your way out of the airport. |
Прислівник. Adverb
Прислівник —
Розрізняють чотири форми прислівників:
1. Прості:
now hard fast too always never ever
2. Похідні:
Утворені від іменників: week — weekly
year —yearly month — monthly day — daily
Утворені від прикметників: quick — quickly
usual — usually happy — happily
3. Складні:
sometimes somewhere inside below
4. Складені (з кількох слів):
at first in vain at last
61
|
|
|
Використовують з метою: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
додати інформацію |
|
The ambulance comes |
|
|
|
про дієслово |
|
immediately |
|
|
|
|
I often talk on the phone. |
|
|
|
|
The sprinter runs quickly |
|
|
|
|
|
|
додати інформацію |
|
The child is seriously injured |
|
|
|
про прикметник |
|
Any help is extremly late. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
додати інформацію |
|
The boy recovers surprisingly |
|
|
про ще один |
|
quickly. |
|
|
прислівник |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
додати інформацію до |
|
Luckily he has a lot of |
|
|
всього речення |
|
friends. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Більшість прислівників утворюється від прикметників за допомогою додавання –ly:
•bad — badly _________________________________________
•careful — carefully ___________________________________
•extreme — extremely _________________________________
•stupid — stupidly ____________________________________
•heavy — heavily _____________________________________
•terrible — terribly ____________________________________
•specific — specifically _________________________________
Правила написання. Spelling rules
Закінчення -ly додається до прикметника і:
1.Якщо прикметник закінчується на -y → i + ly.
•happy — happily
•lucky — luckily
•dirty — dirtily
2. Якщо прикметник закінчується на -e → ely.
• polite — politely |
|
• sure — surely |
Виняток: true — truly |
3. Якщо прикметник закінчується на -le → ly.
•possible — possibly
•probable — probably
4. Якщо прикметник закінчується на -ic → ally.
•economic — economically
•scientific — scientifically
62

Зверніть увагу!
Не всі слова, що мають закінчення -ly, є прислівниками. Деякі прикметники так само мають закінчення -ly.
Запам’ятайте!
lovely_____________, friendly _____________, lonely ___________, lively___________,
elderly ______________, silly _____________ — прикметники.
Не всі прислівники закінчуються на -ly.
Often (часто), always (завжди), now (зараз, тепер), today (сьогодні), ever (колись), never (ніколи), sometimes (інколи), інші прислівники часу,
прислівники способу дії — fast (швидко), well (добре),
прислівники міри та ступеня — much (багато), little (мало), very (дуже), too (надто), so (так), etc.
Activity 7. Adjective or adverb? Choose the correct option. Translate.
1.I write _______________(correct, correctly).
_______________________________________________________
2.I read _______________(careful, carefully).
_______________________________________________________
3.I listen ______________(attentive, attentively).
_______________________________________________________
4.I work _______________ (hard, hardly).
_______________________________________________________
5.I want to speak English ____________(fluent, fluently).
_______________________________________________________
6.Peter is ____________(quiet, quietly) person.
_______________________________________________________
7.Sally is _____________(good, weel) at economics.
_______________________________________________________
8.The teacher speaks _____________(loud, loudly).
_______________________________________________________
9.My mother sings in a ___________(loud, loudly) voice.
_______________________________________________________
10.Children learn languages___________(easy, easily)
_______________________________________________________
Ступені порівняння прислівників
У деяких прислівників ступені порівняння утворюються так, як у прикметників. Однота двоскладові + er + est
Hard |
harder |
the hardest |
Fast |
faster |
the fastest |
Early |
earlier |
the earliest |
Soon |
sooner |
the soonest |
|
|
|
63 |
|
|

Old people get up earlier than young.
_______________________________________________________
Students work harder before exams.
_______________________________________________________
Winter lasts the longest of all seasons.
_______________________________________________________
Прислівники, які закінчуються на -ly за допомогою слів more, the most
Usually |
more usually |
the most usually |
|
Clearly |
more clearly |
the most clearly |
|
Запам’ятaйте! |
|
|
|
Often |
oftener / more often |
|
the oftenest / most often |
Quickly |
quicker / more quickly |
the quickest / most quickly |
|
Slowly |
slower / more slowerly |
the slowest / most slowly |
|
Well |
better |
|
the best |
Badly |
worse |
|
the worst |
Much |
more |
|
the most |
Little |
less |
|
the least |
Far |
farther | further |
|
the farthest | furthest |
Home task: ________________________________________________________________________
Заняття 13.
Тема Минулий тривалий час. Студентське життя. Освіта в Україні і закордоном
Education is what survives when what has been learned has been forgotten.
B.F. Skinner
|
Difference between: bring up and educate. |
|
|
|||
Bring up and |
upbringing i s |
m ost l y |
u sed |
fo r the mo ra l and s o c ial |
tr ain ing |
that |
c hi ldren re ce iv e at ho me . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Educate a nd |
education i s |
u sed for |
th e |
int el le ctual and c ul tu ra l |
t ra inin g |
that |
pe ople get at s ch oo l and un i ver sit y .
S he was brought up by her grandmother and educated at the local secondary school. His son is very badly brought up — always screaming and fighting.
Would you rather have a good upbringing and a bad education, or the opposite?
Activity 1. Read the humorous rhyme.
The more we study, the more we know.
The more we know, the more we forget.
The more we forget, the less we know.
The less we know, the less we forget.
The less we forget, the more we know.
64

Why study?
Is education really important? What do you think?
Education in Ukraine
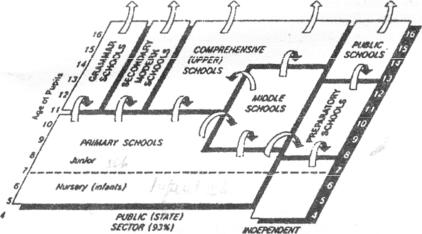
The system of secondary education in Ukraine includes primary forms and junior and senior secondary forms.
Children usually go to school at the age of 6 or 7. There are some pre-school institutions, like nursery schools or kindergartens, but they are not obligatory. Primary forms comprise 1 to 4 forms.
Junior secondary forms comprise 5 to 9 forms. After the 9th form children can enter technical schools of different types. Those who want to enter higher educational institutions should complete 10—11 forms.
Students can also enter higher educational institutions after graduating from specialized colleges or lyceums. They prepare students in different fields, whether the humanities or the sciences. Some of them are organized under the authorities of higher educational establishments.
The system of higher education is presented by universities, polytechnic institutes or specialized institutes. Universities offer a five-year course of study and usually have from six to twelve departments. Institutes train specialists for industry, agriculture and economy. Most of them have been conferred the status of Academy or University recently. Students are also offered post-graduate education and scientific research work. Nowadays due to the state of our national economy not many young people are engaged in the research work. But still in some fields of science there are outstanding discoveries and research papers. Some universities and institutes have refresher courses.
Recently a great number of private educational establishments have appeared. Some institutions have fee-paying groups or departments. The students may get education there at the same high level as in the state institutions.
VOCABULARY PRACTICE
Activity 2. Fill in the blanks with the words given in the box below.
independent |
school(s) |
link(s) |
pupil(s) |
education |
academic |
general |
slant |
secondary |
entrance |
attend |
fee(s) |
types |
ability (ies) |
college(s) |
specialist |
|
|
|
|
Different Types of Secondary School
Over 85 per cent of ___________________________(1) school pupils go to comprehensive schools. These take children of all ___________________________(2), and provide a wide range of secondary______________________(3) for all or most of the children in a district from the age 11 to 16 or 18.
There are also other _______________________(4) of secondary school. Grammar schools offer a mainly _______________________(5) education for the 11 to 18-year age group. Children enter grammar schools on the basis of their abilities, first sitting the 11-plus or_________________________(6) examination. Grammar _____________________(7) cater for 4% of children in secondary education.
A small minority of children ____________________(8) secondary modern schools (around 4%). These schools provide a more ____________________(9) and technical education for children aged 11—16.
City Technology Colleges (CTCs) aim to give boys and girls a broad secondary education with a strong technological and business __________________________(10).
They are non-fee-paying _______________________(11) schools, set up by the Government with the help of business sponsors who finance a large proportion of the initial capital costs and develop
__________________________(12) with the schools. There are now 15 such
____________________________(13) in operation in England and Wales.
Specialist schools, which only operate in England, give ___________________ (14) a broad secondary education with a strong emphasis on technology, languages, art and sports. There are over 250 ______________(15) schools. They charge no___________________(16) and any secondary school can apply for specialist school status.
Activity 3. Look at the picture. Read and translate the text.
EDUCATION IN ENGLAND & WALES (TO AGE 16)
66
Pupils who have passed their GCSEs may remain at school for another two years and take their "A" (Advanced) level exams. All grammar and most comprehensive schools have a sixth form, where pupils study for their "A" levels. Any student who wants to go to university needs to pass at least two or three "A" levels.
(from magazine "England")
Differences in the Organization of Education
in Britain and America
A place of education for young children is a school in both varieties. But a public school in Britain is in fact a "private" school - it is a fee-paying school not controlled by the local education authority. The free local authority school in America is a public school. The word school in BE is never used to refer to a university or other college of higher education.
An American high school student graduates; a British secondary school pupil (never student) leaves school. To graduate is possible only from a university, polytechnic or college of education in British usage.
British universities have 3 terms; American universities have 2 semesters (or in some recent cases, 4 quarters).
A British university student takes 3 years, in the typical case, to get his degree; these are known as the first, second and final years. The American university student typically takes 4 years, known as freshman, sophomore, junior and senior years.
Britain |
American |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Activity 4. Match each AE word or phrase in the left-hand column with its BE equivalent from the right-hand column.
American English
1.public school (free local authority school)
2.student
3.to graduate from a school
4.two semesters or four quarters (at universities)
5.freshman year (at college)
6.senior year (at college)
7.sophomore year (at college)
8.schedule
9.term paper
10.school principal
11.vocation
67
British English
a.first year student
b.public school (private free-paying school)
c.last year student
d.time-table
e.pupil
f.essay
g.second year student
h.holidays
i.to leave school
j.three terms (at universities)
k.headmaster
IDIOMS
Activity 5. Memorize some idioms and idiomatic expressions dealing with the topics "Education". Make up sentences of your own using them.
То learn smth. by heart means to learn smth. so well that it can be written or recited without thinking; to memorise smth.
Вивчити щось папам 'ять.
То live and learn (a proverb, also informal and folksy. Usually said when one is surprised to learn smth.) means to increase one's knowledge by experience
Вік живи, вік учись. Життя коротке, мистецтво вічне.
Synonym: Art is long, life is short.
То hit the books (Am., slang) means to begin to study; to study
Починати вчитись; вчитись.
То cut a lecture (informal) means to skip going to class; to stay away from school without permission or explanation.
Пропустити, не бути присутнім на уроці, лекції; прогулювати (уроки в школі, заняття в університеті)
Synonyms: To cut class (Am., informal)
To play hook(e)y (Am., informal)
To play the wag (informed)
To play truant (informal).
То flunk the exam means to fail at the examination
Провалитися на іспиті.
On paper means a) in writing; b) in theory rather than in reality
а) письмово; б) лише на папері.
A ready tongue means to have an ability to speak fluently, to have a ready answer to any question
Добре підвішений язик
68

Activity 6. How do you understand the following quotations.
Education is what survives when what has been learned has been forgotten. B.F. Skinner
If you educate a man you educate a person, but if you educate a
woman you educate a family. |
Ruby |
|
Manikan |
|
|
A child mid-educated is a child lost. |
John F. Kennedy |
|
There is no sin except stupidity. |
Oscar Wilde |
|
There are no gains without pains. |
Adlai Stevenson |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Past Continuous
I |
|
|
He |
We |
|
was working |
You |
were working |
She |
They |
|
It |
|
|
|
|
|
What were you telling him? |
|
Що ви йому говорили? |
|
|
|
I was not working in the evening. |
Я не працював увечері |
|
|
69 |
|

В усному мовленні в заперечній і питальнозаперечній формах замість was not i were not вживаються переважно скорочені форми wasn't i weren't:
He wasn't working. |
Wasn't he working? |
They weren't working. |
Weren't they working? |
|
Вживання Past Continuous |
1. |
|
|
|
|
|
at two o'clock
at midnight
at that moment
at 5 o'clock
або підрядні речення з дієсловом-присудком y Past Indefinite: He was working at his English at that time.
Він працював над англійською мовою в той час. Carrie was sitting by the window when he came in.
Керрі сиділа біля вікна, коли він увійшов
2.
In the spring of the year 1881 he was visiting his old schoolfellow.
Навесні 1881 року він гостював у свого старого шкільного товариша
Activity 7. Open the brackets using verbs in Present Continuous or Past Continuous.
1.I (to write) an English exercise now.
2.I (to write) an English exercise at this time yesterday.
3.My little sister (to sleep) now.
4.My little sister (to sleep) at this time yesterday.
5.My friends (not to do) their homework now. They (to play) volley-ball.
6.My friends (not to do) their homework at seven o'clock yesterday. They (to play) volley-ball.
7.She (to read) the whole evening yesterday.
8.What you (to do) now? — I (to drink) tea.
9.You (to drink) tea at this time yesterday? — No, I (not to drink) tea at this time yesterday, I (to eat) a banana.
10.My sister is fond of reading. She (to read) the whole evening yesterday, and now she (to read) again.
11.Look! My cat (to play) with a ball.
12.When I went out into the garden, the sun (to shine) and birds (to sing) in the trees.
70
