
- •3)The environment of managers:
- •4)Main Steps of Planning:
- •5)Levels of plannnig
- •9) The strategic planning process:
- •10)External and internal analysis:
- •13)The Benefits and Pitfalls of Planning
- •20. The low-cost value cycle.
- •21. Options for Exploiting Differentiation
- •25. Entrepreneurship and its relation to management
- •27. Evolution of management
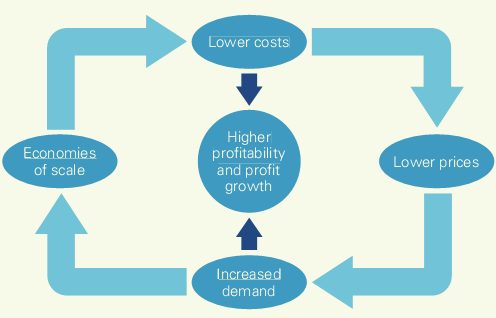
20. The low-cost value cycle.
The successful pursuit of a low-cost strategy lets a firm charge less than its rivals and still make profits. Moreover, firms that charge lower prices might also be able to gain mark et share—as Dell, Wal-Mart, and Southwest Airlines have all done—which allows them to realize economies of scale(cost advantages derived from a large sales volume) and reap further cost reductions. Thus firms that successfully pursue a low-cost strategy can set up a value cycle similar to that illustrated in the figure below, which lets them consolidate their cost advantage over time.
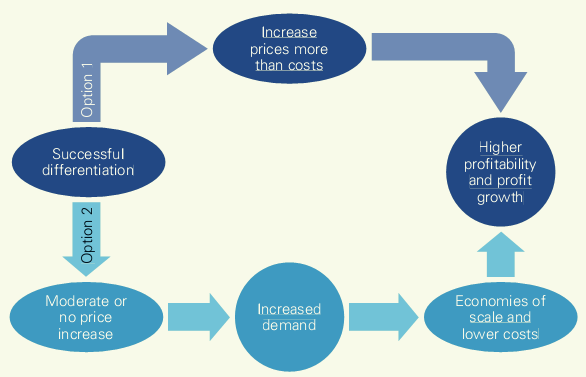
21. Options for Exploiting Differentiation
One option managers have is to raise prices to reflect the differentiated nature of the product offering and cover any increase in costs. This is an option that man y pursue. It can by itself enhance profitability so long as prices in-crease more than costs.
Greater profitability and profit growth can also come from the increased demand associated with successful differentiation, which allows the firm to use its assets more efficiently and thereby simultaneously realize lower costs from scale economies. This leads to another option: The successful differentiator can also hold prices constant (or increase prices only slightly), sell more, and boost profitability through scale economies.
22. There are three dimensions to business-level strategy: the competitive theme managers emphasize (low cost or differentiation), the way they choose to segment the market, and the segments they serve taken together, these dimensions allow a variety of different ways to compete in an industry.
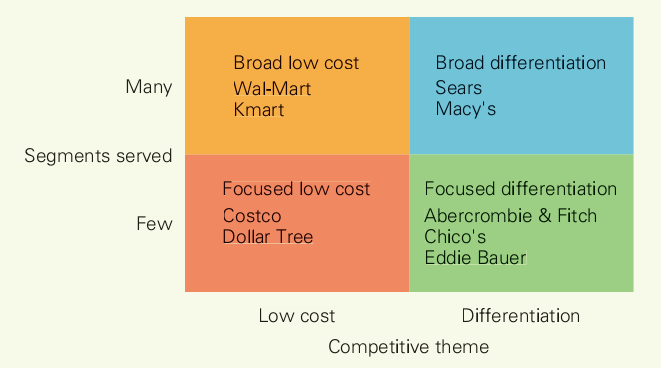
Broad low-cost and broad differentiation strategies aim to serve many segments in an industry and strive for either a low-cost or a differentiated position. Focused low-cost and focused differentiation strategies focus on one or a few specific segments and strive to attain a low-cost or differentiation position relative to that segment.
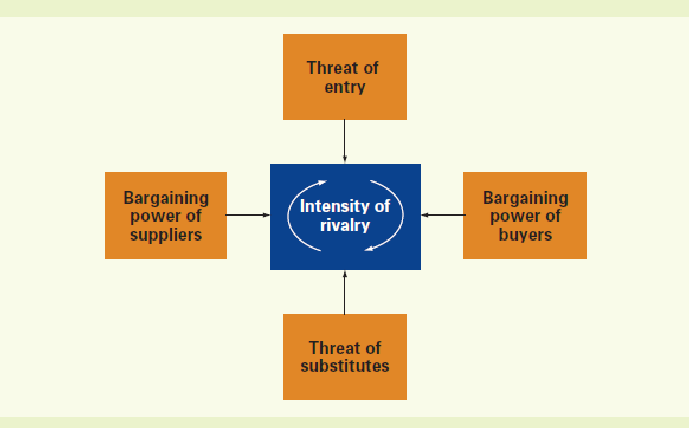
23. One of the most popular frameworks for analyzing the task or industry environment is a model developed by Michael Porter known as the five forces model. According to Porter, the ability of a firm to make a profit is influenced by five competitive forces: the threat of entry by potential competitors, the power of buyers, the power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry between firms already in the industry. In Porter’s framework, the stronger each of these forces, the more difficult it will be for incumbent firms in an industry to make profits. A strong force thus constitutes a threat, whereas a weak force often gives managers the opportunity to increase sales, raise prices, and make higher profits. Porter also notes that by getting their firm to pursue the right strategies, managers can alter the strength of the various forces. Thus managers might pursue strategies that reduce the bargaining power of buyers, thereby decreasing the threat posed by this force.
24. The four functions that we discuss are (1) planning and strategizing, (2) organizing, (3) controlling, and (4) leading and developing employees.
Planning is a formal process whereby managers choose goals, identify actions to attain those goals, allocate responsibility for implementing actions to specific individuals or units, mea-sure the success of actions by comparing actual results against the goals, and revise plans accordingly.
Strategizing is the process of thinking through on a continual basis what strategies an organization should pursue to attain its goals.
Organizing refers to the process of deciding who within an organization will perform what tasks, where decisions will be made, who reports to whom, and how different parts of the organization will coordinate their activities to pursue a common goal.
Controlling is the process of monitoring performance against goals, intervening when goals are not met, and taking corrective action.
Leading is the process of motivating, influencing, and directing others in the organization to work productively in pursuit of organization goals.
