
Лекция 1
.pdf
 Деструктор
Деструктор
вызывается при разрушении объекта класса
имя совпадает с именем класса, перед которым указывается знак ~
не имеет возвращаемого значения

 Пример 2. Деструкторы
Пример 2. Деструкторы
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class MyClass{
int i,j; public:
MyClass(){i=j=0;}
void Init(int a, int b){i=a; j=b;} void Show();
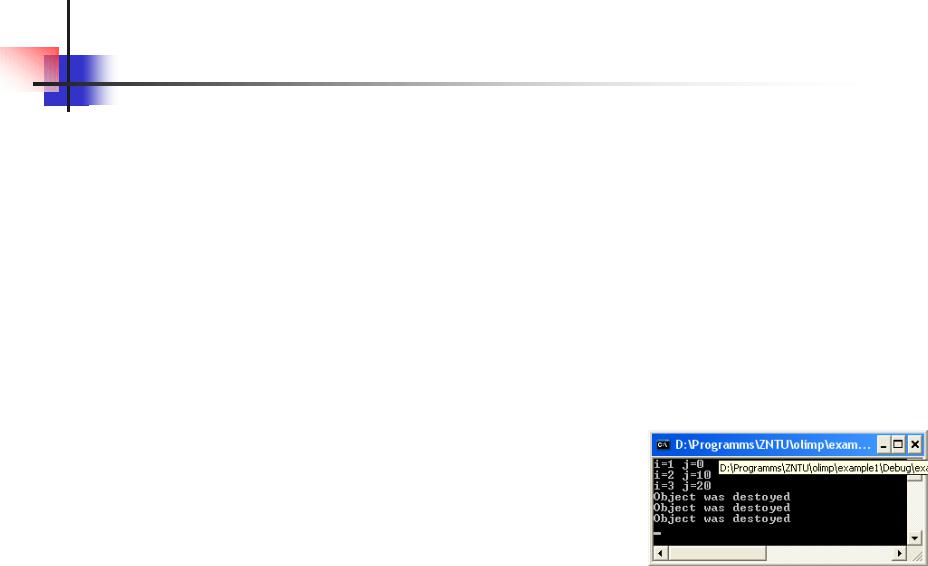
~MyClass(){cout<<"Object was destoyed\n";}
};
void MyClass::Show()
{cout<<"i="<<i<<"
j="<<j<<'\n';}
int main()
{
MyClass *pa=new MyClass; pa->Init(10,20); pa->Show();
delete pa; cin.get(); return 0;
}
 Пример 2. Деструкторы
Пример 2. Деструкторы
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
class MyClass{ int i,j;
public:
MyClass(){i=j=0;}
void Init(int a, int b){i=a; j=b;}
void Show() { cout<<"i="<<i<<" j="<<j<<'\n'; }
~MyClass(){cout<<"Object was destoyed\n";}
};
void MyClass::Show() int main()
{
MyClass *parr; parr=new MyClass [3]; int i;
for (i=0;i<3;i++) parr[i].Init(i+1, i*10);
for (i=0;i<3;i++) parr[i].Show(); delete [] parr;
cin.get(); return 0;
}

 Пример
Пример
Создать класс для работы с комплексными числами
Комплексное число
a + ib,
где
a и b – любые действительные числа,
i – специальное число, которое называется мнимой единицей.

 Пример
Пример
Два комплексных числа a + ib и c + id называются равными тогда и только тогда, когда
a = c и b = d.
Суммой двух комплексных чисел a + ib и c + id называется комплексное число
a + c + i(b + d).
Произведением двух комплексных
чисел a + ib и c + id называется комплексное число ac – bd + i(ad + bc).
Модулем комплексного числа называется длина вектора, соответствующего этому числу:
 Использование объектов
Использование объектов 
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
|
Действи- |
class ComplexNumber { |
тельная часть |
private: |
мнимая |
|
|
int real, imaginary; |
часть |
public: |
Конструк- |
|
|
ComplexNumber(); |
торы |
ComplexNumber(int r, int im); void show();
void plus(ComplexNumber cn); };
ComplexNumber::ComplexNumber() { real = 0; imaginary = 0;}
ComplexNumber::ComplexNumber(double r, double im) { real = r; imaginary = im;}
void ComplexNumber::show() { cout << real;
if (imaginary >= 0) cout << "+"; cout << imaginary << "i" << endl;
}
void ComplexNumber::plus(ComplexNumber cn) { real += cn.real; imaginary += cn.imaginary;
}
int main() {
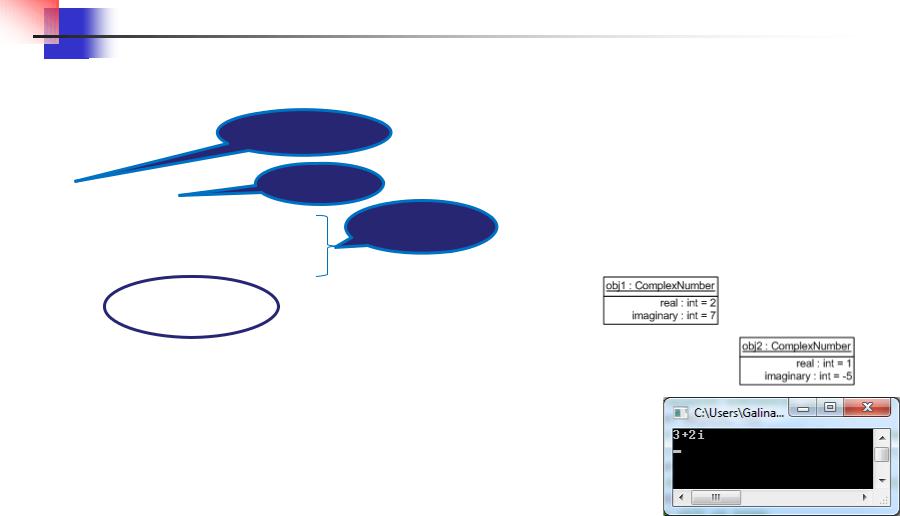
ComplexNumber obj1(2, 7); ComplexNumber obj2(1, -5); obj1.plus(obj2); obj1.show();
return 0;
}
 Использование объектов
Использование объектов 
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
class ComplexNumber { private:
int real, imaginary;
public: объект ComplexNumber() {
real = 0; imaginary = 0;}  ComplexNumber(int r, int im); void show();
ComplexNumber(int r, int im); void show();
ComplexNumber plus(ComplexNumber cn); };
ComplexNumber::ComplexNumber(double r, double im) { real = r; imaginary = im;}
void ComplexNumber::show() { cout << real;
if (imaginary >= 0) cout << "+"; cout << imaginary << "i" << endl;
}
ComplexNumber ComplexNumber::plus(ComplexNumber cn)
{
ComplexNumber temp; temp.real = real + cn.real;
temp. imaginary = imaginary + cn.imaginary; return temp;
}
int main() {
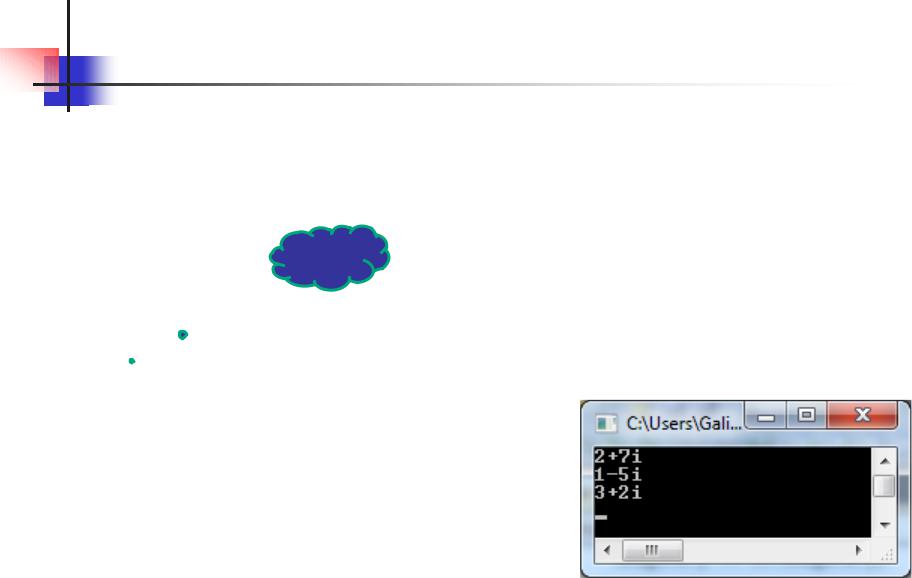
ComplexNumber obj1(2, 7), obj2(1, -5); ComplexNumber obj3;
obj3 = obj1.plus(obj2); obj1.show(); obj2.show(); obj3.show();
return 0;
}
 Использование объектов
Использование объектов 
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
class ComplexNumber { private:
int real, imaginary; public: ComplexNumber() {
real = 0; imaginary = 0;} ComplexNumber(int r, int im); void show();
ComplexNumber plus(ComplexNumber cn); };
ComplexNumber::ComplexNumber(double r, double im) { real = r; imaginary = im;}
void ComplexNumber::show() { cout << real;
if (imaginary >= 0) cout << "+"; cout << imaginary << "i" << endl;
}
ComplexNumber ComplexNumber::plus(ComplexNumber cn)
{
real += cn.real;
imaginary += cn.imaginary; //this->imaginary += cn.imaginary;
return *this;
}
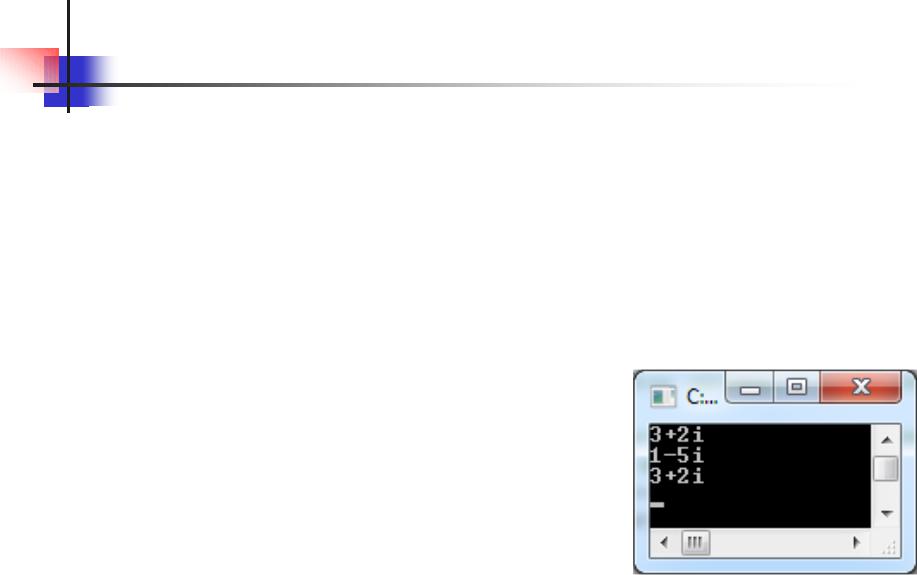
int main() {
ComplexNumber obj1(2, 7), obj2(1, -5); ComplexNumber obj3;
obj3 = obj1.plus(obj2); obj1.show(); obj2.show(); obj3.show();
return 0;
}

 Статические переменные
Статические переменные
Каждый объект класса имеет свою копию член-данных класса
Статический член класса разделяется всеми объектами класса

 Статические переменные
Статические переменные
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; class Alpha { public:
static int totalCount; static int count; Alpha();
~Alpha();
};
int Alpha::count;
int Alpha::totalCount;
Alpha::Alpha() {
Alpha::count++;
Alpha::totalCount++; }cout<<"Object of Alpha created\n";
Alpha::~Alpha() { Alpha::count--;
cout << "Object of Alpha destroied\n"; if (count == 0) {
cout << "This was last object.\n; cout << " Total count of objects is”;
cout << totalCount << endl;
} }
int main()
{Alpha *obj = new Alpha(); Alpha *objects = new Alpha[3]; delete obj;
delete[] objects; return 0;
}
