
- •Державна податкова адміністрація україни національна академія державної податкової служби україни
- •Для студентів-юристів з курсу
- •I. Political system of Great Britain 66
- •II. Political system of the usa 75
- •III. Courts in Great Britain and the usa 89
- •VI. Branches of Law 97
- •Передмова
- •Part I. Texts and Exercises unit 1
- •I am a student of law department
- •Word list
- •About my friend
- •Word list
- •National state tax service academy of Ukraine
- •Word list
- •The political system of Ukraine
- •The Constitution of Ukraine
- •Word list
- •1) Body
- •2) Head
- •3) Policy
- •4) Subject
- •The Higher Bodies of State Authority of Ukraine
- •The political system of Great Britain
- •Word list
- •Information for you
- •Definitions of the courts
- •Insert prepositions:
- •The system of government
- •Word list
- •The crown
- •The political system of the usa
- •1) Office
- •What is law?
- •Word list
- •1. What is the main function of law?
- •2. What threatens a person who continually breaks the rules?
- •3. What should we do in the absence of law?
- •4. What law can be characterized as a perfect one?
- •Classification of law
- •Comments
- •Word List
- •Unit 8 Courts in Great Britain
- •Judiciary in Great Britain
- •Word list
- •The court system of England and Wales
- •The court system of the usa
- •Word list
- •The organization of the federal courts today
- •The federal and state court systems
- •Unit 10 Legal professions
- •Legal professions in GreatBritain and the usa
- •Word list
- •Sentences judge crimes behaviour murder prisoners magistrate imprisonment jury Crown
- •Solicitors and barristers
- •Attorneys in the usa
- •Part II. Additional reading
- •I. Political system of Great Britain
- •Lawmaking process in Great Britain
- •Lawmaking Process in usa
- •1. In which House does new legislation usually start?
- •2. What is a bill? How does a bill become a law?
- •3. Who has the right of veto?
- •Making New Laws: Bills and Acts
- •The Executive
- •Members of Parliament in Great Britain
- •The Election Timetable
- •Political Parties
- •II. Political system of the usa
- •The American System of Government
- •The Constitution and the Bill of Rights
- •Congress
- •The President and Federal Departments
- •Federal Departments
- •Checks and Balances
- •Federalism: State and Local Governments
- •Political Parties
- •Elections
- •Political Attitudes
- •III. Courts in Great Britain and the usa
- •Courts in England and Wales (Part I)
- •Vocabulary Notes to text
- •Criminal Courts
- •Magistrates' Courts
- •Commentary and Notes
- •Courts in England and Wales (part II)
- •Courts in Scotland
- •Vocabulary Notes to text
- •Courts in Northern Ireland
- •Commentary and Notes to the text
- •Coroner's Courts
- •Vocabulary Notes to the text
- •Appeals
- •Vocabulary Notes
- •Growth of the Profession
- •Us Attorneys
- •The Federal Judiciary
- •VI. Branches of Law
- •Law: what is it?
- •Civil law
- •Civil law (family, contract, intellectual property)
- •VI. Find in the text and decide from the context what the word could mean, then choose the appropriate definition.
- •Criminal law
- •Labour Law
- •Administrative law
- •Employment law
- •Part III. Grammar Exercises Дієслово to be
- •Зворот there is (are, was, were, will be)
- •Дієслово to have
- •Зворот have / has got
- •Insert in each blank the form of pronouns which you consider correct (I-me; we-us; you-you; he-him; she-her; it-it; they-them)
- •Часи групи Continuous
- •The Present Continuous Tense
- •Break time
- •The Future Continuous Tense
- •Часи ГрупиIndefinite
- •The Present Indefinite Tense
- •The Past Indefinite Tense
- •Compare using of Present Indefinite and Past Indefinite.
- •In this exercise you have to read a sentence about the present and then write a sentence about the past.
- •In this exercise you have to write questions. A friend has just come back from holiday and you are asking him about it.
- •The Past Continuous Tense
- •Часи групи Perfect
- •The Present Perfect Tense
- •In this exercise you have to read the situation and then write a suitable sentence. Use the verb given
- •In this exercise you have to write sentences with already.
- •In this exercise you have to make questions with the words given
- •In this exercise you have to read the situation and then finish a sentence.
- •The Past Perfect Tense
- •The Future Perfect Tense
- •Reference List
The system of government
What is the Government? The Government is the management of the country. The Government makes the important decisions, e. g. about foreign policy, education, or health, but all these decisions have to be approved byParliament. If Parliament thinks that a particular Government policy is against the public interest, then it can force the Government to change its mind.
State Organs of the United Kingdom include the monarchy, the legislative, executive andjudicial organs of Government.
The monarchy is the most ancient institution in the United Kingdom, with a continuous history stretching back over a thousand years. The monarchy is hereditary. Queen Elizabeth П, whosucceeded to the throne in 1952, is the head of the judiciary, the commander-in-chief of the armed forces of the Crown and the temporal head of the established Church in England. Her Majesty's Government governs in the name of the Queen who must act on the advice of her ministers.
Parliament is the legislative organ of the United Kingdom. What do we mean by Parliament? The Parliament of the United
Kingdom consists of the Queen (hereditary monarch), the House of Lords (almost 1300 unelected members orpeers) and theHouse of Commons (659 elected Members of Parliament). All three combine to carry out the work of Parliament.
The House of Lords is still a hereditary body. It consists of the Lords Temporal and the LordsSpiritual. The House of Lordsis presided over by theLord Chancellor who is the chairman of the House.
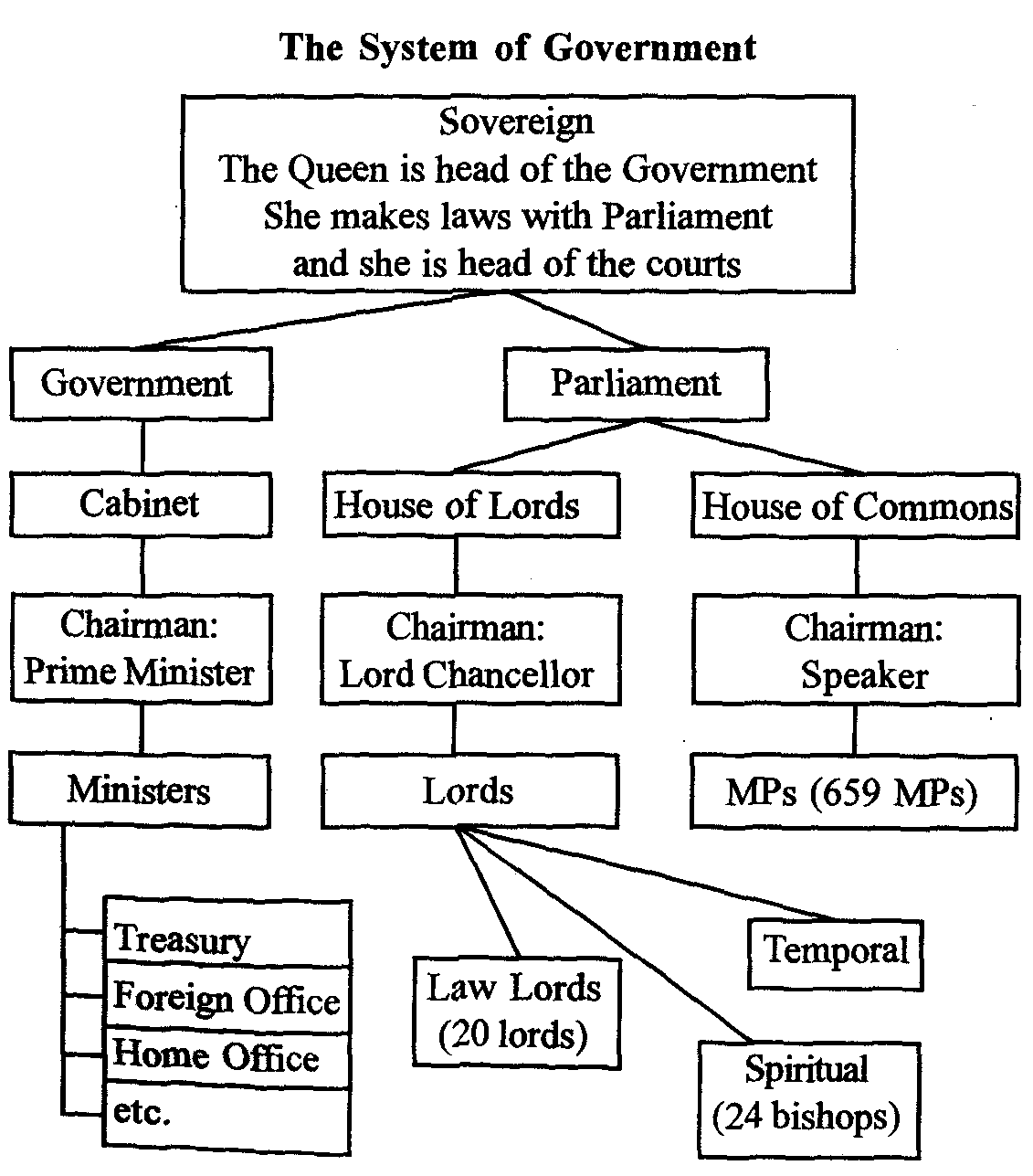
The House of Commons is an elected and representative body. Members are paid a salary and an allowance. The Speaker of the House of Commons is elected by the members of the House immediately after each new Parliament is formed.
The Government consists of approximately 100 members of the political party which has the majority of seats in the House of Commons.
What does Parliament do? Making laws (legislations).
The Queen, Lords and Commons all have to agree to any new law which is passed.
Examining the work of Government. Both the Lords and the Commons examine the work of the Government on behalf of the public. They do this by asking the Government questions, by debate and through committees of inquiry.
Controlling finance. Only the House of Commons can give permission for the Government to collecttaxes. The House of Commons decides what taxes shall be collected and how the money shall be spent.
Protecting the individual. Members of Parliament (Members of the House of Commons)protect therights of the individual. Each Member of Parliament represents the people of a certain area. Britain is divided into 659 of these areas, known asconstituencies.
Hearing appeals. The House of Lords is a Court of Justice, the highest Court of Appeal in Britain.
Executive.The Government consists of the ministers appointed by the Crown on the recommendation of the Prime Minister. The Prime minister is appointed directly by the Crown and is the leader of the political party which has a majority of seats in the House of Commons. The Prime Minister is the head of the Government; he is always a Member of the House of Commons. He consults and advises the Monarch on government business, supervises and coordinates the work of the various ministers and departments in the House of Commons. He also makes recommendations to the Monarch on many important public appointments.
The most senior members of the Government are known as the Cabinet. The Cabinet is the nucleus of the Government. All major decisions of the Government are made by the Cabinet, and therefore it is the Cabinet which forms Government policy.
Who chooses the Cabinet? Members of the Cabinet are chosen by the Prime Minister. The majority of the members of Mr Blair's Cabinet are drawn from the House of Commons. Nevertheless there are always a few members from the House of Lords. All the members of Mr Blair's Cabinet belong to the Labour Party. The Labour Party gained the right to form a Government by winning thegeneral election in May 1997. Mr Blair, the leader of the Labour Party, became Prime Minister. He selected a team of Ministers to serve in his Government. A Cabinet must be large enough to include senior ministers. There is no limit on the size of the Cabinet but the number of salaried Secretaries of state is limited to 21. Cabinet meetings are usually held on a Thursday morning in the Cabinet room at 10 Downing Street.
What happens when there is a change in Government?
During the last 27 years there have been eight general elections. Four of these resulted in a change of Government.
1970 Conservatives took over from Labour.
1974 Labour took over from Conservatives.
1979 Conservatives took over from Labour.
1997 Labour took over from Conservatives.
On each of these occasions the ministers in each Department changed. Ministers of the winning party took over from those of the loosing party. The two main parties have very different ideas - for example, about education, housing and industry.
Departments and ministers are run by civil servants, who are permanent officials. Even if the Government changes after an election, the same civil servants are employed.
The United Kingdom has no Ministry of Justice. Responsibility for the administration of the judicial system in England and Wales is divided between the courts themselves, the Lord Chancellor, and theHome Secretary. The Lord Chancellor is responsible for the composition of the courts,civil law, parts of criminal procedure and law reform in general; the Home Secretary is responsible for theprevention ofcriminal offences, trial andtreatment ofoffenders and for theprison service.
